* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit E - Topic 1.0 Notes
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
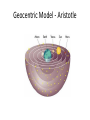
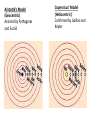
Space Exploration 1.1 Early Views about the Cosmos Celestial objects have fascinated humans throughout history. These include: • • • • • • • • The sun The moon The stars Constellations Planets Meteors Falling stars Northern lights Celestial events of particular interest to humans were / are: • • • • • Solar and lunar eclipses Meteor showers Aurora borealis Comets The Greeks were the first to explain how the universe worked in a logical, systematic manner. Models of Planetary Motion 1. Geocentric model: Aristotle 2000 years ago – The earth is the center of the universe 2. Heliocentric model: Copernicus about 1500 AD - The sun is the center of the universe and all other planets orbit around it. Models of Planetary Motion Geocentric Model Heliocentric Model Proposed by / when: Aristotle – over 2000 years ago Copernicus – 1530 AD Description: Earth is center of universe Sun is center of universe Supported by: Euclidian and Pythagorean math used to calculate the size of the spheres Telescopes allowed scientists to see mountains on the moon and the rings of Saturn What wasn’t explained: Movement of the planets was irregular Planetary motion didn’t follow a circular pathway What next: Replaced with the heliocentric model Updated to account for elliptical pathways of the planets Geocentric Model - Aristotle Heliocentric Model - Copernicus Aristotle’s Model (Geocentric) Assisted by Pythagoras and Euclid Copernicus’ Model (Heliocentric) Confirmed by Galileo and Kepler Revisions to the Heliocentric Model • Galileo Galilei – saw mountains on the moon with a telescope and confirmed Copernicus’ ideas • Tycho Brahe – observed and recorded the movement of the planets, confirmed a circular orbit was not likely • Johannes Kepler – proposed the planets followed elliptical orbits around the sun Cosmological Events • Solstice means “sun” “stop” and represent the shortest and longest periods of daylight. • June 21 – the summer solstice is the longest day of the year • Dec 21 – the winter solstice is the shortest day of the year Equinox • Means “equal” “night” and represents periods of equal day and night. • Vernal Equinox - March 21 – spring equinox • Autumnal Equinox - Sept 22 – fall equinox Ancient peoples celebrated the solstice and equinox occasions by creating large structures Chichen Itza Pyramids at Giza Stonehenge Medicine Wheel Our solar system – size and scale • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D1iK2p8q wdY • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z6yHKE9d g0g&feature=related • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mtKNH2Y 2OJM&feature=related Astronomy tools • Sundial: have been used for more than 7000 years to measure the passage of time - based on the sun's position in the sky • Merkhet: invented by the Ancient Egyptians to chart astronomical positions and predict the movement of stars • Quadrant: Invented in the 2nd century AD by the Egyptian astronomers to measure a star's height above the horizon • Astrolabe: Used by Arabian astronomers to make accurate charts of star positions • Cross-staff: invented by Levi ben Gurson to measure the angle between the Moon and any given star • Early Telescope (late 16th century): invented in the late 16th century and it allowed astronomers such as Galileo to discover details about Earth's closet planetary neighbors and the relative size and distance of what laid beyond Earth • Optical/Radio Telescopes and Space-Based Telescopes: operating from Earth, satellites orbiting around Earth and space-based telescopes have reveals the immensity of objects in space and distances across the universe. Also have discovered that our sun is simply one in the corner of our galaxy that is among of billions of other galaxies. Measuring Distance and Time in Space • Astronomical Units (AU) - Used for….measuring "local distances", inside our solar system 1 AU = average distance from the center of Earth to the center of the Sun = 149 599 000 km Used when…describing positions of the planets relative to the Sun less than 1 = closer to the sun than Earth greater than 1 = further from the sun than Earth The furthest planet (Pluto) from the sun is 39.5 AU away • Light Years Used for….when the vast distances beyond the solar system, out to the stars and galaxies are too great for astronomical units. It equals the distance that light travels in one year Speed of light is…300 000 km/s Light travels 9.5 trillion km in 1 year The nearest star (after the sun) is 4 light years away. Looking In the Past The light we seen has taken time to get to us therefore the images we see are from the past. The time delay for the images coming from the following places is… Light travelling from… The moon The sun Pluto Stars in the center of the galaxy Light captured by the Hubble light telescope Time Delay 1 second 8 minutes 5 hours 25 000 years 13 billion years Do Check and Reflect p. 383, # 1-8