* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aim: The goal of this project is to study a Linear variable differential
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
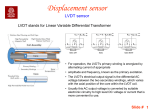
Aim: The goal of this project is to study a Linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) , typical characteristic of measuring devices and possible applications. Apparatus: LVDT, micrometer, analog transducer amplifier Theory Operating principle: Electromagnetic Induction Whenever the flux linkage through an electric conductor changes, a voltage is induced in the conductor. In case of LVDT, an object of ferromagnetic material is moved within the flux path which in effect changes the reluctance of the flux path and brings about the change in flux linkage. Thus mechanical energy (used in moving the ferromagnetic material) is directly converted into electrical energy. The induced voltage is used as a measure of the motion. Construction: LVDT consists of a cylindrical, insulating, non-magnetic form that has primary coil in the mid segment and a secondary coil symmetrically wound in the two end segments. The two secondary coils are connected in series opposition, so that the potentials induced in the two coils segments oppose each other. A core of ferromagnetic material is inserted coaxially in the cylindrical form without actually touching it. Working: The primary coil is energized by AC supply voltage. As a result AC voltage of same frequency is induced in the secondary windings. When the core moves the reluctance of the flux path changes and hence the flux linkage with two secondary windings changes. Since the two secondary coils are connected in series opposition, it is seen that the net induced voltage is zero(Vo = Vs1 - Vs2; Vs1 = Vs2; Vo = 0) when the core is at the centre in between the two secondary windings. This position is known as ’Null position’. Also, since the secondary windings are connected in series opposition, the LVDT provides direction as well as magnitude displacement. At steady state, the amplitude Vo of the induced voltage is proportional, in the linear region, to the core displacement. Note: An error known as ’zero error’ is present in some differential transformer i.e. a nonzero reading at the null position. The main reasons for the zero error are non-uniformities in the windings, harmonic components in the primary signal, and non linearity in the device. The LVDT is a transducer which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy i.e we get output in terms of voltage. Transduced energy levels are generally weak and often need conditioning. The signal conditioning is achieved by analog transducer amplifier which we connect to the LVDT. The signal conditioning associated with the differential transformers includes filtering and amplification. Filtering is necessary to reject the noise i.e. to achieve high signal to noise ratio of the o/p signal .Amplification is necessary to achieve signal strength for data acquisition and processing. Applications: Applications of LVDT are: Automotive appliances Automotive Test Laboratories Die casting machinery Fossil fuel and Nuclear Power Ground attack vehicles Industrial gauging Industrial Robots Injection Moulding Machinery Material handling and testing equipments Missiles Punch presses and Press brakes Simulators Space shuttles Weighing systems Military and Commercial Aircraft Procedure: 1. Connect the o/p of LVDT to the i/p of Analog Transducer Amplifier. 2. Connect the voltmeter to the o/p of Analog Transducer Amplifier. 3. Adjust the micrometer such that voltmeter shows approximately 0 V dc. 4. Take readings for increasing value of displacements till the o/p becomes constant for any number of further increments. 5. Similarly take the readings for decreasing value of displacement till the o/p voltage becomes constant for any number of further decrements. 6. Plot the graph of displacement vs Voltage and observe the linearity. 7. Draw Conclusion.