* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20170228 press-release
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
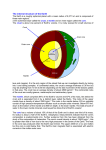
PRESSRELEASE Source:TokyoInstituteofTechnology,CenterforPublicAffairsandCommunications Forimmediaterelease:28February2017 Tokyo Institute of Technology research: New model for deep mantle conveyor belt system at thecoreoftheEarth (Tokyo,28February2017)-GeophysicistsattheEarth-LifeScienceInstitute(ELSI)attheTokyo InstituteofTechnologyreportinNatureGeophysics(online27Feb2017)anewmodelforthe existenceofadeepmantleconveyorbeltsystemthatmayhaveoperatedinsidetheEarthsince itsformationabout4.5billionyearsago. Mostearthquakes,volcanoes,mountainbuilding,sea-floorspreading,andothermajor geologicalactivitiesonEartharedrivenbysocalledplatetectonics,wherelargesectionsofthe Earth’scrustmoveascoherentblocks—orplates—thatcrashtogether,pullapart,slideon topofeachother,andpassoneanotherattheirboundaries.Beneaththeplatesliesthe3000 kmthickrockymantle,composedofhotpliablerockthatslowlydeformsandchurnsunderthe immensepressuresandtemperaturesofthedeepinterior.Thischurningmotion,ormantle convection,actstoremoveheatfromtheEarth’sinterior,similartothecirculationinaslowly boilingpotofstew.Mantleconvectionultimatelydrivesthemotionoftectonicplates.Inturn, theplatesalsostirthemantle,wheretheyaresubductedbecauseofslidingontopofeach other,andsinkthroughthemantletogreatdepths. ScientistshavelongwonderedwhethertheEarth’smantleiswellmixedbythisstirringandthe churningconvectivemotions(mantleconvection),orifthelowerpartofthemantleisdifferent incompositionthantheupperpart.Thatsomeplatesaresubductedtotheverybaseofthe mantle,travelling3000kminabout200millionyears,hasbeentraditionallytakenasevidence forawell-stirredandmixedmantlestew. Thepoorly-mixedEarth’smantlestew Inthisresearch,thescientiststookanewapproachbyconsideringwhetherthechemical compositionofmantlerocksaffectsthechurningconvectivemotion.Somerocksdeformand flowmorereadilythanothers,behavinglikewaterasopposedtohighviscosityliquidssuchas honey.Forexample,pouringwaterintoapotofstewresultsinthewatermixingwiththestew evenwithoutmuchstirring.Needlesstosay,itwouldtakemuchmoretimeforhoneytomix withstew.Notably,ifdumplingsareputintostew,thenbothcomponentswillnevermix.Even thoughdumplingsaregenerallydeformable;theboilingstewjustflowsaroundthedumplings becauseitismuchmoredeformable,orlessviscous,thandumplings. Now,intheEarth,lowermantle-rocksbehavemorelikestewthandumplings(ormorelike waterthanhoney)dependingontheirchemicalcomposition.Ifrocksinthelowermantleare relativelyenrichedinsilica(orSiO2,whichisalsothemaincomponentofsand),theyaremore viscousandbehavemorelikedumplingscomparedtosilica-depletedrocks,whichareweaker andbehavemorelikethestewitself.Thisisintriguingbecausemanymeteoritesthatare consideredthebuildingblocksofEarthhaveahighersilicacontentthanrocksintheupperpart ofEarth’smantle.Tomakeupthebalanceofsilica-depletioninmostmantlerocksthathave beenprobed,atleastsomerocksinthelowermantleshouldberelativelysilica-rich.So,the Earth’smantlemightbeabitlikeawell-mixed,silica-depletedstewwithsomepoorly-mixed silica-richdumplingsnearitsbase. Tostudythechurningmotionofthemantlestew,MaximBallmerandhiscolleaguesatELSI addedastrongsilica-richlayerintonumericalsimulationsofmantleconvection.Theyfound that,afteramajoroverturnoftheinitiallyimposedlayering,themantlebecameorganizedinto largeroll-likeconvectioncells,whereweaksilica-depletedrocksfilltheuppermantleand circulatearoundstrongsilica-richblocksinthelowermantlealongagiantconveyorbelt(Fig.1). GiantblocksofancientrockshiddenbeneathAfricaandthePacific? Inthesimulations,thispatternofchurningconvectionremainedstableformanybillionsof years,andlongerthantheageoftheEarth.Thestrongsilica-richblocksinthelowermantleare probablymorethan1000kmindiameterand10,000skmlong,makingupapproximately15% ofthemantle’smass.BallmerandhiscolleaguesthinkthattheyarehiddenfarbelowAfricaand thePacific,shapedlikegiantsausagesordonuts. Theexistenceofsuchstrongdomainscanexplainwhysomeofthesubductedplatesdonotsink towardthebaseofthemantle,butratherpondatintermediatedepths,wheretheyencounter thestrongsausagesordonuts.Thelong-termstabilityofthesedomainscanfurtheraccountfor thegeochemicaldiversityofdeep-sourcedlavasattheEarth’ssurface.Whilesomelavasare relatedtomeltingofmantlerocksthathavebeenrecycledfromthenear-surfacecrustand circulatedthroughthemantle,otherstraceevidenceofancientdomainsthathaveavoided circulationandrecyclingsincetheearliestdaysofourplanet. Thesurvivalofancientrocksintheconvictingmantlehasbeenalong-standingpuzzletomany scientists,butmaynowberesolvedasaconsequenceofinefficientmixingbetweenstrong silica-enrichedrocksandthemuchweakersilica-depletedmantle. Reference MaximD.Ballmer1,2*,ChristineHouser2,JohnW.Hernlund1,RenataM.Wentzcovitch1,3,4 andKeiHirose1.Persistenceofstrongsilica-enricheddomainsintheEarth’slowermantle. NatureGeoscience,online27Feb.2017. DOI:10.1038/NGEO2898 1Earth-LifeScienceInstitute,TokyoInstituteofTechnology,Meguro,Tokyo,Japan. 2InstituteofGeophysics,ETHZurich,Zurich,Switzerland. 3DepartmentofAppliedPhysicsandAppliedMathematics,ColumbiaUniversity,NewYork,USA. 4DepartmentofEarthandEnvironmentalSciences,ColumbiaUniversity,Lamont-DohertyEarth Observatory,Palisades,NewYork,USA. *e-mail:[email protected] Contact EmikoKawaguchi CenterforPublicAffairsandCommunications,TokyoInstituteofTechnology, 2-12-1,Ookayama,Meguro,Tokyo,152-8550,Japan E-mail:[email protected] Tel:+81-3-5734-2975+81-3-5734-2975 AboutTokyoInstituteofTechnology TokyoInstituteofTechnologystandsattheforefrontofresearchandhighereducationastheleading universityforscienceandtechnologyinJapan.TokyoTechresearchersexcelinavarietyoffields,such asmaterialscience,biology,computerscienceandphysics.Foundedin1881,TokyoTechhasgrownto host10,000undergraduateandgraduatestudentswhobecomeprincipledleadersoftheirfieldsand someofthemostsought-afterscientistsandengineersattopcompanies.EmbodyingtheJapanese philosophyof“monotsukuri,”meaningtechnicalingenuityandinnovation,theTokyoTechcommunity strivestomakesignificantcontributionstosocietythroughhigh-impactresearch. Website:http://www.titech.ac.jp/english/ Caption Mantleconvectionwithinefficientmixing.Silica-poorrocks(green)circulatearoundcoherent domainsofancientsilica-richrocks(grey).Mantledownwellings(subductedslabs,blue)sink, andupwellings(lightred)rise,throughconduitsbetweenthesedomains.Mantleconvectionis dominantlydrivenbyheatingfromthehotcore(darkred)below.