* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A questionnaire for assessing the impact of socio
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Nutrition transition wikipedia , lookup
Health equity wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Preventive healthcare wikipedia , lookup
Social determinants of health wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Diseases of poverty wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
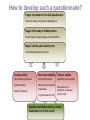
A questionnaire for assessing the impact of socio-economic factors in MG A . H . M A N I A O L , C . TA L L A K S E N D E PA R T M E N T O F N E U R O L O G Y O S L O U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I TA L , U L L E V Å L Determinants of health ECHI: European community health indicators* o Socio-economic factors o Environment o Health behaviours o Biological and personal factors *The ECHI project; health indicators for the European Community; www.ec.europa.eu Determinants of health Socio-economic factors o Socio-economic factors: social and economic factors that characterize the individual or group within the social structure o Occupation Measure SES Socio-economic status (SES): ooEmployment an individual `s or group`s social and economic position o Poverty income distrubution within and a hierarchal social structure, measured by socioeconomic factors o Education How could socio-economic factors affect health? o Mediators: o Social: education, occupation, living conditions, lifestyle… o Economic: health-care access, payment of medications.. o Psychosocial : emotions, stress, depression, anxeity Ref. Socio-economic status and health, a neurobiological perspective •Roy J.; Medical hypothesis(2004) 62, 222-227 o Biological hypothesis? Low SES Psychosocial stress ↑ autonomic and neuroendocrine response Immune system ↑↑ Post-stress infection, disease autoimmunity ? Modifying factors in MG Demographic and socio-economic factors Drugs Alcohol Diet Smoking ? Stress Infections Environmental factors Hormones Myasthenia gravis Genes Immune system Socio-economic factors in MG and other autoimmune diseases Search terms “socio-economic factors” and “disease” and hits in databases Disease Prevalence rate per 100 000* PubMe Medlin EMBAS d e E Type 1 diabetes 300-600 643 618 209 Rheumatoid arthritis 300-800 675 597 218 Systemic lupus erythematosus 30-100 205 162 137 Inflammatory bowel diseases 100-200 (CD) 237 150-290 (UC) 216 14 362 102 Multiple sclerosis 100-180 403 *Recent prevalence data for autoimmune diseases; G.S Cooper et al./ Journal of Autoimmunity (2009) Socio-economic factors in MG Few MG studies have reported the influence of socio-economic Summary factors oo Social A study of social, medical andGravis emotional Few studies! aspects in Myasthenia problems inet.al 26 patients L. Kaukiainen Acta neurol.Scan 55, 377-384, 1977 Lack of powerlarger-scale studies needed! J. Sneddon, Lancetprevalence 1980;1;526-528 1977 oo 210 of 240 (88%), 5,2 per 100 000 (1975) o o o o 26 of 30 answered a questionnaire more intermediary-school and university level Social factors, stress, temperature seemed to have an higher social class impact on disease and course greater part live inonset urban areas But, this study should be considered as a pilot study Socio-economic factors in other autoimmune diseases Type 1 diabetes: Disease RA: Socio-economic •Hassan K, J Pediatr 2006 Oct;149(4):526-31 • Kakleas K, Diabetes Metab 2009 statusNov;35(5):339-50 (SES) •Liao 1KP, Curr Opin Rheumatol - Low SES poor glycemic control, psychiatric -and eating Type diabetes 2009 May;21(3):279-83. disorders, impaired QoL SLE: RA (not RF-neg RA) - lower SES increases risk RF-pos Rheumatoid •Meller S, Autoimmun Rev 2005 arthritis (RA) Increases risk 40% without university degree Inflammatory bowel diseases: Apr;4(4):242-6. •Li X, Inflamm Bowel Dis 2009 - lower SES worsen outcome and prognosis Systemic lupus Apr;15(4):608-15 • Nahon S, Inflamm Bowel- lower Dis SES increases mortality erythematosus MS: 2009 Apr;15(4):594-8 •Marrie R, Mult Scler 2008 not CD Inflammatory bowel - lower SES increases risk UC, Sep;14(8):1091-8 diseases (CD) (UC) - higher SES increases risk CD! • Lowis GW, Sci Total Environ 1992 Sep 11;126(1-2):139-64. -higher SES (urban areas), lower SES (rural areas) Multiple sclerosis increases risk of disease, affects hospitalization and comorbidity ......Socio-economic factors in other autoimmune diseases o SES important environmental modifying factor o SES affects Risk of disease Disease outcome Mortality Comorbidity Risk of hospitalization Health related quality of life (HRQoL) o Other environmental factors related to SES: Health behaviors (smoking, alcohol, diet) Psychosocial factors (stress, depression, mental health) How to develop such a questionnaire o EuroMyasthenia 2006-2009 o Aim of questionnaire: Self-administered MG specific Feasible for patients Standardized in clinical characteristics Standardized in assessing health determinants (ECHI) Valid and reliable Easy to adapt and translate for collaborative partners Suitable in large-scale epidemiological studies How? How to develop such a questionnaire? S tage1: Development of a draft questionnaire Literature review and question development Stage 2: Pilot study of 68 MG patients 57 participants tested and gave critical feedback Stage 3: Validity and reliability tests Self-made MG specific questions Content validity Test-retest reliability Criterion validity Item selection/reduction 4-6 months interval Specificity and sensitivity Specialist advice 28 patients included (first MG questions of responders) symptoms at disease onset (n=24) 24 participated (n=24) Patient comments Questions modified according to results Establishment of a final version How to develop such a questionnaire? Already validated questions o Socio-economic status* Education Occupation Income Employment Disability o Health behavior* Smoking Alcohol Drugs Coffee, tea, vitamins Physical activity *www.ntnu.no/hunt/inenglish Questions to validate o MG specific questions Onset Clinical characteristics Disease severity Treatment Comorbidity other autoimmune diseases Follow up Disease information Women Results How to develop such a questionnaire? Final version: Modifying questions of MG clinical characteristics Pilot version: Ch ew in g Sw all ow in g Br ea th in g lk in g ,l jaw e, Ta ip s k Ne c Fa c b Lo w er lim lim b Up pe r ev isi on Pt os is 1 0,9 0,8 0,7 0,6 0,5 0,4 0,3 0,2 0,1 0 Do ub l Kappa (95%CI) Test-retest reliability Symptoms of regional muscle weakness Question 21a Question 21b revised Final questionnaire* o Valid and reliable o Measures environmental o o o o factors (SES) May be combined with QoL questionnaires, depression scale etc. psychological aspects Suitable for large-scale studies Easy to translate and adapt Designed in Cardiff TeleForm software; direct scan into a database *Submitted for publication in Neuroepidemiology Future aspects o Use the questionnaire in larger-scale epidemiological studies (case-control, cross-sectional) o Norway: On-going postal survey from Nov. 2009 All MG patients in Norway (515) HRQoL included 3 week response rate: 240 o Adapt and translate to other languages Reproduce epidemiological findings Compare data between countries o Genetic-environment studies, epigenetics Conclusive remarks o The impact of socio-economic factors and other environmental factors in MG are still unknown o The questionnaire for assessing these factors is now ready! o Collaborative networks are essential Acknowledgments o Sonia Berrih-Aknin o Nicole Kerlero-de-Rosbo o All associated and collaborative partners in the EuroMyasthenia Network o MG patients in Norway o Funding: The Norwegian Association for patients with muscle diseases