* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHARMACOGENETICS OF MEMBRANE TRANSPORTERS
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
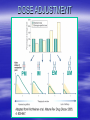
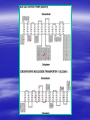
PHARMACOGENETICS OF MEMBRANE TRANSPORTERS Jeff Idle Institute of Pharmacology 1st Faculty of Medicine Charles University, Praha Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1915; 1: 235-238 PHARMACOGENETICS HUNDREDS OR PROTEINS PARTICIPATE IN DRUG DISPOSITION MOST, IF NOT ALL, DISPLAY GENETIC POLYMORPHISM CRITICAL INTER-PATIENT VARIABILITY OCCURS WHEN DRUG LEVELS ARE TOO HIGH/LOW AT SITES OF ACTION HISTORICALLY, THIS HAS BEEN ATTRIBUTED TO A FEW ENZYMES PHARMACOKINETICS PROCESS ENZYMES TRANSPORTERS ABSORPTION - ++ DISTRIBUTION - +++ METABOLISM +++ + - +++ EXCRETION ROUTINE PHARMACOGENETICS CYP2D6 AND ANTIDEPRESSANTS CYP2C9 AND WARFARIN TPMT AND AZATHIOPRINE/6-MP DOSE ADJUSTMENT EXAMPLES OF DOSE ADJUSTMENTS TRANSPORTERS 30 years ago, drugs seen as subject only to passive diffusion from one compartment to another pH, pKa (Henderson-Hasselbach equation) and MW (Fick’s Law of diffusion) were the guiding principles Exceptions were amino acid absorption and renal excretion of a few drugs TRANSPORTERS SLC – SOLUTE TRANSPORTERS PASSIVE TRANSPORT, COUPLED TRANSPORT AND EXCHANGE OF H+, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Zn2+, Cu2+, Cl-, I-, PO43-, HCO3-, Ach, GABA, choline, Nor, Dop, 5-HT, Gly, Tau, creatine, urea, folate, thiamine, moncarboxylates, dicarboxylates, citrate, ornithine, glutamate, aspartate, proline, neutral amino acids, cationic amino acids, bile acids, fatty acids, nucleosides, oligopeptides, glucose, organic cations, acetyl CoA, CMP-sialic acid, UDP-galactose, UDPN-acetylglucosamine, UDP-glucuronic acid, UDP-Nacetylgalactosamine, glycerol-3-phosphate AT PLASMA MEMBRANE, MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANE AND VESICULAR MEMBRANES SLC TRANSPORTERS SLC1A1-1A7, SLC2A1-2A14, SLC3A1-2, SLC4A14A11, SLC5A1-5A12, SLC6A1-6A20, SLC7A1-7A14, SLC8A1-8A3, SLC9A1-9A11, SLC10A1-10A6, SLC11A1-11A2, SLC12A1-12A9, SLC13A1-13A5, SLC14A1-14A2, SLC15A1-15A4, SLC16A1-16A14, SLC17A1-17A8, SLC18A1-18A3, SLC19A1-19A3, SLC20A1-20A2, SLC22A1-22A18, SLC23A1-23A4, SLC24A1-24A6, SLC25A1-25A37, SLC26A1-26A11, SLC27A1-27A6, SLC28A1-28A3, SLC29A1-29A4, SLC30A1-30A9, SLC31A1-31A2, SLC32A1, SLC33A1, SLC34A1-34A3, SLC35A1-35A5, SLC35B1-35B4, SLC35C1-35C2, SLC35D1-35D3, SLC35E1-35E4, SLC35F1-35F5, SLC36A1-36A4, SLC37A1-37A4, SLC38A1-38A6, SLC39A1-39A14, SCL40A1, SCL41A1-41A3, SLC43A1-43A3 SLCO TRANSPORTERS PREVIOUSLY GENE FAMILY SLC21 SOLUTE CARRIER ORGANIC ANION TRANSPORTER FAMILY SLCO1A2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO1C1, SLCO2A1, SLCO2B1, SLCO3A1, SLCO4A1, SLCO4C1, SLCO5A1, SLCO6A1 ABC (ATP-BINDING CASSETTE) TRANSPORTERS ACTIVE EXPORT OF drugs and foreign chemicals AT PLASMA MEMBRANES ABC TRANSPORTERS ABCA1-A13, ABCB1, ABCB4-B11, ABCC1C6, ABCC8-C13, ABCD1-D4, ABCE1, ABCF1-F3, ABCG1-G5, ABCG8 SLC AND ABC TRANSPORTERS SLC transporters 41 families 46 sub-families 316 members Multiple cellular locations Import, export, exchange Wide range of endogenous and exogenous compounds SLCO transporters 6 families 10 sub-families 11 members Wide range of endogenous and exogenous anionic compounds TOTAL NUMBER OF TRANSPORTERS 375 members ABC transporters 1 family 6 sub-families 48 members Plasma membrane Export Wide range of endogenous and exogenous compounds COMMON NAMES AND ASSOCIATIONS ABCB1 ABCA4 ABCB1 ABCC7 SLC2A1-5 SLC22A1-3 SLC22A6-10 SLC4A1 SLC6A4 Tangier disease Stargardt disease (Juvenile macular degeneration) Multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) GLUT1-5 OCT1-3 OAT1-5 Erythrocyte membrane protein band 3 (Diego blood group) Serotonin transporter (SERT) POLYMORPHISM OF TRANSPORTER FUNCTION GENE TRANSPORTER DRUGS EFFECTS OF SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS REF. SLC29A1 ENT1 Nucleoside analogues Haplotypes do not alter uptake of Ribovirin, Cytarabine, 5Fluorouridine Osato et al. (2003) SLC6A2 NET1 Noradrenaline SNP (0.07%) causes reduced affinity for Nor Runkel et al. (2000) Paczkowski et al. (2002) SLC22A2 OCT2 Procainamide Cimetidine Metformin, Quinidine Four SNPs reduce renal elimination Leabman et al. (2002) SLCO1B1 OATP1B1 Pravastatin 17b-estradiol-17bD-glucuronide SNP markedly reduces non-renal clearance Iwai et al. (2004) SLC18A2 VMAT2 Reserpine (inhibitor of amine uptake) Two rare SNPs alter reserpine inhibition Burman et al. (2004) POLYMORPHISM OF TRANSPORTER FUNCTION GENE TRANSPORTER DRUGS EFFECTS OF SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS REF. SLCO1B3 OATP1B3 Digoxin 17b-estradiol-17bD-glucuronide Taurocholate Bile acid transport abolished by 2 SNPs. Letschert et al. (2004) SLC6A4 SERT 5-HT Haplotype associated with Bipolar Affective Disorder (Taiwan) Sun et al. (2004) SLC22A1 OCT1 MPP+ 5-HT SNPs alter substrate specificity of OCT1 Kerb et al. (2002) ABCB1 MDR1 Cyclosporine Tacrolimus (calcineurin inhibitors) 2677TT genotype associated with reduced risk of renal dysfunction Herbert et al. (2003) ABCB1 MDR1 Loperamide ± Quinidine 2677G/3435T haplotype associated with higher plasma concentrations Skarke et al. (2003) PERSPECTIVE SLC, SLCO, and ABC transporters play a critical role in drug pharmacokinetics, affecting absorption, hepatic uptake, hepatic export, tissue distribution, and renal and biliary elimination. A body of unstructured pharmacogenetic data is rapidly accumulating that suggests strongly that membrane transporters are subject to both genotypic and phenotypic polymorphism. PERSPECTIVE Genetically-determined variability in drug and hormone transporter function may explain major inter-patient variability in drug pharmacokinetics and susceptibility to drug resistance and toxicity. These differences may be greater than those due to the known enzyme polymorphisms. There is much to do.