* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polygons - Lesson Corner
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
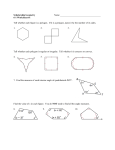
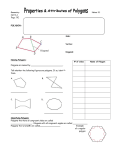
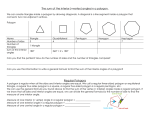
Lesson Plan for Chapter 10 Section 10.1 Title of Lesson: Polygons Goal: ß To give students an appreciation for polygons and the role that they play in nature and in man-made things Objective: ß Students will identify and name polygons ß Students will find the sum of the measures of interior and exterior angles of convex polygons and measure of interior and exterior angles of regular polygons ß Students will solve problems involving angle measures of polygons SOLs Addressed: G.3 – The student will solve practical problems involving complementary, supplementary, and congruent angles that include vertical angles, angles formed when parallel lines are cute by a transversal, and angles in polygons G.8.1 – The student will investigate and identify properties of quadrilaterals involving opposite sides and angles, consecutive sides and angles, and diagonals G.9 – The student will use measures of interior and exterior angles of polygons to solve problems. NCTM Standards Addressed: Analyze characteristics and properties of two and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships Materials: Blank overheads, note handouts, overhead markers, & calculator Methods of Assessment: Formal: The homework assignments given for section 10.1 will be evaluated for correctness and completion. Students will check their own work and place their score in their homework check sheet. This sheet will be collected at the end of the week. In addition, there will be quizzes given that will cover chapter 10 theorems and definition and work-out problems Informal: The students will be informally evaluated as to how well they participate in the guided practice problems throughout the lesson. Prior Knowledge: ¸ Students are expected to know the basic properties associated with triangles Resources Used: ß Geometer’s Sketchpad ß Glencose. Geometry: Integration, Applications, and connections. McGraw-Hill. Publishing. 1998, pp 514-519 ß Incorporated additional notes from co-operating teacher Lesson Overview: This lesson marks the beginning of a new chapter which focus on polygons. The students will learn how polygons are categorized and how to find the sum of the interior / exterior angles of any polygon. For the purposes of time, a sheet with a variety of different kind of polygons will be given to each student and used throughout the lesson for additional examples. The next section to be covered focuses on tessellations. In particular, it will address how tessellations are formed, and how to determine whether a certain shape will in fact tessellate the plane. Class Announcements / Review (5 minutes): • Have students get their calculators • Announce HW assignment • Pass out supplementary lecture notes/pictures Lesson (40 minutes): Motivational Introduction Polygons in nature: mud cracks, surface of mars Polygons man-made: pentagon, traffic signs, temples, quilts Polygon – derived from the Greek work meaning “many angled” Definition of a Polygon: Closed figure formed by a finite number of segments that lie in the same plane such that i. the sides that have a common endpoint are noncollinear ii. each side intersects exactly two other sides, but only at their endpoints **SEE POLYGON SHEET** Convex Polygons – a polygon is said to be convex if no line containing a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon. Concave Polygons – polygons that are not convex **SEE POLYGON SHEET** Polygons can also be categorized by the number of sides they have. #.of Sides 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 n Polygon Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon Heptagon Octagon Nonagon Decagon Dodecagon n - gon Definition of Regular Polygon A regular polygon is a convex polygon with all sides congruent and all angles congruent. Discovery Activity – consider all the diagonals drawn from one vertices to all the other vertices for each polygon. Convex Polygon Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon Heptagon # of Sides 3 4 5 6 7 # of Triangles 1 2 3 4 5 Sum of Angle Measure (1 * 180) or 180 (2 * 180) or 360 (3 * 180) or 540 (4 * 180) or 720 (5 * 180) or 900 Theorem 10.1: Interior Angle Sum Theorem If a convex polygon has n sides and S is the sum of the measure of its interior angles, then S = 180 (n - 2) Theorem 10.2: Exterior Angle Sum Theorem If a polygon is convex, then the sum of the measure of the exterior angles, one at each vertex, is 360 Example1: Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of each convex polygon. a. decagon (10) S = 180 (n-2) S = 180 (10-2) S = 180 * 8 = 1440 b. 16 – gon S = 180 (n-2) S = 180 (16-2) S = 180 * 14 = 2520 Example 2: The measure of an exterior angle of a regular polygon is given. Find the number of sides of the polygon. a. 30 360 / 30 = 12 sides b. 5 360 / 5 = 72 sides Example 3: The number of sides of a regular polygon is given. Find the measures of an interior angle and an exterior angle for each polygon. a. 18 360 / 18 = 20 (exterior angle) 180 – 20 = 160 (interior angle) b. 25 360 / 25 = 14.4 (exterior angle) 180 – 14.4 = 165.6 (interior angle)