* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download League of Nations.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
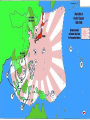
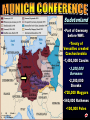
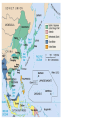
The Versailles Treaty Germany •Blamed for war •Lost colonies •New countries formed out theirs •Paid (war debts) reparations A Weak League of Nations The Ineffectiveness of the League of Nations No control of major conflicts. No progress in disarmament. No effective military force. Afghanistan—1934 Albania—1920 (taken over by Italy league in 1939) Argentina Australia Austria (taken over by Germany Germany--1926, withdrew, 1933 Greece In 1938) Guatemala (withdrew, 1936) Belgium Haiti (withdrew, 1942) Bolivia Honduras, (withdrew, 1936) Brazil (withdrew, 1926) Hungary—1922, withdrew, 1939 Bulgaria---1920 India Canada Iraq—1932 Chile (withdrew, 1938) Ireland—1923 China (invaded by Japan, 1937) Italy (withdrew, 1937) Colombia Japan (withdrew, 1933) Costa Rica—1920, withdrew, 1925 Latvia—1921 Cuba Liberia Czechoslovakia Lithuania—1921 Denmark Dominican Republic—1924 Ecuador—1934 Egypt—1937 El Salvador (withdrew, 1937) Estonia—1921 Ethiopia—1923 (taken over by Italy in 1936) Finland—1920 France Luxembourg--1920 Mexico--1930 Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua (withdrew, 1936) Norway Panama Paraguay (withdrew, 1936) Persia Peru (withdrew,1939) Poland Portugal Romania (withdrew, 1940) Siam Spain (withdrew, 1939) Sweden Switzerland Turkey--1932 Union of South Africa USSR—1934, expelled, 1939 United Kingdom Uruguay Venezuela (withdrew, 1938) Yugoslavia International Agreements Several attempts by U.S. to get countries to agree to disarming Washington Disarmament Conference Geneva Convention Treaties with Japan Kellog-Briand Pact – 1928 Makes war illegal as a tool of diplomacy o No enforcement provisions Japan Invades Manchuria 1931 •1931 into Manchuria •1937 into China and starts WWII in Asia •1937, U.S. refuses trade with Japan until they withdraw from China….. •1940 invades Indochina •US froze Japanese assets, refused to trade oil, gasoline and steel. 1. Rise of Totalitarian Dictatorships 2. • • • Fascist Aggression 1931 to 1941 US Neutrality Acts Weak League of Nations Japanese Expansion begins WWII in Asia • 1937, invasion of China • German Expansion into Europe • Munich Conference, Sept. 1938 • Hitler demands Sudetenland or war • “Appeasement” – French and British gave into Hitler Problems in Europe After WWI Great Depression •Economic = people were jobless •Political = weak governments could not solve problems in their countries………..Fear of Jews and Communists •Social = times of unrest people look for a leader. •Power of government rests in one man. •TOTAL POWER •No freedoms in this society….. •Usually racist and discriminatory towards certain groups…… •Often have large militaries and must expand and conquer to gain approval from their people. dictators dictators Totalitarian dictators came to power during the 1920s and 1930s in Europe. Adolph Hitler Benito Mussolini Joseph Stalin Totalitarian dictators have total power….There are no freedoms in this type of society…..Usually racist and discriminatory towards certain groups……Often have large militaries and must expand and conquer to gain approval from their people. COMMUNISM, FASCISM AND NAZISM ARE TOTALITARIAN DICTATORSHIPS! NAZISM AND FASCISM: a philosophy or system of government that advocates or exercises a dictatorship, state control of industry, racial superiority, supremacy of the leader, limits civil rights, together with an ideology of belligerent nationalism, militarism and expansion….. •opposite of democracy and capitalism NAZISM: STANDS FOR NATIONAL SOCIALISTIC PARTY……A TOTALITARIAN DICTATORSHIP----GERMANY. FACISM: BASED ON A SYMBOL OF AUTHORITY IN THE OLD ROMAN EMPIRE…A TOTALITARIAN DICTATORSHIP----ITALY nazism •Joseph Stalin •1921/Soviet Union Communism Spread Communism throughout the world •Stalin maneuvered himself into becoming the leader of the Soviet Union. •The Russian Revolution was led by the people to overthrow a monarch but when the new ruling class took over, there were no protections of people’s rights…… “NO BILL OF RIGHTS” •Communism and fascism are similar in their ideologies dictators Stalin’s Soviet Union Stalin’s Economic Plans Stalin’s Reign of Terror • Stalin’s state takeover of farmland resulted in a dramatic fall in agricultural production as well as mass starvation. • To eliminate opposition, Stalin began a series of purges, the removal of enemies and undesirable individuals from positions of power. • Stalin poured money and labor into industrialization rather than basic necessities such as housing and clothing. • Stalin’s purges extended to all levels of society. Millions were either executed or sent to forced labor camps. • Due to Stalin’s policies, the Soviet Union soon became a modern industrial power, although one with a low standard of living. • Nearly all of those purged by Stalin were innocent. However, these purges successfully eliminated all threats to Stalin’s power. dictators Benito Mussolini 1922/Italy---Facism Believe, Obey and Fight Revive the Roman Empire FACISM: BASED ON A SYMBOL OF AUTHORITY IN THE OLD ROMAN EMPIRE…………”a philosophy or system of government that advocates or exercises a dictatorship, state control of industry, racial superiority, supremacy of the leader, limits civil rights, together with an ideology of belligerent nationalism, militarism and expansion…..” Fascism in Italy • Benito Mussolini gained power in Italy both by advocating the popular idea of Italian conquest in East Africa and by terrorizing those who opposed him. • Once appointed prime minister by the king, Mussolini, calling himself Il Duce, suspended elections, outlawed other political parties, and established a dictatorship. • Mussolini’s rule improved the ailing Italian economy. Under Mussolini, the Italian army successfully conquered the African nation of Ethiopia in May 1936. The Rise of Adolph Hitler Born in Austria Fought in WWI and was bitter towards the Treaty of Versailles The Rise of Adolph Hitler After the war his job in the army was to keep tabs on different political parties. Hitler already shows anti-Semitic views. Discovers a small political party known as The National Socialist German Workers Party (NAZI) Begins to work himself into the leadership positions of the Nazi party November 1923- The "Beer Hall Putsch“, Hitler and the Nazis try to overthrow the local government of Munich, Germany. The Rise of Adolph Hitler It fails and Hitler is arrested. He is convicted 1924 and serves 9 months out of a 5- year sentence. Hitler writes his book Mein Kampf or “My Struggle” After his release from prison he continued to work with the Nazi party to take over Germany. •In 1923 Adolf Hitler was arrested for attempting to overthrow the government in Munich. •His National Socialist German Workers' Party (the Nazi party) was still relatively small, and he used his trial to attract national attention. •In due course he was convicted and sentenced to prison; while there he wrote Mein Kampf (My Struggle), outlining his political ideas. •Mein Kampf was not taken seriously at first, but eventually becomes popular and includes many of the ideas the Nazis put in practice in the 1930s and mein kampf 1940s. •If, with the help of his Marxist creed, the Jew is victorious over the other peoples of the world, his crown will be the funeral wreath of humanity and this planet will, as it did thousands of years ago, move through the ether devoid of men. •The end is not only the end of the freedom of the peoples oppressed by the Jew, but also the end of this parasite upon the nations. After the death of his victim, the vampire sooner or later dies too. antisemitism Adolph Hitler, appointed chancellor of Germany in 1933 Appoints himself dictator after Reichstag (German law-making body) is burnt to the ground. Create a new empire, “Third Reich” •Revenge towards the Treaty of Versailles Rearm Germany Take back land lost from WWI dictators THIRD REICH HITLER WANTED GERMANY TO BECOME THE THIRD WORLD EMPIRE AND UNITE ALL GERMAN SPEAKING NATIONS THAT WOULD RULE THE WORLD FOR A 1,000 YEARS. Form: A cross with four equal arms, each bent at a right angle. Word: From the Sanskrit word svastika, “creating well-being.” History: An ancient Aryan symbol of the sun Importance: Hitler adopted the swastika as its symbol with the aim of making a connection between the ancient Aryans and the modern German people. In making this connection, the Nazis tried to support their claim that the modern German people were a “master race.” reich dictators •The Nazis used a political police •the Gestapo •the SS corps •Propaganda to gain total power. •Anti-Nazi leaders were arrested. •Violated the privacy of postal and telephonic communications. •Nazis did not need search warrants for house searches or for confiscating or restricting private property. FREEDOMS LOST •FREEDOM OF SPEECH NAZI’S CENSORED WHAT YOU COULD READ. •DUE PROCESS COULD BE ARRESTED WITHOUT PROBABLE CAUSE •NO TRIAL BY JURY NAZI’S PRACTICED RACISM AND PERSECUTION TOWARDS THE JEWS. •THEY WERE STRIPPED OF THEIR CIVIL RIGHTS... •NO LONGER CITIZENS FREEDOMS LOST A Common Enemy • Hitler blames Jews and Communists for problems of Germany • Loss of WWI • German Economic Depression • Jews identified as a “race” –not a religion • Anti-Semitism • A New Education Begins • Save purity of German race. • Aryan Virtues----Nuremberg Laws nuremberg ANTI-SEMITISM •ANTI-JEWISH….THE HATRED OF JEWS, THEIR CULTURE AND RELIGION. •IT IS THE PRACTICE OF RACISM THAT LEADS TO ALL FORMS OF HOSTILITY DIRECTED TOWARDS THE JEWS. antisemitism ANTI-SEMITISM •Jews were defined by German policy as alien, evil, and not capable of being corrected. •Jews were historically the virus which ate at the purity of the Christian Aryans. •They were the international conspirators whose aim was to overthrow Christian Western civilization. antisemitism •German Propaganda against the Jews. •"The Jew: The inciter of war, the pro-longer of war." German children were taught in school that Jews were inferior. •Nazi Government Policy of Anti-Semitism •Purity of German blood was essential to the existence of the German people and nation. •Nuremberg Laws passed in 1935 provided legal basis. •Millions of Jews died in German concentration camps. 1. Marriages between Jews and citizens of German blood are forbidden. 2. Sexual relations outside marriage between Jews and German blood are forbidden. 3. Jews will not be permitted to employ female citizens of German blood as servants. 4. Jews are forbidden to display the Reich and national flag or the national colors. nuremberg 5. Jewish children and German were segregated. 6. The right to citizenship is acquired by the granting of Reich citizenship papers. 7. Only the citizen of the Reich enjoys full political rights in accordance of the laws. 8. A citizen of the Reich is of German blood and who shows that he is both desirous and fit to serve the German people and Reich faithfully. nuremberg THE NIGHT OF BROKEN GLASS •NOV. 1938, OFFICIAL GERMAN POLICY OF PERSECUTION OF THE JEWS IN GERMANY! •1938 WAS THE TIME IN GERMANY WHEN TO BE A JEW IN GERMANY BECOMES DANGEROUS! kristalnacht The first organized night of Nazi violence against German Jews Nov. 8 - 9, 1938 Thousands arrested, including college professors, writers, doctors, etc. Jewish businesses, stores, homes and synagogues burned all through Germany and other German Occupied countries Nazi violence against German Jews led to thousands hurt and many deaths….. The Night of Broken Glass Violence Escalates With Systematic Invasions Took the form of a god Japan’s Manifest Destiny was to expand into China and the rest of Asia. Empire of the Sun Emperor Hirohito dictators 1931/Japan, expansionist and military leader •Would threaten our island possessions and U.S. trade policy into China, Open Door Policy. Hideki Tojo dictators Growing Military Power Chapter 17, Section 3 Democracy in Crisis Rise of Nationalism • After World War I, Japan had established a parliamentary government and granted many citizens the right to vote. • Several radical groups formed in response to the government’s perceived weaknesses. • When economic conditions worsened during the 1930s, many Japanese became dissatisfied with multiparty democratic government. • Radicals demanded an end to Western-style institutions and a return to traditional ways. • These radicals assassinated several business and political leaders, hoping to force the military to take over the government. The Manchurian Incident • By 1930, Japan lacked the land and raw materials to care for its growing population. Many Japanese saw the acquisition of neighboring Manchuria as a solution to these problems. • In September 1931, a Japanese army stationed in Manchuria captured several cities. By February 1932, the army had seized all of Manchuria. This seizure came to be known as the Manchurian Incident. • Japan set up Manchuria as a puppet state, or a supposedly independent country under the control of a powerful neighbor. • After the Manchurian Incident, the military took a much stronger hand in governing Japan, especially in the area of foreign policy. •BETWEEN 1931 TO 1941, JAPAN CONTROLLED MOST OF ASIA AND WAS THREATENING U.S. ISLANDS AND OUR OPEN DOOR TRADE POLICY. •FROM 1935 TO 1939, HITLER REMARMED GERMANY IN VIOLATION OF THE TREATY OF VERSAILLES. •GERMANY/ITALY CONQUERED ALL THE DEMOCRACIES IN EUROPE. •US POLICY WAS STRICT NEUTRALITY BUT ULTIMATELY WOULD BE DRAWN INTO WWII. democracies •1931 into Manchuria •1937 into China and starts WWII in Asia •1937, U.S. refuses trade with Japan until they withdraw from China….. •1940 invades Indochina •US froze Japanese assets, refused to trade oil, gasoline and steel. map/japan GERMAN EXPANSION •1935 to 1939, unopposed by the League of Nations. •Rhineland 1936 •Austria 1938 Munich Conference Sudetenland •Part of Germany before WWI. •Treaty of Versailles created Czechoslovakia •7,450,000 Czechs •3,200,000 Germans •2,300,000 Slovaks •720,000 Magyars •560,000 Ruthenes •100,000 Poles •Leaders met in Munich to decide the fate of Czechoslovakia.. •Hitler believed Sudetenland should be part of Germany. •Adolf Hitler--Germany Neville Chamberlain—England Premier Edouard Deladier---France Benito Mussolini--Italy •Hitler promised the world if he received the Sudetenland, there would be no war. Munich Conference •German demands for the Sudetenland are met = “All I want, is a Germany for Germans” •All Chamberlain wanted was peace at any cost. •Chamberlain believed that by sacrificing Czechoslovakia he had satisfied Hitler and he would stop being aggressive; he promised “a peace with honor… peace in our time.” •Chamberlain gave into Hitler (appeasement) •Hitler got the Sudetenland. •FDR sent a letter to Hitler asking him to honor the Munich Conference •Later in 1939, Hitler would invade and take the rest of Czechoslovakia……. •The United States learned from the Munich Conference that you cannot trust the words of a dictator……… Munich Conference •What is the cartoonist trying to say here? •What is meant by, “we might as well try to appease him”? •How does the cartoonist justify his decision to appease Hitler? •Notice the American countries……. What is this symbolic of? Umbrella Road 1. 1931---Japan invades Manchuria, WWII begins in Asia 2. 1935---Italy invades Ethiopia • US and League of Nations demands Japan to get out---Stimson Doctrine • L/N demands Italy to get out—No US sell of weapons 3. 1936---Hitler invades the Rhineland • L/N demands Germany to get out---US Neutrality and refuses to sell arms to Germany 4. 1937 to 1939---Spanish Civil War • US Neutrality----Spain becomes a fascist dictatorship 5. 1937---Japan invades China • US neutral but demands Japan to withdraw and refuses to sell iron, steel and gasoline products 6. 1938--Hitler takes Sudetenland • Munich Conference--Great Britain and France give into Hitler, Appeasement US Neutral but FDR writes a letter to Hitler & Mussolini asking them to guarantee no more aggression. • CHART CHART 7. 1938, Hitler takes Czechoslovakia • 8. Sept. 1, 1939, Hitler invades Poland • which begins WWII in Europe Cannot trust “the words of a dictator” Britain & France declare war on Germany on Sept. 1, 1939. US neutral, extends Cash and Carry Policy to Allies 9. 1940---Hitler’s inasion of Norway, Denmark, Holland and Belgium • US neutral--freezes German assets-begins military buildup 10. 1940---Hitler takes France • US neutral, begins peacetime draft— Selective Service 11. 1940---Japan’s invades Indochina • US neutral but demands withdrawal and freezes Japanese money, Property and embargo of oil, iron and steel. 12. 1940---Hitler attacks Great Britian • US neutral but extends Lend Lease policy to Great Britain—last Democratic Nation—Battle of Britian US becomes the arsenal of democracy 13. 1941---Hitler’s invasion of Russia • US neutral but extends Lend Lease to Russia…...US & Great Britain draw up war goals in the Atlantic Charter 14. 1941---Japan attacks Pearl Harbor Dec. 7, 1941---Day of Infamy • Neutrality is ended and US declares war on Japan, Germany and Italy declare war on US Answer the following questions from the chart 1. What was the position the US throughout most of the fascist aggression, Why? 2. What was the position of the L/N’s? Why were they so powerless to stop this aggression? 3. Why is the Munich Conference and appeasement a turning point in preventing war in Europe? Does it work? What “principle” does this set? 4. Name the ways the U.S. tried to avoid war and deal with fascist aggression? 5. Even though the US was neutral, what are ways we begin to prepare ourselves for war? 6. Which of the U.S. responses to fascist aggression marked the turning point inmoving the nation from neutrality to war? 7. To what extent was the reversal of neutrality in the best interest of the United States? CHART Hitler’s Rise to Power: 1919 to 1933 • Hitler’s Background: Adolf Hitler, an Austrian painter, hated the way the Versailles Treaty humiliated Germany and stripped it of its wealth and land. • The Nazi Party: Hitler joined and soon led the Nazi Party in Germany. • Nazism, the philosophies and policies of this party, was a form of fascism shaped by Hitler’s fanatical ideas about German nationalism and racial superiority. • Mein Kampf: While imprisoned for trying to take over the government in November 1923, Hitler wrote Mein Kampf (“My Struggle”). • In this book, he proposed that Germany defy the Versailles Treaty by rearming and reclaiming lost land. • He also blamed minority groups, especially Jews, for Germany’s weaknesses. • Hitler Becomes Chancellor: Between 1930 and 1934, the Nazi Party gained a majority in the Reichstag, the lower house of the German parliament. • Hitler became first chancellor and then president of Germany. • He moved to suppress many German freedoms and gave himself the title Der Führer, or “the leader.” The Weimar Republic: 1924-1933 The “Stabbed-in-the-Back” Theory Disgruntled German WWI veterans The Beer Hall Putsch: 1923 The Beer Hall Putsch Idealized Hitler in Landesberg Prison Mein Kampf [My Struggle]