* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test - FloridaMAO
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
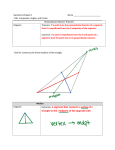
Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #1 Find the sum of the hypotenuses of the triangles shown.(not drawn to scale). All side lengths given are legs. A B 5 8 12 C 15 D 9 13 40 84 Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #1 Find the sum of the hypotenuses of the triangles shown.(not drawn to scale). All side lengths given are legs. A B 5 8 12 C 15 D 9 13 40 84 Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #2 Noah has a string that is 80 inches long. He cuts it into three segments. Segment A, the longest segment, is quadruple the length of Segment C, the shortest segment. Segment B, which is neither the shortest nor longest segment, is 28 inches less than Segment A. What is the simplified ratio of the length of Segment B to the length of Segment C? Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #2 Noah has a string that is 80 inches long. He cuts it into three segments. Segment A, the longest segment, is quadruple the length of Segment C, the shortest segment. Segment B, which is neither the shortest nor longest segment, is 28 inches less than Segment A. What is the simplified ratio of the length of Segment B to the length of Segment C? Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #3 All of the following parts are True or False questions. The final answer is equal to the number of true statements a) A Direct Proof is when you temporarily assume a conclusion is not true in order to prove something b) The smallest angle of a triangle is across from the longest side. c) A triangle with side lengths of 5, 3, and 9 can exist. d) The measure of each exterior angle of a triangle is greater than the measure of either nonadjacent interior angle. Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #3 All of the following parts are True or False questions. The final answer is equal to the number of true statements a) A Direct Proof is when you temporarily assume a conclusion is not true in order to prove something b) The smallest angle of a triangle is across from the longest side. c) A triangle with side lengths of 5, 3, and 9 can exist. d) The measure of each exterior angle of a triangle is greater than the measure of either nonadjacent interior angle. Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #4 For Figure A, assume that all triangles below are congruent and equilateral, with a side length of 4. For Figure B, assume that you have an equilateral triangle inscribed in a rectangle, and the triangle has a side length of 4. Figure A: Figure B: a) Figure A is a trapezoid made up of three triangles. What is the perimeter of the trapezoid? b) In Figure B, the triangle and rectangle share one side (on the bottom) and the triangle touches the top side of the rectangle at one point. What is the perimeter of the rectangle? c) What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? 𝑐 Final Answer: 𝑏 + 𝑎 Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #4 For Figure A, assume that all triangles below are congruent and equilateral, with a side length of 4. For Figure B, assume that you have an equilateral triangle inscribed in a rectangle, and the triangle has a side length of 4. Figure A: Figure B: a) Figure A is a trapezoid made up of three triangles. What is the perimeter of the trapezoid? b) In Figure B, the triangle and rectangle share one side (on the bottom) and the triangle touches the top side of the rectangle at one point. What is the perimeter of the rectangle? c) What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? 𝑐 Final Answer: 𝑏 + 𝑎 Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #5 Find the value for each part and then give your final answer as a + b + c + d . a) Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon with apothem of length 6. b) Find the number of diagonals in a regular polygon with an exterior angle of 30 degrees. c) What is the measure of ONE interior angle of a regular octagon? d) How many diagonals are in a hexagon? Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #5 Find the value for each part and then give your final answer as a + b + c + d . a) Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon with apothem of length 6. b) Find the number of diagonals in a regular polygon with an exterior angle of 30 degrees. c) What is the measure of ONE interior angle of a regular octagon? d) How many diagonals are in a hexagon? Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #6 Find the sum of angles A, B, C, D, E, and F (Not drawn to scale) E F A 50° B D C 30° Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #7 All of the following parts (a, b, and c) are True or False questions. The final answer is equal to the number of true statements. (Note: the conditional statement is not a question. Also, the questions are not asking whether or not the statements are true; the true or false question asks whether or not each statement is correctly identified). CONDITIONAL STATEMENT: If Charmander is a fire-type Pokémon, then Charmander beats Bulbasaur. a) The inverse of the statement is “If Charmander beats Bulbasaur, then Charmander is a firetype Pokémon.” b) The converse of the statement is “If Charmander cannot beat Bulbasaur, then Charmander is not a fire-type Pokémon.” c) The contrapositive of the statement is “If Charmander is not a fire-type Pokémon, then Charmander cannot beat Bulbasaur.” Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #7 All of the following parts (a, b, and c) are True or False questions. The final answer is equal to the number of true statements. (Note: the conditional statement is not a question. Also, the questions are not asking whether or not the statements are true; the true or false question asks whether or not each statement is correctly identified). CONDITIONAL STATEMENT: If Charmander is a fire-type Pokémon, then Charmander beats Bulbasaur. a) The inverse of the statement is “If Charmander beats Bulbasaur, then Charmander is a firetype Pokémon.” b) The converse of the statement is “If Charmander cannot beat Bulbasaur, then Charmander is not a fire-type Pokémon.” c) The contrapositive of the statement is “If Charmander is not a fire-type Pokémon, then Charmander cannot beat Bulbasaur.” Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #8 Find the value of a + b + c given the following information: ̅̅̅̅ ≅ 𝐶𝐹 ̅̅̅̅ , and 𝐷𝐸 ⃡ ̅̅̅̅ ≅ ̅̅̅̅ Triangle ABC is equilateral, 𝐶𝐷 𝐹𝐸 . 𝐴𝐹 ⃡ intersect at point C. and 𝐵𝐷 a) Just based on of the information given in the problem, which of the following could be used to prove Triangle CDE congruent to Triangle CFE (the value for part A is ) SAS = 3 AAA = 6 SSS = 8 SSA = 12 b) What is the measure of Angle DCE in degrees? (for the final answer, leave off the degree sign) c) If ∠𝐶𝐹𝐸 = 85° , what is the measure of ∠𝐶𝐸𝐷 in degrees? *not drawn to scale Vero Beach January 2016 – Math Olympics Geometry Team Test Question #8 Find the value of a + b + c given the following information: ̅̅̅̅ ≅ 𝐶𝐹 ̅̅̅̅ , and 𝐷𝐸 ⃡ ̅̅̅̅ ≅ ̅̅̅̅ Triangle ABC is equilateral, 𝐶𝐷 𝐹𝐸 . 𝐴𝐹 ⃡ intersect at point C. and 𝐵𝐷 a) Just based on of the information given in the problem, which of the following could be used to prove Triangle CDE congruent to Triangle CFE (the value for part A is ) SAS = 3 AAA = 6 SSS = 8 SSA = 12 b) What is the measure of Angle DCE in degrees? (for the final answer, leave off the degree sign) c) If ∠𝐶𝐹𝐸 = 85° , what is the measure of ∠𝐶𝐸𝐷 in degrees? *not drawn to scale Geometry Team Answers: 1. 156 2. 5:3 or 5/3 3. 1 4. 4√3 + 17 5. 198+24√3 6. 540° 7. 0 8. 103 Solutions: 1: Use Pythagorean Theorem (if Pythagorean Triples are not memorized) A) √52 + 122 = 13 B) √82 + 152 = 17 C) √92 + 402 = 41 D) √132 + 842 = 85 2: Set Segment C as the variable X, and then write out the other segments in relation to X. Segment A would be 4X and Segment B would be 4X – 28. The Sum of these segments would equal the length of the string, which is 80 inches. Then, solve for X: 80 = 4𝑋 + 4𝑋 − 28 + 𝑋 = 9𝑋 − 28 108 = 9𝑋 𝑋 = 12 Now that X is found, the lengths of Segment B and C can be found, and the ratio between the two can be solved for as well. 𝑆𝑒𝑔𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐵 𝑆𝑒𝑔𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝐶 3: a) b) c) d) False False False True = 4(12)−28 12 = 48−28 12 20 5 = 12 = 3 4: To find the height of an equilateral triangle, drop an altitude. This will create two right triangles, with the hypotenuse being a side of the equilateral triangle and the legs being half the side of the equilateral triangle and the height: 4 x 2 The Pythagorean Theorem can now be used to find x, which is 2√3. Figure A: Figure B: a) Figure A is a trapezoid made up of three triangles. What is the perimeter of the trapezoid? b) In Figure B, the triangle and rectangle share one side (on the bottom) and the triangle touches the top side of the rectangle at one point. What is the perimeter of the rectangle? c) What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? 𝑐 Final Answer: 𝑏 + 𝑎 a) The perimeter of the trapezoid would be 5(4)=20 b) In this situation, the base and height of the rectangle is equal to the base and height of the triangle. 𝑃 = 2(2√3) + 2(4) = 4√3 + 8 c) Each angle in a equilateral triangle is 60°. 60 ∗ 3 = 180 For the final answer, 4√3 + 8 + 180 20 = 𝟒√𝟑 + 𝟏𝟕 5: a) If a regular hexagon has an apothem of length 6, you can use the special right triangles formed to solve for the side length to be 4√3 , which makes the perimeter 24√3 b) To find the number of diagonals in a regular polygon with an exterior angle of 30 degrees, you can use the information that the sum of all exterior angles in any polygon is always 360 degrees. This makes the polygon a dodecagon. 12(12−3) 2 = 54 c) The equation to find the measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon is the number of sides. 180(8−2) 8 = 180(6) 8 = 1080 8 6(6−3) 2 = 6(3) 2 = 18 2 =9 Final answer: 24√3+54+135+9= 198+24√3 𝑛 , where n is = 135 d) The equation to find the number of diagonals in a polygon is sides. 180(𝑛−2) 𝑛(𝑛−3) 2 , where n is the number of 6: Since there are three pairs of supplemental angles (A and B, C and D, E and F), each of the pairs will equal 180. 180 ∗ 3 = 540 7: a) False b) False c) False 8: a) Since two legs are congruent and the third is shared, SSS proves the two triangles congruent (8) b) Since Triangle ABC is equilateral, angle ACB has to be 60°, which makes angle DCF 60°. Since the triangles are congruent, the corresponding angles must be congruent, making angle DCE 30°. c) The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180°. For triangle CEF, angles ECF and CFE are already known, so subtracting them from 180° will find angle CEF. Angle CEF corresponds to angle CED, so by finding the measure of angle CEF, the measure of CED will be found. 180-85-30=65 8+30+65=103