* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence of Evolution—clues from living things
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
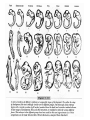
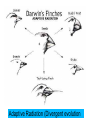
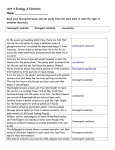
Evidence of Evolution—clues from living things • Homologous structures—similar features that originated in a shared ancestor. --Homologous structures derive from the same embryonic structure --The presence of homologous structures in different species indicates that the species shared a fairly recent common ancestor. --Analogous structures—structures that serve the same function and look somewhat alike. -Analogous structures may have different internal anatomy and derive from different embryonic structures. What 2 parts are homologous structures in the bat and human? Are those structures also analogous? Vestigial Structures • Definition—features that were useful to an ancestor, but do not serve the same use in the modern organism that has them. • Examples: the human appendix, snakes with pelvic and limb bones. • Some whales have vestigial leg bones… • Does this mean they evolved from an ancestor that lived on land? • Vestigial features may come from conserved genes that are not fully turned off. Examples of Vestigial Structures Examples of transitional fossils. See the reduction in hindlimbs (these would have hindered then animal from power swimming. Similarities in Embryology • During the early stages of development, all vertebrate embryos look similar. • Does this mean they share a common ancestor? Similarities in Macromolecules • Homologous proteins—the same proteins that are found in different species. • These proteins are similar but not identical between species. • The more similar the protein, the more recent the two species’ common ancestor. • Human and gorilla hemoglobin have one different amino acid, human and frog hemoglobin have 67 different amino acids. Patterns of Evolution • Coevolution—the change of two or more species in close association with one another. (They become completely dependent on each other) • • – Example: flowers and their pollinators Coevolution example: Flower has long, thin opening that matches butterfly proboscis. Flower advantage: less wasted pollen (butterfly moves from flower to flower) Butterfly advantage: steady food source Examples of convergent evolution. All animals serve same niche but are not directly related. Divergent Evolution • Definition—when two or more related populations or species become more and more different. • Adaptive radiation—when many related species evolve from a single species – Galapagos island finches and mustard plant are examples • Artificial selection--purposeful selection of traits to create a useful variation. – Farm crops are an example. Adaptive Radiation (Divergent evolution Another example of Adaptive RadiationHawaiian Honeycreepers Artificial Selection at Work (~ 10,000 years) Artificial Selection in plants – all from wild mustard Are these examples of convergent evolution, coevolution or divergent evolution? Is this an example of convergent evolution, coevolution or divergent evolution Are these examples of convergent evolution, coevolution or divergent evolution