* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 25 section 3 and 4
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American mutilation of Japanese war dead wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
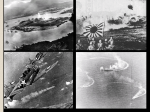
Invasion of Western Europe Operation Overlord Marshall, top American General and Chief of Staff to FDR wanted a massive attack on Germany through France. The invasion code name was Operation Overlord, the Allies began a massive military buildup in southern England. They were supported by French, Polish, Dutch and Belgian troops. The operation was kept top secret. D-Day, my B-Day Took place on June 6, 1944 Surprise attack started at night RAF pounded German defenses in Normandy Allies parachuted behind enemy lines More than 150,000 soldiers landed on the beaches Allies suffered heavy casualties, but the operation was a success France is Liberated!! A month after the D-Day millions of allied troops occupied France. General Patton and his troops destroyed bridges stopping German troops from bringing in reinforcements. With the Allied forces and internal resistance in France, the country would be liberated by the end of August. The day of the bulge Hitler was intense on keeping and defending his conquests He reinforced his army with 1,000’s of draftees, some as young as 15. Hitler’s troops trounced on the allies forcing them back and causing a bulge in the allied lines. Many American forces were cut off from the rest of the army, but in weeks the allied forces would restart their drive. Battle of the Bulge The Battle of the Bulge was the largest battle in western Europe during WW II, and the largest fought by Americans. It involved more than 600,000 GI’s of which 80,000 were killed After the battle, Nazi leaders recognized that the war may be over Soviet forces push on Like the battle of Stalingrad, Soviet soldiers fought hard for he capture of Berlin. As the Soviet troops surrounded the city of Berlin, Hitler refused to take the advice and flee the city. Instead he commits suicide in an underground bunker. A few days later the rest of the German soldiers will retreat The Yalta Yalta Conference Months before the fall of Berlin Churchill, Stalin and FDR met at Yalta, a city in the Soviet Union At the conference they discussed post war Germany. Decided to split Germany into 4 zones each under the control of the major allies as well as Berlin Stalin goes against the agreement and refuses to hold open and democratic elections, FDR and Churchill get a lot of slack for the agreement The Holocaust Anti-Semitism is hatred and hostility against the Jews. They were blamed for the countries economic problems and hardships The Holocaust was the systematic murder of European Jews, roughly 6 million, about 2/3rds of Europe’s Jewish population would lose their lives. Who’s a Jew?? Nuremberg laws stripped Jews of their citizenry A Jew was defined as a person who had three or four Jewish grandparents regardless of their religion. Jews were forced to sew yellow stars on their clothes to represent being a Jew. Hitler’s Police The Gestapo was Hitler’s secret police The SS were an elite guard group responsible for guarding the concentration camps Kristallnacht, the night of broken glass, almost every synagogue was destroyed, all Jewish shops etc. Jews seek refuge As the violence grew against Jews some 130,000 fled Germany seeking refuge in neighboring European countries. As the numbers grew, many sought refuge in the US, and Latin America FDR held the Evian Conference in France to discuss the infiltration of Jews. Of the 32 nations present, only the Dominican Republic agreed to open their doors to immigrants. The first method Many of the Jews that fled Germany would end up in the control of Hitler when he invaded other countries, mostly Poland. Plans for dealing with the Jews first started with the establishment of ghettos, usually surrounded by barbed-wired fences, Jews were forced to pick up their lives and live in these cruel conditions. The Warsaw Ghetto In Warsaw, 400,000 Jews were rounded up, almost 30% of the capital’s population in a living area of only 3% They received little food, were subjected to overcrowding and lack of sanitation Thousands died in the Ghetto, but the Nazi’s were looking for a more proficient way to get rid of the problem. Murder moves to Genocide Hitler ordered the Einsatzgruppen, a mobile killing squad to shoot communist officials and Jews living in Germanoccupied territory They were rounded up and drove to freshly dug graves, and shot there. In Babi Yar alone, 33,000 Jews were murdered in two days, the genocide begins! The final solution to the Jewish question At the Wannsee Conference, Nazi officials met to discuss a better method to come to the final solution. They came up with genocide, or deliberate destruction of an entire ethnic group, this would lead to the construction camps. Most effective way to kill Zyklon B proved the most efficient killer, the first “shower” was built at Auschwitz in Poland, they were known as death camps, not concentration camps. Prisoners were told they were going to the east to work, rounded in cattle cars, put in lines, did hard labor or were gassed. Life expectancy in the camp was a few months The Horror of the camps Hard labor included taking the bodies from the gas chambers to the crematoriums They were tattooed, malnourished, and tortured. The amounts of death at these camps were staggering. In one day at Auschwitz, 12,000 could be gassed and cremated Fighting Back There were some uprisings in the camps, however they were quickly crushed by the Germans. The most successful was the riot at Treblinka, that caused it to close down from all the damage. Every so often someone would escape and return to the ghettos to give word of the death camps. At the Warsaw Ghetto, the Jews held off Germans for 27 days armed with little more than hand guns and homemade grenades. Rescue and Liberation The United States knew of the death camps as early as 1942. Many were uninterested at first. FDR would create the WRB (War Refugee Board) to help people fighting persecution. Although it was late funding from the WRB enabled Sweden to issue special Swedish passports to the Jews and saved 200,000 lives. The US however refused to open their borders wider, in fact their immigration quota was not even met Liberation finally comes When the news of liberation came to the camps, Nazi soldiers marched the prisoners on death marchers back onto German territory. Thousands died too weak to even walk. The United States was first witnessed to this horror Prior to liberation, Belzec and Treblinka were closed the annihilation of the Jews was almost complete Days before Hitler commits suicide (may 7 1945) FDR will die of a cerebral hemorrhage and Truman will take over Years later Treblinka and Belzec were burned and turned into farm land but soldiers still found bodies protruding from the ground Those who were liberated normally died days later The Nazis had killed 12 million people Responsible for your own actions The Nuremburg Trials were composed of members from the US, France, GB and SV There were 24 defendants, 12 received the death penalty Most important thing it did was hold people responsible for their actions, could not just say “I was Following Orders.” War in the Pacific The Japanese attacks on Pearl Harbor, Clark Field were efforts to remove the US from the war so they could gain the needed natural resources in Southeast Asia. In 1942 there was the Battle of the Coral Sea, northeast of Australia. The battle was a draw between America and Japanese forces but stopped Japan from taking Australia The Battle of Midway Japanese forces tried to take the Midway Islands, it resulted in the first major defeat of the Japanese navy Even with the success of Midway, Japanese had a strong hold on the Pacific In an effort to cut this the United States utilized island hopping, a strategy in which captured key islands and cut off Japanese supply lines Battle in the Pacific The first step for the Allies in taking Tokyo was the Battle of Guadalcanal, located on the Solomon Islands, where Japanese were building an airfield. The battle lasted six months, when 11,000 Marines landed on the island, the 2,200 Japanese soldiers retreated into the jungle First time for jungle warfare for Marines, became easy targets for Japanese snipers The battle would be fought by land, air and sea, and be a US victory Kamikazes and Iwo Jima The war became deadlier as Allied troops made their way to Japan. Japanese implemented kamikazes, suicide pilots who flew bomb-laden planes into American ships, they scored 279 US vessels and American Marines suffered 20,000 casualties One of the bloodiest battles took place on Iwo Jima, for 74 days the US pounded the island with bullets and bombs, Marines landed on the beaches with 110,000 troops yet it took a month to secure the island. Japanese fought almost until the last man, 216 were left, from 25,000 Battle of Okinawa Fought from April to June was just as bloody as Iwo Jima Little than 350 miles from Japan, it was the last obstacle to the Allies invasion of Japan Many of the 100,000 Japanese soldiers pledged to fight until death Allies gathered over 180,000 ground troops, thousands of warships They were attacked by kamikazes, and attacks were soldiers would kill as many defenders as possible before dying themselves US lost 50,000 soldiers while the Japanese only had 7,000 left The Manhattan Project The US knew that the end of the war would be costly to US lives, the Manhattan Project was a top secret organized by FDR to develop an atomic bomb, the idea was sent by a physicist who fled Germany In 1945 the first atomic bomb was dropped in the desert of New Mexico Alternatives to dropping the bomb The bomb was completed now the decision was to be made on if they should drop it on Japan Alternatives: – 1. massive invasion of Japan costing millions of US lives – 2. a naval blockade starving Japan along with conventional bombing – 3. a demonstration of the bomb on a deserted island to pressure Japan into surrender – 4. a softening of unconditional surrender of Japan Final Decision It was ultimately up to Truman who had only been in office 3 months Japan had continually refused surrender throughout the war, and the US had already lost thousands of casualties He had no problem deciding to drop the bomb, he said “You should do your weeping at Pearl Harbor,” meant for the critics The Devastation August 6, 1945 an atomic bomb destroyed 60 percent of Hiroshima, a major industrial city Even after the first bomb was dropped, Japan refused to surrender On August 9th, dropped a second bomb on Nagasaki, causing almost as much destruction as the first Took 150,000 Japanese lives Japan will accept American terms of surrender and asks for peace, the surrender will take place on the Missouri, a battleship in the Pacific The War at Home In the US African Americans were fighting desperately to gain equality Laws were passed in the North to open employment to all people regardless of race, or ethnicity African Americans experienced violent discrimination, riots etc. People were afraid of losing jobs or having to be equal African American soldiers were also victim to discrimination Africans and Mexicans African Americans set up the Double V campaign, first V for victory against the axis powers and the other against equality at home Congress of Racial Equality-nonviolent methods to end racism, such as sit-ins A shortage in farm help brought on immigration from Mexico – Braceros were Mexican farm laborers who lived in barrios, or Spanish speaking neighborhoods. They were called “Zoot-suiters” because of their dress and were normally beat up by sailors and locals Japanese Americans After Pearl Harbor, 110,000 Japanese Americans were moved from their homes to detention centers They had only 48 hours to pack their lives up and move Most did not rebel They were put in internment camps, or confined to camps in remote areas far from the coast Challenges of Treatment Some Japanese challenged these actions Korematsu v. United States, where they said it was a military necessity Later, almost 40 years, surviving internees were given 20,000 dollars for their losses Up until 1943, Japanese Americans were not allowed into the military, when they finally were they volunteered in the thousands to prove their patriotism They won more medals for bravery than any other unit in the US New Inventions DDT- an agent to control insects and made jungle fighting more tolerable was developed, bazookas were developed to help destroy tanks, as well as radar The economy was jump started from the war effort, thousands of jobs were created