* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomy Three Posterior Spine
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
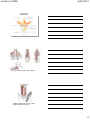
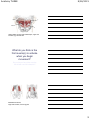
Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Anatomy Three Posterior Spine 1. 6. 2 7 3 8 4 5 Vertebrae Curves of the spine The spine is considered part of the__________skeletal division. Side bending of the spine is called ________________. The function of the spine is __________, __________,and ____________ 1 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Trail 2 - T-7, T-2 and C-7 Trail 2 “Crossing Paths” T-7 and Inferior Angle T-2 and Superior Angle C-7 and Base of the Neck 178 The atlas does not have a body, so there are no discs involved with it. The landmarks of the atlas are on pg 171 The body of the dens forms a pivot joint with the atlas The landmarks of the axis are on pg 171 2 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Facets are angled to about 45̊ and allow for movement in an oblique plane, especially rotation and lateral flexion (transverse and frontal plane) Typical cervical vertebrae are found on pg 172 Movements of the cervical spine Synergists on pg 242-243 Movements of the spine Synergists on pgs 194-195 3 Anatomy THREE Ellipsoidal Joint Atlanto-occiptial joint Allows for Flexion/Extension Lateral Flexion 8/28/2015 Pivot joint Atlantoaxial joint Allows for rotation Gliding joints Articular Facet Joints Allow for movement of the vertebral column, flexion/extension, lateral flexion, and rotation Where the bodies of the vertebrae meet are amphiarthrodial joints Least movable of the vertebrae. Facets are in the frontal plane and allow for free movement of lateral flexion. More information of thoracic vertebrae pg 172 Facets are in the sagittal plane, great for flexion and extension. These vertebrae support a lot of weight. More information of lumbar vertebrae pg 172 4 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Ligaments of the spine, pg 222 Ligaments of the spine, pg 222 Intervertebral discs Make up 25% of the height of the spine. Cervical discs make up 40% of the height of the neck. They bear 80% of the weight placed on the spine, the facet joints get the other 20% Function for weight bearing and shock absorption Nucleus pulposus is 80% water Annulus fibrosis is 10 to 20 layers of fibrocartilage The discs are designed to resist Distraction – vertical movement Shear – horizontal sliding Torsion - rotation 5 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Herniated disc Know your muscle layers , pgs 189-190 Splenius capitis and cervicis, pg 203, Origin, insertion and action 6 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Extension, Rotation to the same side, Lateral flexion Spinalis, pg 197, actions and relationship to other muscles Longissimus, pg 198, actions and relationship to other muscles 7 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Iliocostalis, pg 198, actions and relationship to other muscles Multifidi and rotatores Actions and relationships, pg 200 Transverso spinalis group and Semispinalis capitis Aactions and relationships, pg 200, 201 8 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Suboccipitals, actions and relationships, origin and insertion, pg 192 and 205 What do you think is the first muscle(s) to activate when you begin movement? Do you know of any other muscles the aid with cervical extension? Quadratus lumborum, origin and insertion, actions pg 207 9 Anatomy THREE 8/28/2015 Thoracolumbar Aponeurosis Thoracolumbar Aponeurosis The thoracolumbar aponeurosis is divided into three sections, anterior between the psoas and QL, the middle between the QL and erector spinae and the posterior between the erector spinae and the latissimus dorsi. They meet posterior laterally to these muscles where the obliques and transverse abdominus attach into it. 220 Trail Guide To the Body Student Workbook Pages: 87-90, 106-107, 112, 115-116 • • • • Can you number the bones of the spine 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar And don’t forget the sacrum and coccyx Now you’ve numbered the bones of the spine • Extension comes from the erector spinae • Spinalis, longissimus and iliocostalis • and flexion is helped by the oblique abdominals • The scm helps to flex the cervicals 10