* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular Physiology
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
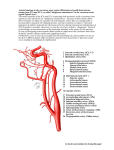
Cardiovascular Physiology Minimal Requirements for Lab Identify Structure and Name Function I. Auscultate the areas of the thorax where valve sounds can best be detected. A. Aortic semilunar valve B. Pulmonary semilunar valve C. Bicuspid valve D. Tricuspid valve II. Explain the causes of the heart sounds. III. Locate the following on models and students should palpate at least three of the following superficial pulse points on themselves A. Common carotid artery B. Temporal artery C. Facial artery D. Brachial artery E. Radial artery F. Femoral artery G. Popliteal artery H. Posterior tibial artery I. Dorsalis pedis artery IV. Use a sphygmomanometer to measure blood pressure. A. Indicate the physiological causes of the following: 1. Sounds of Korotkoff 2. Systolic blood pressure 3. Diastolic blood pressure B. Calculate the pulse pressure and indicate its clinical significance C. Calculate mean arterial pressure (MAP) V. Conduction System of the Heart A. Identify the following intrinsic structures for the conduction system on heart models. 1. Sinoatrial (SA) node 2. Internodal fibers 3. Atrioventricular (AV) node 4. AV bundle (bundle of His) 5. Right and left AV bundle branches 6. Purkinje fibers B. State the function or significance of each component of an EKG listed below: 1. P-wave 2. PR segment 3. PR interval 4. QRS complex (includes the Q, R, and S waves) 5. QRS interval 6. ST segment 1 7. ST interval 8. T-wave 9. ST interval 10. QT interval 11. Where is the atrial repolarization wave? C. Distinguish between normal and abnormal EKGs VI. ADInstruments connected to the computers in the lab will function as our electrocardiograph A. Follow Lab Tutor from ADInstruments instead of what is in the lab manual. 1. Turn on the ADInstruments PowerLab Box (switch is on the back of the machine) and then turn on the computer. 2. Open “Lab Tutor Experiments” from the desktop (green icon) 3. Click “Enter” 4. Click on “ECG and Heart Sounds” 5. Follow the Lab Tutor procedure for setting up the equipment. i. An alternate lead placement − under the clavicle on the left and right chest and the Earth (ground) lead goes at the hip/waist 6. Students should complete the exercises with at least one volunteer in their group. 7. Students can print their results on the lab printers. VII. Histology A. Cardiac muscle characteristics 2