* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20 Sec 1
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Mutual assured destruction wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
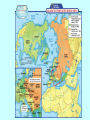
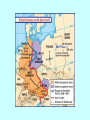
Confrontation of the Superpowers After World War II, the United States and the Soviet Union became fierce rivals. Confrontation of the Superpowers (cont.) • In 1949, the United States and its European allies formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Confrontation of the Superpowers (cont.) • The United States wanted the newly freed countries of Eastern Europe to hold free elections, hoping they would establish democratic governments. • In 1955, the Soviet Union and its European allies formed the Warsaw Pact. Confrontation of the Superpowers (cont.) • The Soviet Union opposed the West’s plans, fearing they would become anti-Communist, and kept forces in the newly liberated countries. Confrontation of the Superpowers (cont.) • U.S. President Harry S. Truman issued the Truman Doctrine to persuade Greece, Turkey, and other nations threatened by Communist expansion to choose democratic forms of government. Confrontation of the Superpowers (cont.) • U.S. secretary of state Dean Acheson explained that the corruption of Greece would likely spread to the nearby countries. • The Marshall Plan was created to prevent the spread of communism by providing $13 billion to rebuild war-torn Europe. • The Eastern European satellite states refused to participate. Confrontation of the Superpowers (cont.) • The U.S. adopted a policy of containment to prevent further Soviet aggressive moves. • Berlin and the rest of Germany were divided into four zones, each occupied by one of the Allies—the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France. • In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany was formally created in West Germany. • The German Democratic Republic was set up in East Germany by the Soviets. The Cold War Spreads As Cold War tensions increased, nations were forced to choose to support the Soviet Union or the United States. The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • Cold War tensions increased when China fell to communism and the Soviet Union exploded its first atomic bomb. • Both sides began stockpiling weapons and building up their armies, resulting in an arms race. The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • The belief was that nuclear weapons were a form of deterrence because neither side would launch a nuclear attack knowing the other side would be able to strike back. • In another attempt to prevent war and provide mutual support, military alliances were formed throughout the world. The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – Formed in April 1949 – Included the United States, Canada, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, the Netherlands, Great Britain, Italy, Denmark, Norway, Portugal, Iceland, West Germany, Greece, and Turkey The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • Warsaw Pact – Formed in 1955 – Included the Soviet Union, Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO) – Formed in 1954 to prevent Soviet aggression in the East – Included the United States, Great Britain, France, Pakistan, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, and New Zealand The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • The Central Treaty Organization (CENTO) – Formed in 1959 to prevent Soviet expansion in the South – Included Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Pakistan, Great Britain, and the United States The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • In order to prevent East Berliners from escaping to West Berlin, Nikita Khrushchev ordered a wall to be built to divide the city. • Fidel Castro set up a Soviet-supported socialist regime in Cuba. U.S. President John F. Kennedy authorized the unsuccessful CIA plan to invade Cuba at the Bay of Pigs. The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • During the Cuban missile crisis in 1962, the United States blockaded a fleet of Soviet ships carrying nuclear missiles to Cuba. The threat of nuclear war was averted when the Soviets turned back their fleet and the United States agreed not to invade Cuba. The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • The United States became involved in the Vietnam War to prevent the Communist regime of North Vietnam from invading and gaining control of South Vietnam. The Cold War Spreads (cont.) • U.S. policy makers believed that if one country fell to communism, the surrounding countries would also fall. This became known as the domino theory. • Vietnam helped show the limitations of the United States and resulted in a new era of American-Soviet relations. THE END