* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology II - Grant County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
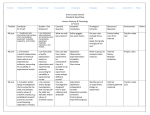
Timeline Standard CSO BII Student I Can Ess. Question Vocabulary Strategies Resources Assessments Notes Strategies/ Activities Resources/ Materials Assessments Grant County Schools Standards Based Map Timeline Standards SC O HAP Student I Can Statement Essential Question Biology II 11th/12th Academic Vocabulary All year 1.1 Implement safe procedures and practices when manipulating equipment, materials, organisms, and models. I can implement safe procedures and practices when manipulating equipment, materials, organisms, and models. What are safe lab practices? Safety goggles Eye wash station Go over rules multiple times. Drill Apply during labs throughout the year. Printed safety rules from internet Teacher made test All year 1.2 formulate scientific explanations based on historical observations and experimental evidence, accounting for variability in experimental results How can data from classic experiments be interpreted? How is it possible to do the same experiment twice and get different results? Skepticism Observation Experimentation Variability Reliability Peer review Work in groups to evaluate classic research. Internet Library Multiple textbooks Project rubric All year 1.3 conduct and/or design investigations that incorporate the skills and attitudes and/or values of scientific inquiry (e.g., established research protocol, accurate record keeping, replication of results and peer review, I can formulate scientific explanations based on historical observations and experimental evidence, accounting for variability in experimental results I can conduct and/or design investigations that incorporate the skills and attitudes and/or values of scientific inquiry. How are investigations designed? How is data collected and analyzed? Experiment Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Constants Control group Experimental group Identify parts of an experiment. Design an experiment. Internet Student gathered materials Teacher made quiz Notes Timeline Standard CSO BII All year All year objectivity, openness, skepticism, fairness, or creativity and logic). 1.4 design, conduct, evaluate and revise experiments (e.g., compose a question to be investigated, design a controlled investigation that produces numeric data, evaluate the data in the context of scientific laws and principles, construct a conclusion based on findings, propose revisions to investigations based on manipulation of variables and/or analysis of error, or communicate and defend the results and conclusions). 1.5 draw conclusions from a variety of data sources to analyze and interpret systems and models (e.g., use graphs and equations to measure and apply variables such as rate and scale, evaluate changes in trends and Student I Can Ess. Question Vocabulary Strategies Resources I can design, conduct, evaluate and revise experiments. How can I design an experiment? How do I determine which will be the experimental group vs. control group? How many subjects do I need in each group to make it valid? How will I know if my results support my hypothesis? Experiment Hypothesis Independent variable Dependent variable Constants Control group Experimental group Give students Library multiple examples Internet of experiment to textbook have them identify parts. Have them design their own experiments and put them on the board or posters. Have other groups of students review their work. I can draw conclusions from a variety of data sources to analyze and interpret systems and models . How can I take information from various sources and combine it to understand models and graphs? How do I use information in Data Interpretation System Model Graph Rate Scale Trends Evaluate Use graphs and models in textbooks in every chapter. Textbook Assessments Notes Experimental procedure will be evaluated before they do experiment. All parts of experiment must be present and identifiable. When experiment is complete, it will be graded on whether results are interpreted correctly, whether or not they support hypothesis. Teacher made activities that include graphs and diagrams. Questions from text Timeline Standard CSO BII All year cycles, or predict the influence of external variances such as potential sources of error, or interpret maps). 1.6 investigate, compare and design scientific and technological solutions to address personal and societal problems. All year 1.7 given current science-technologysocietal issues, construct and defend potential solutions. All year 1.8 relate societal, cultural and economic issues to key scientific innovations. All year 1.9 synthesize concepts across various science disciplines to better understand the natural world (e.g., form and Student I Can Ess. Question Vocabulary Strategies Resources Assessments Notes models to predict an extension of the givens? I can investigate, compare and design scientific and technological solutions to address personal and societal problems. When given current sciencetechnologysocietal issues, I can construct and defend potential solutions. I can relate societal, cultural and economic issues to key scientific innovations. I can synthesize concepts across various science disciplines to better understand the natural world, How can technology be used to address issues of society? Society Technology Use TV news, internet, or newspaper to research an issue, and then design solutions. TV Newspaper internet Projects will be graded according to a rubric What is the best solution for a given issue? Bioethics Ethics Use TV news, internet, or newspaper to research an issue, and then design solutions. TV Newspaper internet Projects will be graded according to a rubric How do new scientific discoveries affect societal, cultural and economic issues? How do all the branches of science relate to each other within the natural world? Society Culture Economics innovation Use TV news, internet, or newspaper to research an issue, and then design solutions. TV Newspaper internet Projects will be graded according to a rubric Vocabulary that fits with subject at hand. Relate each concept to the “real world” as much as possible, and have students make connections where feasible. Internet Textbook Video clips Embedded in subject matter Timeline Standard CSO BII function, systems, or change over time). T1 2.4 analyze the properties of water and its importance in biological systems: Polarity Solubility Specific heat pH and buffers T1 2.1 Correlate functional groups to unique properties of organic molecules to biochemical pathways T1 2.2 Describe the transfer of energy during condensation and hydrolysis reactions of organic molecules (e.g. ATP, enzyme substrate and active site) T1 2.3 Summarize the electrochemical gradients in various Student I Can Ess. Question such as form and function, systems, or change over time. I can explain how water’s polarity, solubility, specific heat function in biological systems How does the world change over time? I can Correlate functional groups to unique properties of organic molecules to biochemical pathways. I can describe the transfer of energy during condensation and hydrolysis reactions of organic molecules (e.g. ATP, enzyme substrate and active site) I can summarize the electrochemical How do functional groups affect the properties of organic molecules in biochemical pathway?? How is energy transferred during chemical reactions in organic systems How do the properties of water affect living systems? What are electrochemical gradients, and Vocabulary Strategies Resources Assessments Notes Textbook Work book internet TMT TM Lab Activity Polarity Solubility Specific heat pH buffers acid base aqueous solution solute solvent Activation energy Substrate Active site Carboxyl Hydroxyl amino Online pH lab Video clips from Internet Internet. Textbook Denaturization lab Workbook Teacher made test Lab report Condensation/ Dehydration Synthesis reactions Hydrolysis Enzyme Substrate Active site Activation energy Demonstrate reactions on board Internet video clips Textbook C-3 Teacher made test Lab report Gated channels Chemiosmosis ATP synthetase Internet video clips Textbook Work book Teacher made test Timeline Standard CSO BII cells and their corresponding environments. Student I Can Ess. Question Vocabulary gradients in various cells and their corresponding environments. I I can describe the flow of energy in photosynthesis and cellular respiration. how to they allow cells to perform their functions? How does energy from the sun power our cells? Chloroplast Photosynthesis ATP chemiosmosis Electron transport Glycolysis Citric acid cycle Mitochondria NADH FAD Thylakoids Stroma Calvin cycle Photosystems I & II Strategies Resources Assessments Notes Create a poster of a specific step in cellular respiration and in photosynthesis Prepared slides microscope Textbook workbook Students will present projects to the class/teacher according to a rubric Teacher made test and quizzes T1 2.5 Examine the flow of energy through specific molecules in: light dependent and light independent photosynthetic reactions glycolysis Kreb’s cycle EPS fermentation T2 2.14 predict phenotypic ratios of crosses: pleiotropy epistasis multiple alleles polygenic inheritance I can set up, work and interpret Punnet squares for multiple types of inheritance. How do pleiotropy and epistasis affect expected outcomes? How do traits with multiple alleles and polygenic traits differ? Mendelian inheritance Pleiotropy Epistasis Multiple alleles Polygenic traits Multifactorial traits Codominance Incomplete dominance Punnet Squares Pedigree interpretation and construction Create a family with a given trait and work problems Textbook Genetics textbook internet 2.13 analyze a karyotype to determine chromosomal abnormalities I can identify Down’s syndrome, Klinefelter’s syndrome, How is chromosome placement on a karyotype determined? Centromere G banding Online karyotyping activity Textbook Workbook internet T2 project Teacher made test and quizzes Timeline Standard CSO BII Student I Can Ess. Question Jacobson’s syndrome by examining a karyotype. What effect do extra or missing chromosomes or pieces of chromosomes have on phenotype? Why are chromosome disorders usually so much more devastation than gene mutations? How does the work of each scientist contribute to the knowledge of the whole? T2 2.12 Distinguish between chromosomal and gene mutations and their potential effects. I can distinguish between chromosomal and gene mutations and their potential effects. T2 2.6 Interpret important research leading to the current knowledge of molecular genetics: Griffith Avery Hershey & Chase Chargaff Franklin & Wilkins Watson & Crick 2.9 analyze the process of DNA replication including: DNA polymerase Semiconservative replication I can explain the steps leading to the current knowledge of DNA by showcasing the works of the scientists who discoveries in the field. T3 I can analyze the process of DNA replication What is the central dogma of molecular biology? Vocabulary Strategies Resources Assessments Notes Point mutation Frame-shift mutation Addition Delection Students will select a chromosome disorder or a gene disorder, research it, and prepare a presentation. Textbook Workbook Genetics text Project rubric Lab report Teacher made quizzes and test nucleotide nuclein blender experiment genetic recombination bacteriophage X-ray diffraction Video clips from internet Internet Textbook workbook Teacher made quizzes and test Replication DNA polymerase Helicase DNA ligase Okazaki fragments Replication fork Leading strand Lagging strand Lab report Teacher made quizzes and tests Timeline Standard CSO BII T3 Base-pairing 2.10 Apply the processes of transcription and translation to gene expression T3 2.11 demonstrate the role of DNA in determining phenotype and illustrate ways of controlling and regulating expression and function of genes T3 2.15 evaluate treatment of viral diseases based on lytic and lysogenic cycles T3 2.7 Explain the use of restriction enzymes, vectors, plasmids and probes in recombinant DNA Student I Can Ess. Question I can apply the processes of transcription and translation to gene expression What is the central dogma of molecular biology? Antigens Antibodies rH factor ABO system Hemolytic disease of the newborn Hemoglobin I can demonstrate the role of DNA in determining phenotype and illustrate ways of controlling and regulating expression and function of genes I can evaluate treatment of viral diseases based on lytic and lysogenic cycles How does DNA control phenotype? DNA mRNA tRNA rRNA transcription translation How does the lytic cycle differ from the lysogenic cycle? Specific defense Nonspecific defense Cell-mediated immunity Antibodies T cells B cells Primary response Secondary response Nasal cavity Pharynx epiglottis Larynx Trachea Bronchus I can explain how How is cloning cloning is accomplished? accomplished Vocabulary Strategies Resources Assessments Notes Do ABO / rH Punnett squares. Determine paternity based on same. Complete chart on donors/recipients Internet video clips of blood compatibility Teacher made problems Teacher made quizzes and test Students will do replication, transcription and translation problems. Students will explain when and where in the cell each process occurs. Research a disease and make electronic presentation. Read textbook and complete activities from workbook. Show video clips from internet. Paper Dry erase board Textbook Video clips Teacher made quizzes and test Internet Textbook Workbook Prezi or PowerPoint software Teacher made quiz and test Presentation rubric Have students identify parts of system on a torso model and on a diagram. Torso model Anatomy Coloring Book. Fetal pig Practical exam on torso model and fetal pig. Timeline Standard CSO BII Student I Can Ess. Question T3 2.8 conduct and interpret DNA investigations such as RFLP and PCR I can interpret gel electrophoresis results How can the sequence of DNA nucleotides be determined with gel electrophoresis? How do algea differ from protozoans and ameboid forms? T3 2.16 analyze the criteria for classifications of protists I can classify protists into kingdoms based on their characteristics. T3 2.17 survey the fungi kingdom: Characteristics Reproduction Relationship to humans and the ecosystem I can describe the types of fungi and explain how they reproduce. Which fungi are important to humans, and why? T3 2.18 compare and contrast members of the plant kingdom in terms of their reproductive systems I can differentiate among seedless plants and seedbearing plants in cones or flowers Q: Why did the botanist slap her boyfriend on their first date? A: He brought her flowers (flowers are reproductive organs-and of course Vocabulary Strategies Resources Assessments Notes Bronchiole Alveolus Capillaries hemoglobin Identify structures in fetal pig gel electrophoresis restriction enzymes DNA polymerase Examine various gels to determine paternity, or criminal activity Internet textvook Euglena Ameba Paramecium Red algae Green algae Brown algae Mycorrhizae Erotrophic Hyphae Mycelium Examine prepared slides of various protists microscope Concept maps of organization of major components of Kingdom Fungi. Color code same Textbook Workbook Biology coloring book Teacher made quizzes Concept maps of organization of major components of Kingdom Plantae. Color code same Textbook Workbook Biology coloring book Assessments Seeds Cones Petals Pistil Stamen Sporophyte gametophyte Teacher made test for physiology. Notes Timeline Standard CSO BII Student I Can Ess. Question reproductive organs really should not be mentioned or exposed on a first date!) How do sponges differ from vertebrates? T4 2.19 compare and contrast members of the animal kingdom in terms of their complexity Tissues Nervous Digestive systems I can differentiate among animal phyla in terms of their complexity T4 2.20 survey embryonic development of animals: Gastrulation Development of different body cavities Tissues develop from germ layers 2.21 examine types of innate and learned animal behaviors: Competitive Reproductive Social Cyclic communicati on I can describe embryonic development of animals in terms of germ layer, tissues and body cavities. How the embryonic development of a mammal differ from that of other animal phyla? I can describe innate and learned animal behaviors. How do animals communicate with each other? T4 Vocabulary Strategies Resources Zygote Blastocyst Blastula Gastrula Endoderm Mesoderm ectoderm Zygote Blastocyst Blastula Gastrula Endoderm Mesoderm ectoderm Altruism Assessments Notes Teacher made test Work in groups to create posters of embryonic development in various animal phyla Internet Library Multiple textbooks Project rubric Internet research on animal behavior Internet Student gathered materials Teacher made quiz