* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download G7Q2W4 (Polygons, Protractors and SPT Conferences)
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
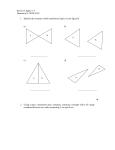
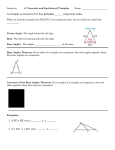
Name: Hage Performance Objective* Learning Objective*: I can Essential Questions* Vocabulary* Anticipatory Set* Congruent to Objective Active Participation Past Experience Direct Instruction Subject: Classifying Polygons and How to use a Protractor Plans for week of: 10/27/2014 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday 7.M.G.A.02: Draw geometric shapes with given conditions. Focus on constructing triangles from three measures of angles or sides, noticing when the conditions determine a unique triangle, more than one triangles or no triangle. I can describe and draw different polygons base on their properties. *What are examples of unique polygons? *How do their specific properties make them unique? Parallelism, perpendicularity, congruent, protractor, rules, line segments, points, vertex, angles, polygons, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, right triangle, scalene triangle A triangle is a closed figure with three sides. 7.M.G.A.02: Draw geometric shapes with given conditions. Focus on constructing triangles from three measures of angles or sides, noticing when the conditions determine a unique triangle, more than one triangles or no triangle. I can describe and draw different polygons base on their properties. *What are examples of unique polygons? *How do their specific properties make them unique? Parallelism, perpendicularity, congruent, protractor, rules, line segments, points, vertex, angles, polygons, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, right triangle, scalene triangle Do the three lengths form a triangle? Is it a right triangle? 7.M.G.A.02: Draw geometric shapes with given conditions. Focus on constructing triangles from three measures of angles or sides, noticing when the conditions determine a unique triangle, more than one triangles or no triangle. I can describe and draw different polygons base on their properties. *What are examples of unique polygons? *How do their specific properties make them unique? Parallelism, perpendicularity, congruent, protractor, rules, line segments, points, vertex, angles, polygons, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, right triangle, scalene triangle What is the difference between a parallelogram and a rectangle? 7.M.G.A.02: Draw geometric shapes with given conditions. Focus on constructing triangles from three measures of angles or sides, noticing when the conditions determine a unique triangle, more than one triangles or no triangle. I can describe and draw different polygons base on their properties. *What are examples of unique polygons? *How do their specific properties make them unique? Parallelism, perpendicularity, congruent, protractor, rules, line segments, points, vertex, angles, polygons, equilateral triangle, isosceles triangle, right triangle, scalene triangle Draw a quadrilateral with congruent sides and no right angles. What type of quadrilateral did you draw? Using a protractor 1) Generally the straight side of the protractor is a ruler that can be used to measure a straight line 2) You can measure the degrees in an angle by placing the vertex on the circle/dot and one of the rays onto the line. 3) Count up from the line, starting at zero until you reach the next ray. (Complete activities from yesterday If necessary) Other polygons and regular shapes Quadrilaterals 4 sides The sides have to be straight, and it has to be 2-dimensional Parallelograms – opposite sides are congruent parallel Rectangle – opposite sides are congruent and parallel. Must have 4 right angles Rhombus – all 4 sides are congruent and Shapes that are not triangles (3 sides) and that are not quadrilaterals (4 sides) are named by their sides 5 sides: Pentagon 6 sides – Hexagon 7 sides: Heptagon or Septagon 8 sides: Octagon 9 sides: Nonagon 10 sides: Decagon Anything bigger than 10 sides will generally be called an “n-gon” Students will complete their CFA Reminders about the classifications for triangles and quadrilaterals What types of measurements can make a triangle Correct use of a protractor Discuss Student Led Conferences *Remind students that they are responsible for three things - Go through your assignments Friday NSC S/P/T Conferences NSC S/P/T Conferences NSC S/P/T Conferences NSC S/P/T Conferences NSC S/P/T Conferences NSC S/P/T Conferences Name: Hage Subject: Classifying Polygons and How to use a Protractor *Vocabulary – Scalene, isosceles, equilateral, acute, right, obtuse Introduction to Pythagorean Theorem. Also, discuss the triangle side theorem which states that the two shorter sides when added up must be greater than the length of the longest side. Interior angles add up to 180° Guided Practice Checking for Understanding* Independent Practice Closure* Congruent to Objective Active Participation Past Experience Student Summary Sorting Activity – Students will use notes and protractors to determine which categories to sort their triangles into categories opposite angles are equal Square = all 4 sides are congruent and all 4 angles are 90° Trapezoid – only one pair of parallel sides Kite – two adjacent sides are congruent and the angles are equal where the pairs meet The only “REGULAR” quadrilateral is a square, so all other quadrilaterals are irregular. Interior angles add up to 360° Use website to view examples of different quadrilaterals: http://www.mathsisfun.com/ge ometry/quadrilateralsinteractive.html *Check for correct usage of the protractor *Check for correctly sorted groups by side *Check for correctly sorted groups by angle Students are able to look at various quadrilaterals and correctly name them. Students determine if three given lengths will form a triangle. Will they form a right triangle? Given the three lengths, determine if a triangle can be formed. Student worksheet Plans for week of: 10/27/2014 where “n” is the number of sides in the polygon. Regular vs Irregular A regular polygon is a figure in which all of the sides and all of the angles are congruent (an equilateral triangle and a square are examples of regular polygons) An irregular polygon has the given number of sides, but they are not all congruent. Students draw, label and define the various types of polygons including examples of regular and irregular polygons. Students correctly identify polygons when shown their image. Complete Graphic Organizer and sort them into assignment type -> Classwork, assessments, homework. -Students prepare by filling out their conference agenda -Fill out the handout with appropriate goals (discuss how to set a good goal – one that is specific with how they plan to attain that goal.) After students have completed their corrections they will write a letter of invitation to their family members. Emphasize the value of the conference; discuss what you are most proud of and what work still needs to be done. Make sure that students understand should not make excuses but must present samples of work to parents that accurately depict their performance – both successes and challenges NSC S/P/T Conferences NSC S/P/T Conferences NSC S/P/T Conferences Check worksheet for correctness and review those answers missed by multiple students. What is the difference between a regular and an irregular polygon? NSC S/P/T Conferences Name: Hage Assessment Subject: Classifying Polygons and How to use a Protractor Plans for week of: 10/27/2014 Sorting Vocabulary Quadrilateral Worksheet Define, Label, and Draw graphic organizer Notes Triangle sorting Protractors Homework Given Notes Quadrilateral Worksheet Notes Plain white paper Polygon Classify assignment NSC S/P/T Conferences Specific Resources P/T/S Conference Sheet Progress Reports NSC S/P/T Conferences