* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thermal Energy
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
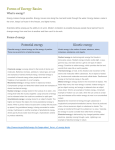
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
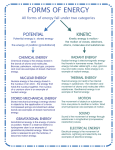
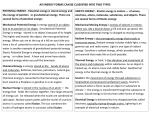
WELCOME TO 1104 PERIOD 2 Homework Exercise #1 is due at the beginning of class. Please put it on the stool in the front of the classroom. PHYSICS 1103 – PERIOD 2 •What are the fundamental forces? •How is work done? •How are forms of energy defined? •What happens when one form of energy is converted into another form? Fundamental force – gravity The gravitational force is an attractive force that exists between all objects. The gravitational force between the center of the Earth and objects near it causes objects to fall toward the surface of the Earth. The gravitational force between the Earth and the Sun holds the Earth in an orbit around the Sun. Fundamental force – electromagnetic The electromagnetic force holds matter together by providing the force that binds atoms into molecules. The force between particles of opposite charge is attractive. + The force between particles of the same charge is repulsive. + + Since positive charges repel one another, how can positively charged protons exist closely packed in an atomic nucleus? Fundamental force – strong nuclear The strong nuclear force holds protons +P and neutrons together in atomic nuclei. n It is the strongest force. It acts over very short distances inside a nucleus. +P n n n +P +P n +P Fundamental force – weak nuclear The weak nuclear force is responsible for some kinds of radioactive decay. The fission (splitting) of Uranium-235 nuclei into smaller fragments in nuclear power plants is an example of the weak force. The weak force acts only when particles are close together. The weak force is the next to the weakest force. (The gravitational force is the weakest of the forces.) Summary of the fundamental forces The gravitational force is an attractive force that exists between all objects. The electromagnetic force holds matter together by providing the force that binds atoms into molecules. The strong nuclear force holds protons and neutrons together in atomic nuclei. The weak nuclear force is responsible for some kinds of radioactive decay. Frictional force The frictional force is NOT one of the fundamental forces. Friction arises from the electromagnetic force between the atoms in an object and the atoms in the surface the object moves across. The gravitational force pressing an object down onto a surface can increase the frictional force between the object and the surface. Friction results in wasted thermal energy. Forces, work, and energy Work is done when a force moves an object over some distance in the direction of the force. Work = Force x Distance W = FxD W = work (joules or foot-pounds) F = force applied (newtons or pounds) D = distance moved in the direction of the force (meters or feet) Work and energy are measured in units of joules. 1 joule = 1 kg m2/s2 Work done against friction Work is done to move the box horizontally against the force of friction. The work done goes into thermal energy. Applied Force Force of friction W=FxD Work done against gravity Work is done to raise the box vertically against the force of gravity. The work done goes into gravitational potential energy. Applied Force equals the weight of the box = Mg Force of gravity h = height the center of gravity of the object is raised W = F x D can be written W = M g x h Work and gravitational potential energy Raising an object gives it gravitational potential energy, which can be used to do work. E pot = M g h M = mass of object (kilograms) g = acceleration of gravity = 9.8 m/s2 h = change in vertical height (meters) Neglecting the energy wasted by friction, the gain in gravitational potential energy from raising an object equals the work done to raise it. Forms of energy: motion Three forms of energy are related to energy of motion: Kinetic Energy: All moving objects exhibit kinetic energy. Thermal Energy: The unorganized kinetic energy of vibrating molecules and atoms within an object. The higher the temperature of an object, the faster its atoms and molecules vibrate. Sound Energy: When atoms and molecules vibrate in an organized way, their vibrations may travel as a sound wave. Forms of energy: electric charge Energy that results from the forces between electric charges is called electromagnetic energy. Electrical Energy: The result of forces between charged particles. Magnetic Energy: Charges moving within some types of materials produce magnetic forces. Magnetic energy results from these forces. Radiant Energy: Radiant energy results from vibrations of charges. Radiant energy (electromagnetic radiation) Radiant energy results from vibrations of charges. As the charges vibrate, they produce waves of energy. The type of radiant energy depends on the wavelength. Shorter wavelengths transmit more energy than longer wavelengths. Forms of stored (potential) energy Stored energy, which can be used to do work, is called potential energy. Gravitational Potential Energy: Energy stored in a raised object that has the potential to fall, slide or roll to a lower position. Strain Potential Energy: Energy stored in a stretched or compressed spring or elastic. Electrical Potential Energy: Energy stored when static positive and negative charges are separated. Capacitors store electrical potential energy. Chemical Potential Energy: Energy existing because atoms and molecules can take in or give off energy when their chemical bonds are formed or broken. Batteries store chemical potential energy. Nuclear Energy: Energy available in the nuclei of atoms that are radioactive and undergo nuclear changes. Summary of the forms of energy Kinetic The energy exhibited by objects in motion. Thermal The unorganized energy of motion of vibrating atoms and molecules. Sound The organized energy of motion of vibrating atoms and molecules. Electrical The energy resulting from forces between charged particles. Magnetic The energy resulting from the forces between magnets. Radiant The energy resulting from vibrations of charges, such as radio waves, microwaves, or visible light. Gravitational The energy stored in raised objects that could fall. Strain The energy stored in a stretched or compressed spring. Chemical The energy available in the chemical bonds binding atoms together. Electrical The energy stored by static electric charges. Nuclear Energy available in the nuclei of radioactive atoms. Every conversion has some wasted energy! Energy Conversion Useful energy out Total energy in Wasted energy out Efficiency = Useful energy out < 100% Total energy in Law of conservation of energy • Energy can be neither created nor destroyed. • The total amount of energy we have now in the Universe is the same amount that existed at its beginning. • All the energy that goes into a conversion process must come out – no energy can be lost or destroyed. • In every energy conversion, some energy is wasted. • Wasted energy is often in the form of thermal energy from the force of friction. Efficiency of the water wheel Efficiency = Epot Gravitational potential energy in Useful work out Total work in = Mgh Conversion Process Wasted energy out Kinetic energy out BEFORE THE NEXT CLASS… Read textbook chapter 3 Print out Activity Sheet 3 and bring it to class. Complete Homework Exercise 2