* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio. Unit 10 Invertebrates Test
Animal locomotion wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
Animal cognition wikipedia , lookup
Animal communication wikipedia , lookup
Animal coloration wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Pain in invertebrates wikipedia , lookup
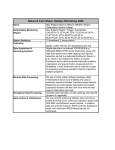
Biology Invertebrates Test Unit 10 Invertebrates Name ________________________ “The greatness of a nation and its moral progress can be judged by the way its animals are treated. - Mahatma Gandhi Part 1. Short Answer. Place the letter of the best answer in the blank to the left of the question. ______1. These fossils were the first multicellular animals with bilateral symmetry and segmentation. a. Burgess Shale b. Mongolia c. Ediacaran hills d. La Brea tar pits _____ 2. The ancestors of most modern animal phyla first appeared during this period. a. Pre-cambrian b. Ediacaran c. Silurian d. Cambrian _____ 3. The only phyla that does not exhibit either bilateral or radial symmetry. a. Cnidaria b. echinoderms c. Mollusks d. Sponges _____ 4. Cells that work together to do a specific task (i.e. muscles) a. tissues b. organs c. systems _____ 5. A cladogram shows which type of relationship? a. evolutionary b. size c. symbiotic above d. organisms d. functional _____ 6. This is one of two phyla that exhibits radial symmetry a. flatworms b. mollusks c. annelids d. arthropods e. none of the e. echinoderms _____ 7. This phyla is the first to show three germ layers, ecto, meso and endoderm. a. Cnidarians b. flatworms c. roundworms d. arthropods e. chordates _____ 8. An example of an echinoderm. a. Barrel sponge b. Planaria c. Sea cucmber _____ 9. One of the two main forms of cnidarians. a. worm-like b. polyp c. asymmetrical d. Octopus e. Earthworm d. bilateral _____ 10. The concentration of nervous and sensory tissue at one end of an organism. a. sensorization b. collectivation c. cephalization d. brain development _____ 11. Cells of the mesoderm specialize to become a. lung tissue b. muscles c. nervous d. blood e. b & d _____ 12. An advantage of segmentation. a. different segments can have different functions. b. segments are easier to replicate c. segments allow for longer size d. a & b _____ 13. A fluid filled cavity between the digestive tube and the outer body wall. It serves as a buffer between the outer wall and the inner organs. a. coelom b. stomach c. mesoderm d. intracellular space e. a & c _____ 14. Body cavities that are partially lined with mesoderm as are found in roundworms. a. acoelomates b. coelomates c. deuterostomes d. pseudocoelomates _____ 15. An example of a freshwater cnidarian polyp. a. Daphnia b. Hydra c. moon jellyfish _____ 16. The chamber in the Hydra where food is digested. d. sea anemone a. cnidocysts b. basal disc c. gastrovascular cavity d. stomach _____ 17. The type of nervous system a Hydra has. a. dorsal nerve cord b. ventral nerve cord c. double nerve cord _____ 18. Hydra can reproduce asexually by a. laying eggs b. live birth through the mouth c. fission d. nerve net d. budding _____ 19. The cell layer found on the outside of the Hydra’s body. a. endoderm b. mesoderm c. epidermis d. ectoderm e. outerderm _____ 20. Daphnia, a favorite food source for Hydra, are in the phylum a. porifera b. Platyhelminthes c. arthropoda d. crustacean _____ 21. Daphnia are more evolved than Hydra in that they have a. a heart b. eye spots c. stomach d. gills e. buggers e. all of the above _____ 22. An animal that relies primarily on intracellular digestion is the a. sponge b. clam c. dragonfly d. earthworm e. the blob _____ 23. Which of the animals, listed below, is not a member of the phyla Mollusca? a. crayfish b. clam c. snail d. squid e. nautilus _____ 24. The three trends that invertebrates show in the development of the nervous system are centralization, cephalization and a. specialization b. ganglia formation c. nerve net formation d. eye formation _____ 25. The invertebrate, listed below, that does not exhibit cephalization. a. planaria b. Giant squid c. monarch butterfly d. glass sponge _____ 26. Invertebrates have one of three main kinds of skeletons, exoskeletons, endoskeltons and a. hydrostatic skeletons b. cartilage skeletons c. bony skeleons d. chitin _____ 27. An example of an invertebrate with an exoskeleton composed of chitin. a. Hydra b. Giant clam c. Spiny lobster d. Nautilus _____ 28. In early development, this type of blastopore has its opening developing into the mouth. a. protostome b. zygote c. deuterostome d. blastula e. wormy _____ 29. In order for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide an animal’s respiratory system must be kept a. cold b. moist c. dry d. hot e. none of the above _____ 30. In a closed circulatory system, blood a. comes in direct contact with tissues c. remains within blood vessels b. empties into sinuses d. carries just oxygen _____ 31. An example of an invertebrate with an open circulatory system. a. crayfish b. earthworm c. Giant squid d. Leech _____ 32. This toxic waste is a natural by-product of protein digestion and must be eliminated by all animals. a. carbon dioxide b. ammonia c. uric acid d. urea e. c & d _____ 33. The excretory organ of the earthworm. a. Nephridia b. flame cells c. malpighian tubules d. kidneys _____ 34. An example of the phylum annelida. a. Hydra b. Planaria c. leech _____ 35. How the earthworm is able to obtain oxygen. a. gills b. diffusion through the skin d. earthworm e. c & d c. lungs d. book lungs _____ 36. A belt-like glandular swelling in the earthworm that is part of the reproductive system of the Earthworm. a. clitellum b. setae c. prostomium d. septa e. periproct _____ 37. This part of Earthworm’s digestive system is a strong, muscular organ that helps to grind food. a. crop b pharynx c. intestine d. gizzard e. nephridia _____ 38. Since earthworms carry both ovaries and testes they are considered a. hermaphrodites b. androgenous c. males d. females e. different _____ 39. This type of reproduction involves the fertilization of the eggs inside the female’s body. a. external fertilization b. parthenogenesis c. internal fertilization d. budding _____ 40. This phyla contains animals that have spiny skin, tube feet, an endoskeleton and radial symmetry. a. porifera b. flat worms c. round worms d. echinoderms e. crustaceans Part 2. Short answer. Answer the following questions, briefly but completely. 1. Complete the comparing invertebrates table shown below. (12 points. .5 pts. each answer!) Sponges Germ layers Body symmetry Cnidarians Flatworms Annelids absent radial Cephalization Coelom Circulatory system Digestive system Nervous system absent closed 2. Hydra diagram. Fill in the correct names for the parts of the Hydra shown below. (1 pt. each) 1. ________________________ 2. ____________________________ 3. ________________________ 4. ____________________________ 5. ________________________ 6. ____________________________ 7. _________________________ 8. ____________________________ 9. _________________________ 10. ___________________________ 11. ________________________ 3. Earthworm Diagram. Fill in the correct names for the parts of the Earthworm shown below. (1 pt. each)