* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Can you guess where all this content is stored?
Tandem Computers wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Team Foundation Server wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
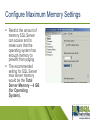
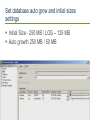
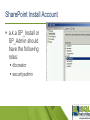
Configuring SQL Server for a successful SharePoint Server Deployment Haaron Gonzalez Solution Architect & Consultant Microsoft MVP SharePoint Server http://msmvps.com/haarongonzalez @haarongonzalez Thanks to Sponsors SQL Saturday Gold Sponsor Silver Sponsor Bronze Sponsor Swag Sponsor Hashtag #SQLSat449 Agenda SharePoint Features History Server Architecture Topologies Service Applications Requirements Recommendations Configuration Optimizations Best Practices What is SharePoint? Share Organize Discover Build Manage Share Connect with employees across the enterprise use SharePoint to engage with people, share ideas and reinvent the way you work together Organize Whether working as a team or an individual, SharePoint helps you organize information, people and projects Organize all your team communications in one place Discover SharePoint makes it easy to find answers, discover insights and connect with the experts answers insights Build design using web standards Developers and web designers can create new experiences on SharePoint using familiar tools and internet standards apps Manage SharePoint provides powerful controls that allow IT departments to manage cost, risk and their time cost risk time Run SharePoint in the cloud Deliver new features and updates faster Reduce storage footprint Improve scalability and performance Server Architecture Evolution of Topology Routing & Caching Front-End More & More Users < 1,000 <100 10KUsers Users Users More Workloads More Workloads Evaluation Search Query Specialized Simple Workload More Usage MoreLight Very Resources And Simple Workload Small Content Large < 10M Content Items Fault Tolerance Multiple Index Partitions Batch Processing Crawl Database Advanced Routing Schematic Diagram: Machines could be virtual or physical. Topologies are rough estimates. A Look at a SharePoint Farm with All Components Distributed Cache Front End Services Distributed Cache Front End Services Distributed Cache Workflow Manager Workflow Manager Workflow Manager Query Processing Query Processing Query Processing Replica Replica Replica Analytics Back End Services Analytics Crawl Crawl Admin Admin Content Processing Content Processing Availability Group #1 Search Content Configuration Availability Group #2 Service Applications Content Availability Group #3 Back End Services Front End Services Web and Application Servers: Single Server Farms Minimum Hardware Requirements Processor: Load balanced or routed requests Web tier Web servers with query component 64-bit, 4 cores RAM: Single server installation – 24GB WFE or app server in a three-tier farm – 12GB Hard disk: 80 GB free for system drive Maintain 2x free space as available RAM Application tier Database tier Application servers with: Central Administration Search administration component Crawl component Database server with: Central Administration configuration and content databases Content databases Search administration database Crawl database Property database Database Servers Minimum Hardware Requirements Processor: Load balanced or routed requests Web tier 64-bit, 4 cores for “small” deployments 64-bit, 8 cores for “medium” deployments Web servers with query component RAM: 8 GB for “small” deployments 16 GB for “medium” deployments RAM depends on usage models & data size Application tier Application servers with: Central Administration Search administration component Crawl component Hard disk: 80 GB free for system drive SP Data Storage dependent on corpus size, performance requirements, etc. Database tier Database server with: Central Administration configuration and content databases Content databases Search administration database Crawl database Property database Recommendations Dedicated SQL Server named instances One instance for all the databases Multiple instances for each type Services Content Search Collation Latin1_General_CI_AS_K S_WS Data Directories Don’t use C:\ to store SQL Server data directories, use other volumes Data root directory User database directory User Database log directory Temp DB directory Temp DB log directory Naming convention More than 20 databases to begin with: Farm Service Applications Content [ENV]_[Type]_[Name] Set Max Degree of Parallelism Set the max degree of parallelism option to 1 (MAXDOP) Setting the max degree of parallelism option to 1 may boost performance and this setting suppresses parallel plan generation. Configure Maximum Memory Settings Restrict the amount of memory SQL Server can access and to make sure that the operating system has enough memory to prevent from paging The recommended setting for SQL Server max server memory would be the Total Server Memory – 4 GB (for Operating System). Set database auto grow and initial sizes settings Initial Size - 250 MB / LOG – 125 MB Auto growth 250 MB / 50 MB SQL Alias Configure SharePoint using a SQL Alias to point to the actual SQL Server SharePoint Install Account a.k.a SP_Install or SP_Admin should have the following roles: dbcreator securityadmin SPDocKit Use SharePoint Documentation Toolkit to generate a Best Practices Analyzer report and evaluate: Data partitions that holds databases should have an allocation unit size of 64k (in most cases) to get the best performance from SQL server. You should put TempDB on a separate (faster) drive to boost performance because this database is I/O intensive. Logs for your databases shouldn’t be on same drive as the database files, again for performance reasons. MAXDOP must be set to 1 for SharePoint to work normally. You should restrict the minimum and maximum memory values for your SQL server. Do not enable auto-create statistics on a SQL instance that hosts SharePoint databases because is not supported. Use reasonable initial settings for your SharePoint databases, especially the growth value (the default is 5 MB). Resources Best practices for SQL Server in a SharePoint Server farm https://technet.microsoft.com/enus/library/hh292622(v=office.15).aspx Evaluations Event evaluations http://www.sqlsaturday.com/449/eventeval.aspx Session evaluations http://www.sqlsaturday.com/449/sessions/sessionevaluation.aspx