* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slideshow
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
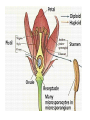
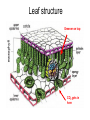
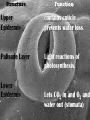
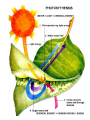
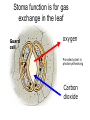
What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? – Reactants = water, CO2, and sunlight – Products = glucose and O2 Fold your sheet in half. Cut flaps on lines by cutting the first layer only. Structure and function of plants Structure Functions Adaptations Open your foldable and label it like this. Flowers Structure and Function Anther: produces pollen Pollen: haploid male gametes (sex cells) Stigma & Style: Sticky top of style where pollen lands. The style transports it to the ovary. Ovary: Female organ which produces female gametes. Adaptation to Environment 1. Bright colors and sweet nectar to attract pollinators. 2. Development of fruit for seed dispersal. Leaves Leaf structure Greener on top CO2 gets in here Structure Function Upper Epidermis contains cuticle prevents water loss Palisade Layer Light reactions of photosynthesis. Lower Epidermis Lets CO2 in and O2 and water out (stomata) Function of leaves • Trap light energy for photosynthesis • Produce sugar from photosynthesis • Exchange of gases – carbon dioxide (in) and oxygen (out) Structure Wide Helps to catch more light energy Thin Helps get carbon dioxide from bottom to top of leaf for photosynthesis Stoma is a small hole Its size is controlled by 2 guard cells closed open Stoma function is for gas exchange in the leaf Guard cell oxygen Provided plant is photosynthesising Carbon dioxide Adaptations to environment Thick cuticle in dry climates. Few stomata to prevent water loss. Reduced surface area to prevent water loss. (cactus) Stems Structure Xylem Phloem Function vascular tissue (tubes) that carries water from the roots to other parts of the plant Vascular tissue that carries sugar (food) Stems • Stems can be herbaceous like the bendable stem of a daisy or woody like the trunk of an oak tree. Adaptation to the Environment Stiff cell walls for trunks and branches. Dead Xylem becomes the wood on the inside of tree trunks. Can be modified to store food. ex: Tubers (potatoes) and Bulbs Roots Structure Function Epidermis -protection and absorption and root cap of water and minerals. Root hairs -increase surface area for absorption Root tips (apical meristem) - tip of root that is growing into the soil (area of mitosis). Wheat seed Root hairs Fragile parts of cells that grow from the main root They massively increase the surface area for absorption Root ‘B’ has had the hairs damaged - Adaptation to the Environment 1. Can be modified to store starch and sugar. (Carrots, Beets, Turnips) 2. In dry climates root systems can be extremely long to reach water.