* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SBI3C: The Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
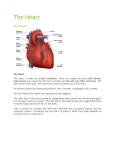
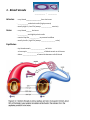
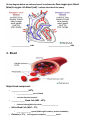
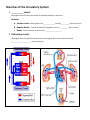
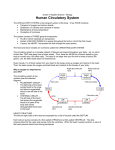
SBI3C: The Circulatory System: Name _____________ The body’s transport system: Functions: 1. ______________________: • ___________ and ___________ etc are distributed to body cells. • __________ ____________ and _________ are taken away from the cell. 2. Maintenance of body temp & chemical balance. 3. Circulation of hormones, components of the immune system etc. Structures: 1. ______________ which carries materials to be transported (____________) 2. ______________ _________________ or tubes for the blood to move through (_________________, ___________, ______________________) 3. A _______________ that pushes the fluid through the blood vessels (_________) 1. Blood Vessels ____________ ; __________ Arteries: - carry blood _________________from the heart - ____________and elastic walls (high pressure) - usually high O2, low CO2 (except ____________ arteries) Veins: - carry blood ______ the heart - ___________ and slightly elastic walls - contain flap-like ___________ to prevent backflow - usually low O2, high CO2 (except ________________ veins) Capillaries: - tiny blood vessels ________________ cell thick - microscopic ___________________ of blood vessels at all tissues - allows ________________ of materials between cells & blood 2. The Incredible Heart Muscle/Pump Great ______________: – __________ 4-5 L of blood through ~160 000 km of blood ____________. High _______________: – __________ on average 72 beats / minute, ~ 100 000 beats / day – During a lifetime, could fill an ocean tanker full of blood TWICE Size: – Size of your ___________ & weighs ~ 300 grams Pace Maker: – Makes its own ‘_____________!’ – ________________ the beating of heart cells Right Side Pump: – Pumps blood that is _______ in ________ to the lungs to pick up oxygen. – Deoxygenated blood from the body drains into the right __________ via the ________ __________ (large veins.) – Blood goes from the right ___________to the right ____________ which pumps the blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery. Left Side Pump: – Pumps blood that is ________ in oxygen to the body to give oxygen to body cells (for cell ________________) – Oxygenated blood from the lung enters the left _____________via the pulmonary veins. – Blood goes from the left atrium to the left ______________ which pumps the blood to the body via the _____________ (largest artery in the body) On the diagram below use coloured pencil to indicate the flow oxygen poor blood (blue) & oxygen rich blood (red). Indicate the side of the pump. __________________ side _____________________ side 3. Blood Major blood component: • ________________ (55%): – __________________ part of blood – contains dissolved material • _____________ Blood Cells (RBC - 44%): – Contains haemoglobin that carries __________________ • White Blood Cells (WBC – 1%): – ________________ system (WBC engulf invaders/ produce antibodies) • Platelets (< 1%): Cell fragments needed to ___________ blood Branches of the Circulatory System 1. __________ circuit: Blood goes from the heart to the rest of the body and back to the heart. Includes: a. Cardiac circuit: Blood goes to the _____________ muscle(__________arteries & veins) b. Hepatic-Portal: Transports blood from digestive tract to __________ then to heart c. Renal: Carries blood to, and from the ___________________ 2. Pulmonary circuit: Blood goes from the right side of the heart to the lungs & back to left side of the heart (______________________ arteries & veins) Heart Cycle: • Systole: Heart _____________________ – Ventricles ___________________ – Blood is pumped _________ of the heart • Diastole: Heart _______________ with blood – The heart muscles _____________ – Atria ___________blood & drains it into ventricles Heart Sounds: Lubb – Dubb - Closing of the heart valves – Ventricles contract & increase in pressure causes the _________ valve to close shut Lubb sound (Systole: Heart __________________) – Ventricles relax, causing blood to rush in from Atria – Decrease in pressure as blood flows in, causing ____________ valves to shut Dubb sound (Diastole: Heart ________ with blood)









![Thecirculatorysystem1[CompatibilityMode].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015667685_1-cf93819f362946148df968ab0ffa5720-150x150.png)