* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an animal? Part 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
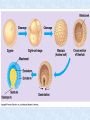
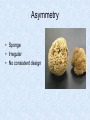
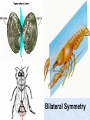
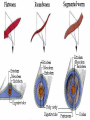
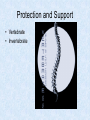
What Is an Animal? Biology Post Falls HS Characteristics • • • • Heterotroph Movement (and sessile) Energy from nutrients Eukaryotic with adaptations Development of Animals • Fertilization of haploid gametes to form zygote • Blastula forms (hollow sphere) • Gastrula forms (indents to give 2 layers) • Ectoderm and endoderm • Ectoderm forms skin and nerves • Endoderm forms digestive lining • Mesoderm forms later into muscles, reproductive and circulatory Development (cont) • Gastrula opening becomes mouth in protostomes • Gastrula opening becomes anus in deuterostomes • Some develop larval forms before adult • Birth occurs after development reaches a satisfactory stage • Viviparous, oviparous, ovoviviparous Symmetry • Balance in proportions of an organism • General body plan or layout • Asymmetry, radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry Asymmetry • Sponge • Irregular • No consistent design Radial Symmetry • Hydra, sand dollar • Central area with parts radiating outwardly like spokes of a wheel • Can be divided along any plane along its axis into relatively equal halves Bilateral Symmetry • Humans • Can be divided down its length into mirror image halves • Anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral • More muscular control so more efficient food gatherers Bilateral Symmetry Body Plans of Bilats • Coelom – true body cavity that develops from the fluid-filled cavity inside the mesoderm • Acoelomate, pseudocoelomate, coelomate • Examples Protection and Support • Exoskeleton • Endoskeleton Protection and Support • Vertebrate • Invertebrate