* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development and Genes
Survey
Document related concepts
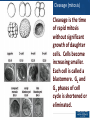
Transcript
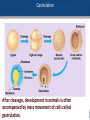
Agenda 3/24 • Development Quick Lecture • Development Documentary and Notes • Homework: Developmental Biology Worksheet, Study for Unit Exam • Turn in: Gene Expression Essay • Warm Up: Summarize three major things that occur during the development of embryo to fetus. 1 Development and Genes What you need to know • How we go from one unspecialized cell to many specialized cells – Determination – Differentiation – Morphogenesis – Role of Mitosis and Gene Expression 3 Characteristics of Development for Multicellular Organisms Development is the process of timed genetic controlled changes that occurs in an organism’s life cycle. • Mitosis • Cell differentiation • Pattern formation • Morphogenesis All four processes are anchored by differentiation with regard to gene expression. Most cells in a multicellular organism have the same genome or DNA. Genes must be turned on and turned off during development. 4 Cleavage (mitosis) Cleavage is the time of rapid mitosis without significant growth of daughter cells. Cells become increasing smaller. Each cell is called a blastomere. G1 and G2 phases of cell cycle is shortened or eliminated. 5 Gastrulation After cleavage, development in animals is often accompanied by mass movement of cells called gastrulation. 6 Cell, Genes and Development Cells have two general classes of genes. • Housekeeping genes which are necessary to go about the “business” of life. • For example genes that code for the enzymes for cellular respiration are housekeeping genes. Most cells have all of these activated • Specialized genes that produce unique gene product important to the cells differentiation. • For example the activation of the crystallin gene that produces product necessary for the development of the lens of the eye. 7 Genes and Development It would be wasteful for lens cells to produce albumin, and in the same way it would be wasteful for the liver cells to produce crystallin. These specialized genes must be regulated so that they are only activated when they are needed and timing is critical. 8 Determination comes before Differentiation. Determination are those things or processes necessary to commit a cell to a particular type of cell or fate. Differentiation is those changes that occur in a cell to make it a certain cell type. 9 Determination Determination – Events that lead to the observable differentiation of a cell. Once determination has occurred then the final fate of the cell is sealed. If a determined cell is placed in another location in the organism, it will still differentiate into the cell that was its normal fate. 10 Determination 11 How Determination Occurs . There are two sources responsible for determining the fate or development of cells. • Cytoplasmic Determinants • Induction via signals secreted by neighboring cells 12 Initial Development Governed by Cytoplasmic Determinants Development can begin with fertilization of an egg and subsequent division of cytoplasmic determinants during cytokinesis. There is unequal distribution of the cytoplasmic determinants to the daughter cells as illustrated. 13 Initial Development Governed by Once there are a multitude of cells, Inductive Signals neighboring cells may produce signal molecules that can interact with receptor sites and receiving cells. This causes the activation of a signal transduction pathway for the receiving cell. This can send the cell down a specific developmental pathway. 14 Initial Development Governed by Cytoplasmic Determinants Cell Differentiation • Differentiation of activated genes and inactive genes • Appearance of mRNA for cell specific proteins • Changes in cellular structure 15 Morphogenesis • How the organism gets it shape • Hormones, cell signaling, and various other stimuli can all affect morphogenesis 16 Morphogenesis Can Involve Cell Death Occurs Apoptosis occurs in the development of the digits of a hand or paw. Shown is the development of a mouse paw. The genes that regulate apoptosis are similar in both vertebrates and invertebrates such as nematodes. Fungi including yeast also have genes that regulate apoptosis indicating these are ancient genes. 17 During Development Cell Death Occurs Apoptosis- Is a programed cell death. Occurs in • Infected cells • Development • Cells that are aged and no longer functional The cell below is a normal leukocyte and the cell above is a cell undergoing apoptosis 18 What you need to know • How we go from one unspecialized cell to many specialized cells – Determination – Differentiation – Morphogenesis – Role of Mitosis and Gene Expression – *Take notes on all the examples you see of these in the film! 19 20