* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - CAP-TB
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
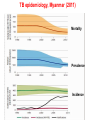
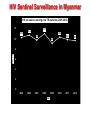
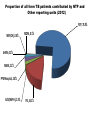
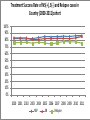
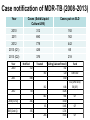
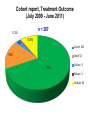
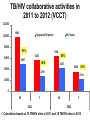
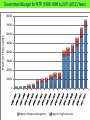
TB, MDR – TB control updates, Myanmar CAP-TB Strategic Planning Meeting, Bangkok, Thailand, 1-2 August, 2013 TB burden TB is a major public health problem One of the world’s 22 high TB burden countries, 27 high MDR-TB burden countries and 41 high TB/HIV burden countries Estimates of the TB burden in Myanmar, 2011 (based on 2009-2010 prevalence survey), source: WHO TB Control Report 2012 Population 60 million - Number Rate (per 100,000 population) Prevalence 240,000 506 (390-637) Incidence 180,000 381 (326-439) Incidence (HIV positive) 18,000 38 (31-45) Mortality (excluding TB/HIV) 23,000 48 (22-84) Notifications (new and relapse) 136,737 283 TB epidemiology, Myanmar (2011) Mortality Prevalence Incidence HIV Sentinel Surveillance in Myanmar HIV prevalence among new TB patients (2005-2012) 12 10.3 11.1 10.8 10.4 9.8 10 9.9 9.7 2011 2012 9.2 Percent 8 6 4 2 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 Year 2005 – 5 tsps 2012 – 25 tsps 2010 Goal, Objectives & targets Goal To reduce morbidity, mortality and transmission of TB until it is no longer a public health problem and to prevent the development of drug resistant TB. Specific Objectives are set towards achieving the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) for 2015. To reach and thereafter sustain the targets • achieving at least 70% case detection and successfully treat at least 85% of detected TB cases under DOTS (MDGs: Goal 6, Target 6.c, Indicator 6.10) To reach the interim targets of halving TB deaths and prevalence by 2015 from the 1990 situation. (MDGs: Goal 6, Target 6.c, Indicator 6.9) WHO-recommended Stop TB Strategy TB case notifications 160000 147984 140000 133547 143164 134023 137403 123593 120000 107991 Cases Load 100000 97909 128739 New SS + New SS neg EP All Cases Load 80000 77231 58243 60000 42455 40000 31703 20000 17008 1555 0 20196 16113 19626 14756 Years Proportion of all form TB patients contributed by NTP and Other reporting units (2012) NTP, 75.8% MSF(CH), 0.4% MDM, 0.1% AHRN, 0.2% MMA, 2.1% PPM Hospital, 2.8% AZG(MSF-H), 2.5% PSI, 16.1% Treatment Success Rate of NS(+), S(-) and Relapse cases in Country (2000-2011)cohort 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 NSP SN Relapse 9 MDGs for TB Control No 6.9 Indicator 1990 2005 2007 2011 2015 Incidence, prevalence and death rates associated with tuberculosis 1 . Incidence 404 404 404 381 To halt and reverse 2. Tuberculosis Prevalence all cases / 100,000 pop. 922 628 596 506 (45%) 461 3. Tuberculosis Death rate / 100,000 133 67 58 48 (64%) 66 6.10 # Proportion of tuberculosis cases detected and cured under directly observed treatment, short course 1. Proportion of tuberculosis cases detected 38 95 90 2. Proportion of tuberculosis cases treated successfully 78 85 85 77 85.4 At least 70% At least 85% 6.9 Global Tuberculosis Control 2010, WHO, Geneva # 6.10 National Tuberculosis Programme, Department of Health, Ministry of Health, Annual Reports (2000-2009) Estimates of MDR-TB burden (2012) • WHO estimates that there were 5,500 MDR-TB cases among notified pulmonary TB cases in 2011 • Among the total annual TB cases 9,000 are estimated to have MDR-TB • A total of 6 XDR-TB cases have been confirmed New cases Cases with DST results (H+R) Previously treated cases Multidrug-resistant No. % Multidrug-resistant Cases with DST results (H+R) No. % 20022003 3.90% 15.50% 20072008 4.2% (3.1-5.6) 10.0% (6.9-14.0) 2013 1,071 45 299 30 Third survey to be completed in 2013 MDR-TB suspects definition and diagnostic algorithms Patient to be tested for drug sensitivity • Retreatment cases including Category II failure, Category I failure, relapse and return after default and other cases • Close contacts of MDR-TB patients who develop active TB • All TB patients living with HIV/AIDS Three diagnostic algorithms developed based on Xpert MTB/RIF: • Diagnosis of TB in HIV-negative patients with no significant risk for MDR-TB • Diagnosis of TB/MDR-TB in HIV-positive TB patients • Diagnosis of MDR-TB in patients with risk factors for resistance Treatment Regimens Standardized treatment regimens • 6 Am + Lfx + Eto + Cs + PAS + Z • 18 Lfx + Eto + Cs + PAS +Z OR • • 6 Am + Lfx + Eto + Cs + Z 18 Lfx + Eto + Cs + Z Key activities to date to combat drug resistant TB • • • • • • • • DOTS-Plus pilot project started in July 2009 The Global Fund supported MDR-TB management started in December 2011 SOP of pilot phase was reviewed and revised in 2012. Model of MDR-TB care –community-based Patients enrolment category – expanded beyond Cat II failure Treatment regimen revised – PAS to be included only for Cat II failure MDR-TB patients MDR-TB township expansion started in 2012 according to scale up plan (2011-2015) MDR townships expanded from 22 to 38/ 330 townships in 6 States/Regions (Yangon 18, Mandalay 11, Sagaing 3, Magway 2, Mon 2, Shan 2) Case notification of MDR-TB (2008-2013) Year Cases (Solid/Liquid Culture/LPA) Cases put on SLD 2010 312 192 2011 690 162 2012 778 442 2013 (Q1) 426 65 2013 (Q2) 376 218 Year 2010 2011 Notified Treated 312 690 Waiting (Lab confirmed) 312 192 120 810 162 2012 778 442 2013 (1st Q) 426 65 2013 (2nd Q) 376 218 648 1426 984 1410 1345 1721 1503 Fund UNITAID 112 (UNITAID) 50 (GF) GF GF GF Number of MDR enrolled on treatment 2009-2013 (2nd quarter) 1200 MDR TB Patients Pilot YGN: 266 MDY: 43 Cumulative number 1000 1084 GF YGN: 631 MDY: 107 Other State and Region: 37 800 861 796 Total = 1,084 523 600 426 400 287 247 125 200 43 64 158 192 304 354 376 End DOTS-Plus pilot project 92 0 2009 2009 2010 2010 2010 2010 2011 2011 2011 2011 2012 2012 2012 2012 2013 2013 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Cohort report, Treatment Outcome (July 2009 - June 2011) Cured Died Failure Refuse Default Total YGN 172 45 3 1 28 249 MDY 29 7 0 0 2 38 Total 201 70% 52 17.7% 3 1 (1%) (0.3%) 30 10.5% 287 Total cohort cases (July 2009 – June 2011) ---- 309 cases Died before treatment ---- 6 cases Still on treatment ---- 16 (MDY- 5 cases & YGN- 11 cases) Cohort report, Treatment Outcome (July 2009 - June 2011) n = 287 0.3% 3% 10.5% Cured: 201 18% Died: 52 70% Failure: 3 Refuse: 1 Default: 30 MDR-TB patients at Aung San TB Hospital, Yangon, and in Meiktila Township, Mandalay Region Laboratories, drugs, staff and information systems Key activities to improve management of TB in hospitals • MDR-TB management in hospitals (free of charge to the patient): – Vehicle is available for referring and transfer of patients to various Specialist Hospitals if needed – Nutritional support for MDR-TB patients hospitalized – Side effect management – Laboratory investigations • Infection control measures have been upgraded • TB Control in Hospitals: – 23 hospitals are under Public-Public Mix DOTS, however, weak commitment to treat MDR. Family Health International 360 • FHI 360 work in close collaboration with the National Tuberculosis Programme and implement activities in Mandalay and Yangon initially through 4 local partners: 1. Myanmar Medical Association (MMA) 2. Pyi Gyi Khin (PGK) 3. Myanmar Health Assistant Association (MHAA) 4. Myanmar Business Coalition on AID (MBCA) Local Partners Project Township Activity Current Status MMA 1.South Okkalapa 2.Chan Mya Thazi. -DOT to MDR-TB Patients -Manage minor adverse effects -Refer cases -PMDT training-- 5 sessions (135) -Community supporter training ---- 1 session (15) PGK 1.Mingalardon 2.Mayangone 3.Hlaing 4.North Dagon -Community outreach -Case finding & referral -Infection control and support package of services to MDR-TB patients -176 MDR TB patients were provided with package of support -Total 1,483 beneficiaries were reached with TB prevention and treatment message MHAA 1.Aungmyay Tharzan 2.Chanaye Tharzan 3.Mahar Aungmyay 4.Pathein Gyi Implementing the same activities as PGK -38 MDR TB patients were provided with package of support -Total 2,294 beneficiaries were reached with TB prevention and treatment message MBCA 1.Monywa (Industrial zone) -Community outreach -Case finding & referral -Total number of volunteer trained --- 39 -Total 1,619 factory workers and their family members were reached with TB prevention message. TB/HIV collaborative activities in to townships 2012 -(VCCT) TB/HIV2011 collaborative VCCT (2011-2012) 12000 10000 9683 Registered TB patient HIV Tested 8000 51% 6000 6394 65% 5626 4937 48% 4000 4137 61% 3530 2700 2134 2000 0 M F 2011 M F 2012 Calculation based on 15 TB/HIV sites in 2011 and 18 TB/HIV sites in 2012 Key activities to improve management of TB by private providers • Private providers engaged at national scale: – Population Services International (PSI): 190 tsps, 855 GPs – Myanmar Medical Association (MMA): 116 tsps, 1443 GPs • Contributing to about 16% of TB notifications • ISTC adopted & disseminated since 2009 Major Challenges in combating drug resistant TB • • • • • • • • • Strengthen human resources (number and skills), willingness of physicians Referral network for utilization of Xpert Timely arrival of second-line anti-TB drugs Ensure ancillary drugs and support for infection control Geographical expansion Expand MDR-TB follow-up sites (decentralization) Provide more incentive for Basic Health Staff Ensure/sustain nutritional support for MDR-TB patients Infection control measure for health care settings Expansion plan (with committed resources) Number of regions or states with Number of TB/MDR-TB centers treatment with Xpert center Number of townships with MDRTB treatment center Secondline antiTB drugs committed from donors Year Reference diagnostic labs with culture/ DST 2012 2 6 2 38 442 2013 3 24 7 53 984* 2014 4 38 13 68 500 2015 5 38 13 100 800 2016 5 38 13 100 1000 2017 5 38 13 130 • Patients to be treated also in 2014 • Reference labs and Xpert MTB/RIF more ambitious that MDR-TB scale-up plan • MDR-TB patient enrollment less ambitious than MDR-TB scale-up plan Planned activities • Case detection and diagnosis of MDR-TB by Xpert MTB/RIF, Liquid Culture and LPA for all retreatment cases • Second-line anti-TB drug procurement: – – – – • • • • 2013: 508 (Global Fund and UNITAID) 2014: 1084 (Global Fund) 2015: 800 (Global Fund) 2016: 1000 (Global Fund) MDR-TB support package for providers and patients Procurement of infection control materials Expansion of an additional three culture & DST laboratories Timely procurement of lab. consumables for culture and DST Planned activities • Publication and dissemination of new guidelines • Geographical expansion 15 townships per year to 38 townships in 2014 (major training activities planned) • Xpert MTB/RIF will be expanded in 20132014 – – – – 12 machines up and running 4 machines from UNITAID (2013) 6 machines from PEPFAR 16 from GF (8 in 2013 and 8 in 2014) • Increase of DOT provider allowance and patient support (nutrition and transportation) Future Plan (FHI) Expansion of Activities in Yangon PGK : 2 new townships (Shwe Pyi Thar and NorthOkkalarpa Township) MHAA: 2 new townships (Insein and Hlaing Thar Yar) Activities will be the same as current townships Expansion of Activities in Mandalay (MHAA) To expand 3 more townships and activities will be the same. Expansion of Activities in Monywa (MBCA) To support package of services to MDR-TB patients by conducting home base care activities Progress and achievements (2011-2013) in implementing the Stop TB Strategy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Nationwide DOTS EQA system on sputum smear microscopy for 425 laboratories, introduced iLED fluorescence microscope to district. TB-HIV sentinel surveillance in 25 sites, TB/HIV collaborative activities in 28 townships. MDR-TB pilot successful and now expanding to programmatic MDR-TB management. Successful PPM at nationwide scale, 20 partners involving in TB control. Community based TB control activities with NGOs started in 154 townships (international NGOs in 23 townships). Operational Research are conducting in collaboration with Dept. of Medical Research. Government Budget for NTP (1995-1996 to 2011-2012) Years 800,000 Kyats in thousands 700,000 600,000 500,000 400,000 300,000 200,000 100,000 0 Budget for Programme Management Budget for Drug Procurement 32 Funding gap (2011-2015) (USD in million) Sr N Funding sources 1 Gov. 2 2011 2012 2013 2014 2014 Total 1.23 1.93 1.93 1.93 1.93 8.98 GF 14.59 15.54 14.73 16.11 17.61 78.59 3 3DF 4.37 1.71 4 3MDG 5 JICA 6 USAID 7 TB Rearch 8 WHO 0.14 0.13 9 UNITAID 0.19 0.19 10 GDF 0.84 0.93 1.03 11 NGOs 0.24 1.87 1.34 1.34 1.3 6.1 Total 23.79 26.94 21.98 22.33 23.78 118.84 Fund needed 30.28 30.6 35.71 40.61 48,77 186.00 6.48 3.65 13.73 18.28 24.99 67.15 Gap 6.08 2.8 2.8 2.8 8.4 0.16 0.19 0.35 2.0 2.0 4.0 2.422 2.422 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.69 0.39 2.81 GF (NFM) – 82.3 Million USD, 3MDG - ~ 17 Million USD (2013-2016) Issues and challenges Sustainability of current achievement is limited due to following issues: Limitation in human resource development Limitation in capacity building Improving case finding and treatment outcomes in selected townships (border and remote) with high treatment interruption rates and low community involvement in TB control Limited access to HIV care for TB/HIV co-infected patients Limited resources for MDR-TB management (Availability of diagnostic facilities and SLD, infection control measures) Need technical assistance for new tools Paper based R&R New technology LPA FM MGIT X pert