* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download February 2011 Instructor`s Guide (MS Word format)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
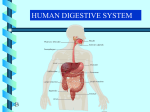
EMTB Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Drill Instructor Guide Session Reference: 1 Topic: Anatomical Terms and Body Systems Level of Instruction: 3 Time Required: 3 hours Materials: · Chalkboard · Anatomy visuals · Anatomy handouts References: · Emergency Care,11th Edition, Brady ============================================================== PREPARATION: Motivation: Page 1 www.mfri.org An understanding of basic anatomy contributes to accurate communications between field providers as well as hospital personal. Understanding anatomy is critical to be able to use the mechanism of injury to determine potential injuries sustained by the patient. Objective (SPO): 1-1 The student will be able to identify, from memory and without assistance, topographic anatomical landmarks, positions, body systems and their functions. Overview: Review of Anatomical Terms and Body Systems · Directional Terms · Positional Terms · Body Systems Page 2 www.mfri.org Anatomical Terms and Body Systems SPO 1-1 The student will be able to identify, from memory and without assistance, topographic anatomical landmarks, positions, body systems and their functions. EO 1-1 Identify the standard directional terms used to describe directions and positions of the body. EO 1-2 Identify the standard positional terms used to describe directions and positions of the body. EO 1-3 List the body systems and describe their component functions. Page 3 www.mfri.org Instructor Guide Instructor Notes I. Directional Terms (1-1) A. Anatomical position 1. Person standing erect 2. Facing forward 3. Palms facing forward B. Planes 1. Flat surface dividing a body into halves 2. Midline a. center of body b. between eyes, extending through umbilicus c. creates left and right halves 3. Medial a. position close to the midline 4. Lateral a. position further away from the midline Page 4 www.mfri.org 5. Bilateral a. refers to both sides of the body 6. Mid-axillary line a. vertically from mid-armpit to the ankle b. creates front and back halves 7. Anterior a. front half b. also referred to as ventral 8. Posterior a. back half b. also referred to as dorsal 9. Superior a. above 10. Inferior a. below 11. Proximal a. closer to the torso 12. Distal a. farther away from the torso Page 5 www.mfri.org 13. Palmar a. refers to palm of the hand 14. Plantar a. refers to sole of the foot 15. Mid-clavicular line a. runs through the center of clavicle and the nipple below 16. Abdominal quadrants a. created by drawing horizontal and vertical lines through the navel b. left upper quadrant (LUQ) 1) stomach 2) spleen 3) portion of the colon 4) small intestine c. right upper quadrant (RUQ) 1) liver 2) gall bladder 3) portion of the colon 4) small intestine d. left lower quadrant (LLQ) 1) small intestine 2) large intestine Page 6 www.mfri.org e. right lower quadrant (RLQ) 5) small intestine 6) large intestine 7) appendix II. Positional Terms (1-2) A. Supine 1. Patient lying on back B. Prone 1. Patient lying on abdomen C. Recovery position 1. Preferred position for unconscious nontrauma patient 2. Patient lying on side 3. Also know as laterally recumbent a. left laterally recumbent b. right laterally recumbent D. Fowler’s position 1. Seated position 2. Generally 45 - 60 degree angle 3. Legs may be straight out or bent Page 7 www.mfri.org E. Semi-Fowler’s position 1. Semi-sitting position F. Trendelenburg position 1. Patient lying with head slightly lower than feet a. patient may lie flat and elevate legs b. If on spine board, tilt the board c. sometimes called the shock position III. Body systems (1-3) A. Musculoskeletal System 1. Components a. bones b. muscles c. ligaments - connects bone to bone d. tendons - connects muscle to bone 2. Functions a. gives body shape b. protects vital internal organs c. provides for body movement 3. Skull a. encloses and protects brain Page 8 www.mfri.org b. cranium 1) top, back and sides of skull c. face 1) front of skull 2) mandible - lower jaw 3) maxilla - upper jaw 4) zygomatic bones - cheek bones 5) nasal bone 6) orbits - surrounds eyes 4. Spinal column a. houses and protects the spinal cord b. vertebrae 8) 33 9) cervical spine - neck 10) thoracic spine - chest a) ribs attach posteriorly 11) lumbar spine - mid back 12) sacral spine/sacrum 13) coccyx - tailbone 5. Thorax a. chest b. thoracic cavity 1) formed by bones 2) contains heart, lungs, major blood vessels Page 9 www.mfri.org 3) ribs 4) sternum a) manubrium - superior portion b) body - center portion c) xiphoid process - inferior tip 6. Pelvis a. ilium b. ischium c. pubis d. acetabulum - hip joint socket 7. Lower extremities c. femur - thigh d. patella - kneecap e. tibia - shin bone f. fibula - lower leg g. lateral malleolus 14) distal end of fibula h. medial malleolus 15) distal end of tibia i. tarsals - ankle j. metatarsals - foot k. calcaneus - heel l. phalanges - toes 8. Upper extremities Page 10 www.mfri.org a. clavicle - collarbone b. scapula - shoulder blade c. acromion process - highest portion of the shoulder d. acromioclavicular joint e. humerus - upper arm f. radius – forearm g. ulna - forearm h. carpals - wrist i. metacarpals - hand j. phalanges - fingers 9. Joints a. ball and socket - hip b. hinge - elbow 10. Muscles a. voluntary 1) skeletal muscles 2) conscious control of the brain b. involuntary 1) smooth muscle 2) no direct, conscious control c. cardiac 1) found only in heart 2) automaticity a) ability to generate and conduct Page 11 www.mfri.org electrical impulses B. Respiratory system 1. Function a. move oxygen into bloodstream. .b. remove carbon dioxide from the bloodstream 2. Anatomy a. oropharynx b. nasopharynx c. pharynx d. epiglottis e. larynx f. cricoid cartilage g. trachea - windpipe h. lungs i. bronchi j. alveoli k. diaphragm 3. Physiology a. inhalation 1) active process 2) intercostal (rib) muscles and diaphragm contract b. exhalation Page 12 www.mfri.org 16) passive process 17) muscles relax C. Cardiovascular/Circulatory System 1. Heart a. atria b. ventricles c. vena cava 1) superior vena cava 2) inferior vena cava d. aorta e. cardiac conduction system 1) sinoatrial (SA) node 2) atrioventricular (AV) node 2. Blood circulation a. arteries 1) carry blood away from heart 2) major arteries a) coronary b) aorta c) pulmonary d) carotid e) femoral f) brachial g) radial h) posterior tibial Page 13 www.mfri.org i) dorsalis pedis b. arterioles 1) smallest branch of arteries c. capillaries 18) cellular level gas exchange d. venules 1) smallest branch of veins e. veins 1) carry blood to the heart 2) major veins a) superior vena cava b) inferior vena cava c) pulmonary f. composition of blood 1) plasma a) watery liquid b) carries solids 2) red blood cells a) carry oxygen and carbon dioxide b) give blood color 3) white blood cells a) fights infection 4) platelets a) creates blood clots D. Nervous System 1. Central nervous system Page 14 www.mfri.org a. brain b. spinal cord c. controls all basic bodily functions 2. Peripheral nervous system a. sensory nerves 1) transmit information to the brain from the body b. motor nerves 1) transmit information to the body from the brain 3. Autonomic nervous system a. division of the peripheral nervous system b. controls involuntary motor function c. controls digestion, heart rate E. Skin 1. Function a. protection b. water balance c. temperature balance d. excretion e. shock absorption (impact) 2. Layers Page 15 www.mfri.org a. epidermis 19) outermost layer 20) comprised of 4 or 5 layers of cells b. dermis 1) below epidermis 2) contains blood vessels, nerves, sweat glands, hair follicles 3) contamination/infection a major problem 4) bleeding and pain associated with injury c. subcutaneous layer 1) below dermis 2) fat and soft tissues 3) major functions are shock absorption and insulation F. Endocrine System 1. Produces hormones to help chemically regulate the body 2. Examples are a. insulin b. epinephrine Page 16 www.mfri.org SUMMARY: Page 17 www.mfri.org Review: Review of Anatomical Terms and Body Systems · Directional Terms · Positional Terms · Body Systems Remotivation: Assignment: ============================================================== EVALUATION: Page 18 www.mfri.org Page 19 www.mfri.org