* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Based Predator Stomach Content Analysis for Single and
Survey
Document related concepts
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
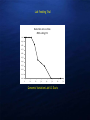
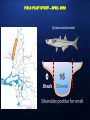
DNA BASED PREDATOR STOMACH CONTENT ANALYSIS FOR SINGLE AND MULTIPLE PREY SPECIES USING QUANTITATIVE POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (QPCR) Gregg Schumer, Cramer Fish Sciences/Genidaqs Scott Brandl, University California Davis Melinda Baerwald, University California Davis Brian Schreier, California Department of Water Resources Veronica Wunderlich, California Department of Water Resources Scott Blankenship, Cramer Fish Sciences/Genidaqs BRIEF OVERVIEW OF POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR) DNA copies PCR was first described in 1983 by Kerry Mullis and awarded the Nobel Prize in 1993 PCR “primers” are designed to amplify targeted sequences of DNA giving PCR its inherent specificity Cycle 1 cycle Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) qPCR follows the principles of PCR (primer selectivity); its key feature is that with the addition of a labeled probe the amplified DNA is detected as the reaction proceeds in real time. QPCR AS A MONITORING TOOL : STOMACH CONTENT ANALYSIS Traditional Visual ID Molecular ID: • • • • • • • • • • • Laborious Time consuming Expensive Ineffective in many instances Limited by the sample qPCR Rapid Cost effective Highly specific High throughput Not limited by sample type All methods have been thoroughly vetted(SNP genotyping, disease detection, gene expression) DNA Sequence TTAATTCAACTACAAGAACCC TAATGGCCAACCTTCGGAAA Design and validation of species specific q-PCR assays TTAATTCAACTACAAGAACCC TAATGGCCAACCTTCGGAAA 1. Determine species “barcode” CO1, CytB 2. Design species specific primer probe sets (qPCR assay design) 3. Validate primer probe sets 4. Test samples presence/absence for species of interest General workflow for stomach contents analysis Presence absence of target species Lab Feeding Trial Detection rate vs time MSS eating DS 1.00 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 Genomic Variation Lab UC Davis 70 FIELD PILOT STUDY – APRIL 2010 658 dissected silversides 0 15 Shoals Channel Silversides positive for smelt 2011 EXPANDED FIELD STUDY March - July 2011 Species (Predators) Number tested for smelt DNA Positive for smelt DNA Mississippi silverside 559 69 Striped bass 73 1 Pikeminnow 44 2 Sunfish 38 1 Largemouth bass 30 2 Gobies 25 1 Threadfin shad 21 1 Chinook salmon 16 1 Golden shiner 10 1 Tule perch 6 1 Exopalaemon shrimp 4 1 Three-spine stickleback 1 1 If you can do this for a single prey species why not multiple prey species? Multi Species/High Throughput Fluidigm Dynamic Array Technology Time Labor Reagents Highlights • Less time = Less cost • Fewer reagents = less cost • Dynamic format (species x samples) • 48x48, 96x96, 24x192 Striped Bass Predation Study 2013-14 General workflow for stomach contents analysis Presence absence of target species Take home message • When appropriate, qPCR is a viable technique for detecting single species individually and multiple species simultaneously. • Once you have the DNA you can always go back and re-analyze later • Dynamic platform. Detection of different species from different sample types Acknowledgements QUESTIONS?