* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MPP1D1
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
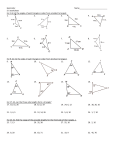
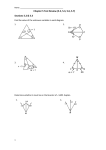
MPP1D1 Chapter 6 Test: Geometry Name:_______________ KNOWLEDGE 1. Match the diagram or definition on the right with the correct term listed below. Pentagon _____ A Right triangle _____ Median _____ Alternate angles _____ Bisector _____ Supplementary angles_____ Altitude _____ Circumcircle _____ Corresponding angles _____ Line segment _____ C H – It is a straight line from a vertex perpendicular to the side opposite the vertex. I – A line dividing an angle into 2 equal parts. J – A line perpendicular to the side of a triangle through its midpoint. K – A circle constructed using the circumcentre as the centre, that passes through each vertex of the triangle. L – A circle inside a triangle. It is constructed using the incentre as the centre of the circle, and it meets each side at exactly one point. M – A line drawn from the midpoint of one side of a triangle to the opposite vertex. 2. Fill in the Blanks a. The supplement of an 80º angle is ________. b. Two angles that add up to 90 º are called ___________________. c. The centroid divides each median in the ratio __________. d. The circumcentre lies ___________ an acute triangle, ____________ an obtuse triangle, and ___________________ of a right-angles triangle. e. A midsegment of a triangle is ______________ to the opposite side. f. A diagonal of a rhombus _______________ the angles at the verticies. g. The sum of the angles in any hexagon is ___________. h. The sum of the exterior angles in a pentagon is ____________. i. The diagonals of a kite are ________________ to each other. 3. Find the measures indicated by the variables. a = _______ b = _______ c = _______ d = _______ e = _______ f = _______ g = _______ h = _______ i = _______ j = _______ APPLICATION 4. Use a compass to construct each of the following. Leave all pencil marks on you sketches. (a) Orthocentre (b) Inscribed circle 5. In the diagram below, CY and AX are two medians of triangle ABC. If PX = 5 cm, find the length of AX. Show the steps of your solution. 6. In ABC, point M is the centroid. If BM = x – 1 and MP = x – 4, find the length of BP. Show the steps of your solution. 7. Solve for all indicated variables and angle measures. a. x = _______ b. c. d. x = ________ a = ________ e. Communication 8. Determine and describe what is wrong with the measures of the angles in triangle ABC. 9. Explain why the straight lines AB and CD are not parallel.