* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 - History of the Atom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
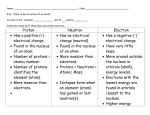
History of the Atom Democritus · Suggested matter was made of very small particles that could not be broken down further. · He called the particles atoms, after the Greek word atomos, which means "uncuttable". Aristotle · Believed that matter was composed of four "elements": (earth, air, fire and water) despite the more recent "atomic" model. John Dalton ·In 1808, Dalton proposed the first "modern" atomic theory: o the atom is the smallest particle of matter. o atoms cannot be created or destroyed o each element has its own kind of atom. o compounds are created when atoms of different elements combine. ·He proposed the atom was a solid sphere that looked like a billiard ball. Jons Berzelius · In 1811, he introduced the classical system of chemical symbols · In 1826, he published a table of atomic weights Dmitri Mendeleev · In the 1860’s, he created the first periodic table J.J. Thomson ·He was the first person to discover electrons. ·He presented the "plum pudding" model of the atom. ·In his model, most of the atom was one large positive charge (pudding) with several small negative charges (plums) embedded in it. Marie Curie · The first woman to win a Nobel Prize and the first to win twice. · Discovered the radioactive elements polonium and radium. Ernest Rutherford ·Well known for conducting the "gold foil experiment". ·In 1911, he presented the "nuclear model" of the atom: the first model to suggest a nucleus with positively charged protons and all the mass of the atom. Negatively charged electrons are distributed in the space surrounding the nucleus. Neils Bohr ·Developed a theory that electrons have different amounts of energy and travel in stable orbits around the atom's nucleus. · In 1913, he presented the "Bohr model" or "planetary model" of the atom which is similar to a model of the solar system. Max Planck · Won the Nobel Prize for developing quantum theory (a subset of physics explaining the physical behaviours at the molecular, atomic and sub-atomic levels). Albert Einstein · Developed the general theory of relativity · Won the Nobel Prize for his discovery of the photoelectric effect. Robert Millikan · Won the Nobel Prize for his measurement of the charge of an electron Erwin Schrodinger · In 1926, he developed a mathematical equation that describes the behaviour of the electron as a wave. · A solution to his equation indicates the highest probability of finding if an electron is in an energy level. Louis de Broglie · Proposed the idea that moving electrons could be considered as waves, similar to X-rays or visible light. · He developed a formula for calculating the wavelength associated with particles in motion such as electrons. Schrodinger AND de Broglie ·By 1930, these two proposed the "atomic" model of the atom. ·Just like the Bohr model, electrons have distinct energy levels. However the exact locations of electrons are not defined, but the cloud location in a region of space around the nucleus can be predicted. Werner Heisenberg · He developed the "Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle" which stated that it is impossible to determine both the position AND the speed of an electron at the same time. James Chadwick · In 1932, he discovered the neutron which was a particle in the nucleus of an atom.