* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Otitis Media with Effusion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Page 1 of 8
View this article online at: patient.info/doctor/otitis-media-with-effusion
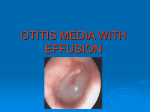
Otitis Media with Effusion
Synonym: glue ear
Otitis media with effusion (OME), also called glue ear, is characterised by a collection of fluid in the middle-ear
cleft. there is chronic inflammation but without signs of acute inflammation. OME is the most common cause of
hearing impairment (and the most common reason for elective surgery) in childhood, where it usually follows an
episode of acute otitis media (AOM). It is uncommon in adults, in whom Eustachian tube dysfunction is the
predominant cause and suspicious aetiologies should be considered. [1]
Most cases of OME will resolve spontaneously. However, in affected ears the average hearing loss is 20 decibels
(dB) but may be as much as 50 dB. Surgery, in the form of grommet insertion, with or without adenoidectomy, is
the most effective treatment in persistent, symptomatic cases. [2]
Epidemiology [1]
OME is the most common cause of acquired hearing loss in childhood.
It is more common between the ages of 1 and 6.
The prevalence at the age of 2 is approximately 20%. This drops after the age of 5 and is about 8%
between the ages of 7-8.
By the age of 10, 80% of children will have had one or more episodes of OME.
The incidence of OME in adults is not known, but it is much less common.
Risk factors (children) [1]
OME is most common in children aged between 1 and 6 years, in the winter.
Most cases are thought to follow an episode of AOM, particularly in children aged under 3 years.
Page 2 of 8
OME may then occur because of one or more of the following:
Impaired Eustachian tube function reducing aeration of the middle ear.
Low-grade infection (bacterial or viral).
Chronic colonisation of the adenoids, which may act as a source of bacteria entering the
middle-ear cleft.
Persistent inflammation.
Adenoidal infection or hypertrophy.
OME is more common in children with craniofacial malformations, particularly cleft palate.
OME is more common in individuals with Down's syndrome, allergic rhinitis and conditions of impaired
ciliary motility including cystic fibrosis.
In children risk is increased by the following factors:
Male gender.
Daycare attendance.
Frequent upper respiratory tract infection.
Having older siblings.
Lower parental socio-economic group.
Parents who smoke.
Winter.
One study found a link between gastro-oesophageal reflux in children and OME: it is postulated that
reflux increases the level of inflammatory cytokines present in the nasopharynx and middle ear. [3]
Risk factors (adults) [4]
Middle ear fluid in adults needs to be viewed with suspicion, particularly if unilateral. In one series of 167 cases,
4.8% were ascribed to an underlying head and neck tumour.
AOM is uncommon in adults and is thus not a common precursor to OME.
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is the main aetiological factor in adults. Causes of ETD include:
Infection/inflammation:
Severe nasopharyngeal infection (eg, sinusitis) inflames the Eustachian tube
openings, resulting in ETD.
Severe or chronic allergy may produce the same effect.
Anatomical blockage:
Severe nasal septal deviation with an obstructed airway.
The presence of tonsils and adenoids with obstruction to Eustachian tubes.
A nasopharyngeal tumour near Eustachian tube openings.
Radiation to the head and neck following cancer treatments.
Radical head and neck surgery, on maxillary sinuses and/or palate, that
transects the Eustachian tube.
Secondary inflammation from allergic rhinitis.
Frequent upper respiratory infection. Some viruses may directly damage the
Eustachian tube lining, decreasing ciliary clearance.
Trauma (usually barotrauma - eg, after a dive or flight).
One Taiwanese study (where nasopharyngeal carcinoma is more prevalent than in Western Europe) found that
the incidence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in adults with OME alone was 5 of 87 patients. [5]
Spectrum of otitis media [6]
Otitis media (OM) is an umbrella term for a group of complex infective and inflammatory conditions affecting the
middle ear. All OM involves pathology of the middle ear and middle ear mucosa. OM is a leading cause of
healthcare visits worldwide and its complications are important causes of preventable hearing loss, particularly in
the developing world. [7]
Page 3 of 8
There are various subtypes of OM. These include AOM, OME, chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM),
mastoiditis and cholesteatoma. They are generally described as discrete diseases but in reality there is a great
degree of overlap between the different types. OM can be seen as a continuum/spectrum of diseases:
AOM is acute inflammation of the middle ear and may be caused by bacteria or viruses. A subtype of
AOM is acute suppurative OM, characterised by the presence of pus in the middle ear. In around 5%
the eardrum perforates.
OME is a chronic inflammatory condition without acute inflammation, which often follows a slowly
resolving AOM. There is an effusion of glue-like fluid behind an intact tympanic membrane in the
absence of signs and symptoms of acute inflammation.
CSOM is long-standing suppurative middle ear inflammation, usually with a persistently perforated
tympanic membrane.
Mastoiditis is acute inflammation of the mastoid periosteum and air cells occurring when AOM
infection spreads out from the middle ear.
Cholesteatoma occurs when keratinising squamous epithelium (skin) is present in the middle ear as a
result of tympanic membrane retraction.
Presentation in children [1]
History
Hearing loss is the usual presenting symptom, although this is easily missed in very young children.
Hearing loss is not invariably present. Hearing loss in children may present as:
Mishearing, difficulty with communication in a group, listening to the TV at excessively high
volumes or needing things to be repeated.
Lack of concentration, withdrawal.
Impaired speech and language development.
Impaired school progress.
Mild intermittent ear pain with fullness or popping.
There may be a history of recurrent ear infection, upper respiratory tract infections or nasal
obstruction.
Occasionally balance problems may be a feature.
Examination findings
Opacification of the drum (other than due to scarring).
There are usually no signs of inflammation or discharge on examination.
Loss of the light reflex, or a more diffused light reflex.
Indrawn, retracted, or concave drum.
Decreased or absent mobility of the drum.
Presence of bubbles or fluid level.
Yellow or amber colour change to the drum.
Fullness or bulging of the drum, although this is not typical.
A pneumatic tympanogram typically shows an immobile eardrum or negative middle ear pressure
(which retracts the drum). This is not generally available in primary care in the UK.
Presentation in adults [8]
Adult OME is more often unilateral than in children, which may reflect the underlying causes.
Typical symptoms include:
OME in adults usually presents with hearing loss.
A feeling of aural fullness.
Crackling or popping tinnitus.
A foreign body sensation in the external auditory canal.
Mild, diffuse aural pain.
Complaints of acute ear pain are rare.
A vague sense of unsteadiness without true vertigo may be seen.
Page 4 of 8
Investigations in children [1]
Children with persistent symptoms or signs should be referred for a hearing test or directly to an ENT specialist if
GP access to audiometry is not available.
Not all cases require referral. Spontaneous resolution often occurs, so it worth observing for three months to see
whether the symptoms and signs resolve ('active observation'). [9] One study found that 50% of children with 20
dB hearing loss will recover in three months without treatment.
Hearing assessment
Hearing tests typically show a mild conductive hearing loss.
Pure-tone audiometry is the best way to assess hearing in children of 4 years or older. [10]
The McCormick Toy Test and the distraction tests are suitable for children younger than 4 years: [11]
These tests do not provide a quantitative level of loss.
A hearing loss of 25 dB or greater in the better ear is usually important:
With a hearing loss of 30 dB, normal conversation may sound like a soft whisper. [12]
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends a second hearing test three
months after the first.
Investigations in adults [2, 4]
OME has a lower prevalence in adults and is frequently associated with other underlying diagnoses. Unilateral
OME in an adult is a suspicious finding.
Paranasal sinus disease is the main underlying cause of OME in adults, accounting for two thirds of cases in one
series. However, other causes included head and neck tumours (4.8%).
Adults with OME should therefore be fully evaluated for underlying conditions.
Nasopharyngeal tumours are relatively more common in patients of Southern Chinese ethnicity. One study in
Taiwan suggested that all adults with OME in whom a cause is not clearly understood should have full
nasopharyngeal evaluation, including biopsy. [5]
Management [1, 9]
Management in children
Advice
Give written information about OME to parents of affected children and reassure parents that:
OME is a self-limiting illness and 90% of children will have complete resolution within one year,
although recurrence is common.
There is no proven benefit from treatment with any medication or alternative therapy.
Parental smoking increases the risk of OME.
Advise parents of children with hearing loss to assist them by:
Facing their child when speaking to them.
Slowing their speech.
Keeping speech clear.
Increasing speech volume slightly.
Turning off competing stimuli such as radio or TV.
Encouraging daily reading, which helps language development.
Page 5 of 8
Hearing aiding
NICE recommends hearing aids for children with bilateral OME and hearing loss where surgery is not
acceptable or is contra-indicated.
Each case needs to be considered on its own merits: the need to assist hearing during a period of
active observation, for example, has to be weighed against evidence that the use of aids in children
can increase anxiety. [13]
Pharmacological [14, 15]
Medical management (eg, antibiotics, topical or systemic antihistamines or decongestants) is not recommended.
A Cochrane review found that current guidelines developed by both the UK's National Collaborating
Centre for Women's and Children's Health (2008) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (2004)
recommends against using oral or topical nasal steroids in treating children with OME.
High-quality evidence of multiple short- and long-term outcomes repeatedly and unequivocally
demonstrated no benefit for use of antihistamines and decongestants over placebo for treating OME.
Additionally, the reviewed studies found evidence of side-effects and harms with the use of these
medications.
A second Cochrane review looked at the use of antibiotics in OME in over 3,000 children and
concluded that the results do not support the routine use of antibiotics for children up to 18 years of
age with OME. The largest effects of antibiotics were seen with continuous use over weeks or months
but these were felt to be balanced by the potential adverse effects of this approach, including sideeffects and increased bacterial resistance.
The treatment of adults with uncomplicated OME is generally extrapolated from that of children. If there
is an underlying cause then this should be treated appropriately. There is a lack of clear evidence on
the treatment of uncomplicated OME in adults.
Referral
Most children who present with OME can be safely managed with active observation.
Earlier referral may be considered for children with significant hearing difficulties, particularly if there
are developmental, social or educational difficulties, or if there is pre-existing hearing impairment.
Active observation is not appropriate for children who have significant disability or who have
associated high-risk conditions - eg, Down's syndrome, cleft palate.
Children with hearing loss demonstrated by the second hearing test should be referred to ENT.
Active observation [9]
The use of surgical treatment for OME has fallen dramatically in recent years with the recognition that many
cases resolve with active observation.
Autoinflation
This is a harmless technique used to induce a Valsalva manoeuvre. NICE does not oppose its use but the
evidence base is limited.
The recommended method is with an Otovent® device. A balloon is inflated by blowing into it from one
nostril, while sealing the other nostril with a finger. This action results in an increase in intranasal
pressure and opening of the Eustachian tube (ie a Valsalva manoeuvre).
Surgery [1, 9]
NICE recommends that children who most benefit from surgery are those with:
Persistent bilateral OME lasting three or more months.
A hearing loss in the best ear of 25-30 dB or worse, averaged at 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 kHz.
Children with better hearing but who have social, educational or developmental difficulties may
exceptionally also benefit from surgical treatment.
The application of these criteria has generated concern that surgery may be withheld from children who would
otherwise benefit from it.
Page 6 of 8
Insertion of grommets (ventilation tubes)
This is the first-line treatment.
NICE concludes that insertion of grommets results in an improvement in hearing over a twelve-month
period, which starts to tail off after six months. There is little evidence that language or speech
development improves in the long term. [1]
Tympanosclerosis frequently occurs after grommet insertion, although the long-term consequences of
this are uncertain. [1]
Infection after grommet insertion may occur and there is also a slightly increased incidence of chronic
perforation. [1]
Grommet insertion has traditionally been performed under general anaesthetic, although it is possible
to perform the procedure under local anaesthetic. Topical anaesthetic is applied to the ear canal
approximately 30 minutes prior to the procedure.
A Cochrane review of 2011 concluded that: [14]
In children with hearing loss induced by OME the effect of grommets on hearing appears small and
diminishes after 6-9 months (by which time natural resolution leads to improved hearing in those
children not treated surgically).
No effect was found on other child outcomes but data were sparse in this area.
No study has been performed in children with established speech, language or developmental
problems, so no conclusion can be drawn in the case of these children.
Adenoidectomy
Adenoidectomy is recommended only if recurrent upper respiratory tract symptoms are a feature.
Grommets and adenoidectomy reduce time with OME and improve hearing in the short term. Both treatments
have associated harms. Large, well-controlled studies could help resolve the risk:benefit ratio by measuring AOM
recurrence, functional outcomes, quality of life and long-term outcomes. Further research is needed to support
treatment decisions in sub-populations, particularly in patients with comorbidities. [16]
Laser myringotomy [17, 18, 19]
Myringotomy is an incision in the tympanic membrane. Historically, in the pre antibiotic era, it was
performed with a myringotomy knife to allow drainage (or suction) of middle ear fluid (it was described
by Sir Ashley Cooper in 1802). It was popular until the arrival of antibiotics in the 1940s.
Laser myringotomy (also called laser fenestration) uses a laser diode to incise the tympanic
membrane, with a view to allowing middle ear fluid sampling or drainage without general anaesthetic
or grommet insertion. (Laser diodes are tiny, portable, low-voltage lasers which produce a cone rather
than a cylinder of light.) Laser myringotomy is safe, quick and painless and the hole it leaves in the
tympanic membrane remains patent for longer than those made by incision with a blade. However, the
duration of patency it produces is still too short (3-4 weeks) to achieve long-term clearance of the
effusion in OME in adults or children.
Laser diodes may also be used to perform myringotomy prior to ventilation tube insertion.
Management in adults
Adults with persisting OME and no sinister underlying cause which needs treatment are managed as for children.
Outcomes for surgery and myringotomy appear to be similar.
Complications
OME may adversely affect speech, language development, behaviour and education:
Evidence shows only a weak association between OME and delayed speech and language
development. Most studies suggest that any adverse effect is temporary in the majority of
children. [1]
One study found an increased incidence in anxiety/depression disorders and attention deficit disorders
compared with controls. [20]
Page 7 of 8
Prevention
One study found that A (H1N1) pandemic influenza vaccine afforded a two- to nine-fold protection
against OME. [3]
Pneumococcal vaccine did not confer similar benefits. [21]
Prognosis [1, 8]
Spontaneous resolution of OME is common in children. The effusion normally resolves in 6-10 weeks
and 50-90% of children are clear within 12 weeks.
However, 30-40% of children have recurrent episodes and 5-10% of episodes last for more than a
year.
In most children, problems with OME do not persist beyond early childhood but sometimes they can
last much longer.
The impact of OME is magnified if there are co-existing problems such as deafness of other causes,
visual problems, or speech or educational difficulties.
Poorer prognosis in children is associated with multiple occurrences and mucoid effusion.
Poorer prognosis in adults with no sinister underlying cause prognosis is associated with a history of
previous grommet use.
Further reading & references
1. Otitis media with effusion; NICE CKS, March 2011 (UK access only)
2. Atkinson H, Wallis S, Coatesworth AP; Otitis media with effusion. Postgrad Med. 2015 May;127(4):381-5. doi:
10.1080/00325481.2015.1028317.
3. Cuhaci Cakir B, Beyazova U, Kemaloglu YK, et al; Effectiveness of pandemic influenza A/H1N1 vaccine for prevention of
otitis media in children. Eur J Pediatr. 2012 Nov;171(11):1667-71. doi: 10.1007/s00431-012-1797-2. Epub 2012 Sep 30.
4. Finkelstein Y, Ophir D, Talmi YP, et al; Adult-onset otitis media with effusion. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994
May;120(5):517-27.
5. Ho KY, Lee KW, Chai CY, et al; Early recognition of nasopharyngeal cancer in adults with only otitis media with effusion. J
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008 Jun;37(3):362-5.
6. Qureishi A, Lee Y, Belfield K, Birchall JP, Daniel M. Update on otitis media – prevention and treatment. Infection and Drug
Resistance. 2014;7:15-24. doi:10.2147/IDR.S39637.
7. Monasta L, Ronfani L, Marchetti F, et al; Burden of disease caused by otitis media: systematic review and global
estimates. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36226. Epub 2012 Apr 30.
8. Chang C-W, Yang Y-W, Fu C Y, Shiao A-S: Differences between children and adults with otitis media with effusion treated
with CO2 laser myringotomy Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 75 (2012) 29e35
9. Surgical management of children with otitis media with effusion (OME); NICE Clinical Guideline (February 2008)
10. Bamford J, Fortnum H, Bristow K, et al; Current practice, accuracy, effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the school entry
hearing screen. Health Technol Assess. 2007 Aug;11(32):1-168, iii-iv.
11. Hall AJ, Munro KJ, Heron J; Developmental changes in word recognition threshold from two to five years of age in children
with different middle ear status. Int J Audiol. 2007 Jul;46(7):355-61.
12. Screening for otitis media with effusion: recommendation statement from the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health
Care; CMAJ. 2001 Oct 16;165(8):1092-3.
13. Theunissen SC, Rieffe C, Kouwenberg M, et al; Anxiety in children with hearing aids or cochlear implants compared to
normally hearing controls. Laryngoscope. 2012 Mar;122(3):654-9. doi: 10.1002/lary.22502. Epub 2012 Jan 17.
14. Browning GG, Rovers MM, Williamson I, et al; Grommets (ventilation tubes) for hearing loss associated with otitis media
with effusion in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Oct 6;(10):CD001801. doi:
10.1002/14651858.CD001801.pub3.
15. van Zon A, van der Heijden GJ, van Dongen TM, et al; Antibiotics for otitis media with effusion in children. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;9:CD009163. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009163.pub2.
16. Wallace IF, Berkman ND, Lohr KN, et al; Surgical treatments for otitis media with effusion: a systematic review. Pediatrics.
2014 Feb;133(2):296-311. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-3228. Epub 2014 Jan 6.
17. Koopman JP, Reuchlin AG, Kummer EE, et al; Laser myringotomy versus ventilation tubes in children with otitis media with
Laryngoscope. 2004 May;114(5):844-9.
18. Zanetti D, Piccioni M, Nassif N, et al; Diode laser myringotomy for chronic otitis media with effusion in adults. Otol Neurotol.
2005 Jan;26(1):12-8.
19. Youssef TF, Ahmed MR; Laser-assisted myringotomy versus conventional myringotomy with ventilation tube insertion in
treatment of otitis media with effusion: Long-term follow-up. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2013 Mar;5(1):16-20. doi:
10.1556/IMAS.5.2013.1.3. Epub 2013 Mar 19.
20. Gouma P, Mallis A, Daniilidis V, et al; Behavioral trends in young children with conductive hearing loss: a case-control study.
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011 Jan;268(1):63-6. Epub 2010 Jul 28.
21. El-MakhzangyAM, Ismail NM, Galal SB, et al; Can vaccination against pneumococci prevent otitis media with effusion? Eur
Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Sep;269(9):2021-6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-012-1975-x. Epub 2012 Mar 3.
Page 8 of 8
Disclaimer: This article is for information only and should not be used for the diagnosis or treatment of medical
conditions. Patient Platform Limited has used all reasonable care in compiling the information but makes no
warranty as to its accuracy. Consult a doctor or other healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of
medical conditions. For details see our conditions.
Original Author:
Dr Laurence Knott
Current Version:
Dr Mary Lowth
Peer Reviewer:
Dr Helen Huins
Document ID:
2154 (v25)
Last Checked:
02/02/2016
Next Review:
31/01/2021
View this article online at: patient.info/doctor/otitis-media-with-effusion
Discuss Otitis Media with Effusion and find more trusted resources at Patient.
© Patient Platform Limited - All rights reserved.