* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SO-eyeball_NEU_14
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Corrective lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Corneal transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
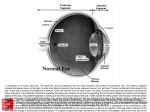
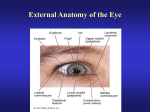
THE EYEBALL Prof. Dr. Selda Önderoğlu Department of Anatomy THE ORGAN OF VISION • Located in the orbit- embedded in orbital fat • Fascial sheath- capsule of Tenon • Two spheres - anterior segment --transparent , 1/6 - posterior segment -- opaque, 5/6 AXES OF EYEBALL OCULAR AXIS - anterior poleposterior pole - parallel in two eyeballs OPTIC AXIS - posterior pole of lensfovea centralis - Not parallel in two eyeballs EQUATOR OF EYEBALL LAYERS (TUNICS) 1-FIBROUS LAYER 2-VASCULAR LAYER (uveal tract) 3-NERVOUS LAYER (retina) FIBROUS LAYER- FUNCTIONS • A place for the attachment of muscles. • Maintain a constant intraocular pressure. • Protect the deeply located structures. FIBROUS LAYER • SCLERA ( characteristics ) -5/6 POSTERIOR PART White part Opaque, hard Thickest behind . CORNEA -1/6 ANTERIOR PART Transparent SCLERA • Tenon’s capsule (Fascial Sheath-Vagina Bulbi) • Episcleral space • SCLERA • Perichoroidal spacedelicate cellular tiss. . VASCULAR LAYER SCLERA IS POSTERIORLY PIERCED BY: fibers of the optic nerve(LAMINA CRIBROSA SCLERAE) ciliary vessels and nerves central vessels of retina venae vorticosae ( 4-5 in number) SCLERA meets the CORNEA at the • SCLEROCORNEAL JUNCTION ( LIMBUS CORNEA ) • SINUS VENOSUS SCLERAE ( SCHLEMM’S CANAL ) -At the sclerocorneal junction. SCLERA Vessels ----- few. Nerves-------ciliary nerves CORNEA • The major site of refraction of light entering the eye. • 1/6 anterior part More convex. • Transparent. • Avascular. • Rich in nerves-opthalmic n. • Does not have lymph vessels. VASCULAR LAYER (UVEAL TRACT ) • CHOROID • CILIARY BODY • IRIS CHOROID • 5/6 posterior part of the eyeball. • highly vascular • Color– dark brown • Extends as far as the ora serrata. • Outer surface is related to—suprachoroid lamina • Inner surface—pigmented layer of retina CILIARY BODY CHOROID continues anteriorly as the ciliary body CILIARY BODY • Rich in blood supply • CILIARY PROCESSES secrete AQUEOUS HUMOUR • SUSPENSORY LIGAMENTStowards the lens CILIARY BODY-FUNCTIONS • SUSPENSION OF LENS • PRODUCTION OF AQUEOUS HUMOUR • CHANGING THE ANTERO-POSTERIOR DISTANCE OF LENS (FOR THE MECHANISM OF ACCOMODATION ) CILIARY MUSCLE • Smooth muscle• Nerve-psympOCULOMOTORpostganglionic fibers from ciliary ganglion • Function-changes in anteroposterior distance of lens. ---contract-susp. Lig. Relax.-thickness of lens increases. (or opposite) IRIS • Coloured (blue- dark brown ) • Surrounds the pupil • Adjustable diaphragm • Has two margins - CILIARY - PUPILLARY IRIS • Somewhat suspended in aqueous humour and divides the area between cornea and lens into two chambers • ---ANTERIOR ---POSTERIOR Cornea – iris meet at —IRIDOCORNEAL ANGLE. AQUEOUS HUMOUR CILIARY PROCESSES -> POSTERIOR CHAMBER - > PUPIL –> ANTERIOR CHAMBER –> SINUS VENOSUS SCLERAE (at the iridocorneal angle) –> ANTERIOR CILIARY VEINS- > OPHTHALMIC VEINS –> CAVERNOUS SINUS MUSCLES OF THE IRIS • SPHINCTER PUPILLA MUSCLE—smooth musclemeiosis—innervated by parasymp.-short ciliary nn. ( oculomotor n.) • DILATOR PUPILLA MUSCLE—smooth musclemidriasis- innervated by symp.—sup. cervical symp. gang.-int. car. a.-long ciliary nn. ARTERIES OF IRIS long posterior ciliary aa.(ophthalmic a.) • Short posterior ciliary aa.-(muscular brs.) • --MAJOR ARTERIAL CIRCLE—(at the ciliary margin) Brs. From major arterial circle and anterior ciliary aa. --MINOR ARTERIAL CIRCLE RETINA • Innermost layer of the eyeball. • The neural- sensory layer • Composed of 2 layers ----outer— PIGMENTED LAYER ----inner--NERVOUS LAYER ORA SERRATA • The place where nervous layer of retina ends. • But the pigmented layer continues anteriorly over the back of the ciliary processes and the iris—ciliary partiridial part. PARTS OF RETINA OPTIC PART from optic disc-to ora serrata pigmented+ nervous layers present here. PARS CAECA RETINABlind part. from ora serrata Anteriorly.Only pigmented layer present. MACULA LUTEA-FOVEA CENTRALIS • MACULA LUTEA=YELLOW SPOT • Oval yellowish area near the the centre of posterior part of retina. • FOVEA CENTRALIS-is the central depression located in the macula lutea---where VISUAL RESOLUTION IS HIGH. HAS ONLY CONES. OPTIC DISC-araea where optic n. Leaves the eyeball • OPTIC DISC = BLIND SPOT insensitive to light. 3mm. Nasal to macula lutea. --central a. And v.of retina. ---in normal ophthalmoscopic examinations color= PINK --- if optic n. Atrophies,color = WHITE CENTRAL RETINAL ARTERY • Courses through optic nerve fibers • The first branch of ophthalmic artery • Branches – superior and inferior each divides into temporal & nasal brs. -So 4aa. Supplies each quadrant of retina. CENTRAL RETINAL VESSELS • ARE THE ONLY VESSELS IN THE BODY WHICH CAN BE INSPECTED DIRECTLY WITH NAKED EYE ( through an ophthalmoscope). OCULAR REFRACTIVE MEDIA • • • • CORNEA AQUEOUS HUMOUR LENS VITREOUS HUMOUR AQUEOUS HUMOR • Fills the anterior and posterior chambers. • Secreted by ciliary processes- Functions -intraocular pressure -shape of eyeball -metabolic avenue for avascular structurescornea, lens. VITREOUS HUMOR • Occupies vitreous body (chamber)- posterior to lens. • Colorless,structureless, transparent gel LENS • • • - Biconvex, transparent body. Has a capsule. Central points anterior pole posterior pole-AXIS equator, faint sutural lines(radii lentis) devoid of vessels. ARTERIES AND VEINS OF EYEBALL • Artery- Ophtalmic artery • Veins- Opthalmic veins