* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypertension (HTN)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
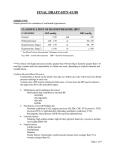
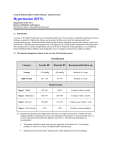
Hypertension (HTN) What Is Hypertension Persistent blood pressure that is higher than the recommended blood pressure range About 60% of all Americans have some form of high blood pressure (pre-hypertension or hypertension) HTN means the heart is working harder than normal putting extra strain on the heart and vessels. Blood Pressure Ranges Normal blood pressure range < 120/80 Pre-Hypertension >120/80 but <140/90 Hypertension - >140/90 Both systolic and diastolic pressures do not have to be out of range Only Systolic or Diastolic must be out of range to qualify as hypertension Two Stages of HTN Stage 1 HTN >140/90 but <160/100 Stage 2 HTN >160/100 What Causes HTN 90%-95% of the time hypertension is elevated blood pressure without an identifiable cause. Exact cause is unknown Many contributing factors have been identified as predisposing factors to HTN Predisposing Factors for HTN Hereditary Predisposition (Family History) Sodium intake Weight Diabetes Mellitus Alcohol Consumption Smoking Serum Lipid Levels (Cholesterol and LDL) Sedentary Lifestyle Ethnicity Age Gender Socioeconomic Status Stress Signs and Symptoms Known as the Silent killer If BP is very high, you may experience: -fatigue -decreased activity tolerance -dizziness -palpitations -angina -dyspnea How HTN is diagnosed Based on the average of 2+ seated BP measurements at the MD’s office Must be averaged Must be seated BP measurements Must be in the MD’s office Complications Related to HTN Heart Failure Enlarged Left Side of the Heart Coronary Artery Disease Cerebrovascular disease (Brain) Peripheral Vascular Disease Kidney Failure Retinal Damage (Eyes) Treatment of HTN Different types require different treatments Pre-Hypertension – Lifestyle modifications Stage I Hypertension – Lifestyle modifications and a thiazide-type diuretic Stage II Hypertension – Lifestyle modifications, thiazide-type diuretic and one another antihypertensive drug Not definitive Treatment is personalized How to Prevent HTN Lifestyle modifications prevent HTN and include: -Maintaining a Healthy Weight -Reduce Salt/Sodium Intake -Increase Physical Exercise Smoking Cessation Limit Alcohol Consumption Limit Fat Intake Control Diabetes Stress Relieving Techniques Take BP Meds as Ordered Home Monitoring of BP References Lewis, S. L., Heitkemper, M. M., Dirksen, S. R., O’Brien, P. G., & Bucher, L. (2007). MedicalSrugical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems. Missouri: Mosby.