* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Gaia hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
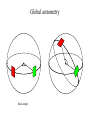
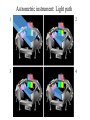
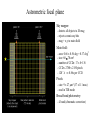
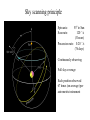
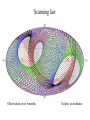
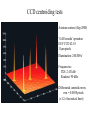
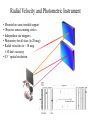
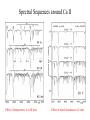
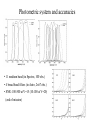
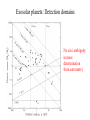
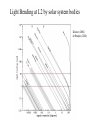
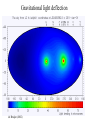
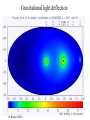
GAIA Composition, Formation and Evolution of our Galaxy thanks to Michael Perryman, the GAIA Science Team (present and past) and 200+ others M83 M83 image (with Sun marked) (AAO, D. Malin) ‘the Sun’ GAIA: Key science objectives • Structure and kinematics of our Galaxy: – – – – shape and rotation of bulge, disk and halo internal motions of star forming regions, clusters, etc nature of spiral arms and the stellar warp space motions of all Galactic satellite systems • Stellar populations: – physical characteristics of all Galactic components – initial mass function, binaries, chemical evolution – star formation histories • Tests of galaxy formation: – dynamical determination of dark matter distribution – reconstruction of merger and accretion history Origin, Formation and Evolution of the Galaxy Overview 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Measurement principles The GAIA satellite and mission Some science examples Schedule, organisation of work Current situation Summary Some history… 610 B.C.: Obliquity of the ecliptic (Anaximander) 125 B.C.: Precession of the equinoxes (Hipparchus) 1717: First proper motions (Halley) 1725: Stellar aberration (Bradley), confirming: – Earth’s motion through space – finite velocity of light – immensity of stellar distances 1761/9: Transits of Venus across the Sun (various) – solar parallax 1783: Sun’s motion through space (Herschel) 1838-9: First parallaxes (Bessel/Henderson/Struve) Principle of parallax measurement parallax angle Orbit about Sun Star of interest Background stars Measurement Principle Measurement principle: b Global astrometry basic angle GAIA: complete, faint, accurate Hipparcos GAIA Magnitude limit Completeness Bright limit Number of objects 12 7.3 – 9.0 ~0 120 000 Effective distance limit Quasars Galaxies Accuracy 1 kpc None None ~1 milliarcsec Broad band photometry Medium band photometry Radial velocity Observing programme 2-colour (B and V) None None Pre-selected 20-21 mag ~20 mag ~3-7 mag 26 million to V = 15 250 million to V = 18 1000 million to V = 20 1 Mpc ~5 106 - 107 4 arcsec at V = 10 10 arcsec at V = 15 200 arcsec at V = 20 4-colour to V = 20 11-colour to V = 20 1-10 km/s to V = 16-17 On-board and unbiased Scientific design considerations • Astrometry (V < 20): – completeness on-board detection – accuracies: 10 as at 15 mag (science) – continuously scanning satellite, two viewing directions global accuracy, optimal with respect to observing time • Radial velocity (V < 17-18): – third component of space motion – account for perspective acceleration (nearby, fast stars) • Photometry (V < 20): – astrophysical diagnostics (4-band + 11-band) + chromatic correction extinction, Teff ~ 200 K, [Fe/H] to 0.2 dex Satellite • Deployable: solar array/sun-shield • Size: 8.5m diameter (4.2m stowed) 2.9m height (2.1m for payload) • Mass: 3100 kg (800 kg payload) • Power: 2600 W • Launch: dual Ariane 5 • Orbit: Sun-Earth L2 (Lissajous) • Data rate (phased array): 1 Mbs-1 sustained 3 Mbs-1 downlink (1 ground station) • Launch date: 2010-12 • Attitude control: FEEP thrusters • Design lifetime: 5 years • ESA only mission Payload overview • Two astrometric instruments: • field of view = 0.6o 0.6o • separation = 106o • Monolithic mirrors: 1.7 m 0.7 m • Non-deployable, 3-mirror, SiC optics • Astrometric focal planes: TDI CCDs • Radial velocity/photometry telescope • Survey principles: • revolving scanning • onboard detection • complete and unbiased sample Astrometric instrument: Light path 1 2 3 4 Astrometric focal plane Sky mapper: - detects all objects to 20 mag - rejects cosmic-ray hits - mag + x,y to main field Main field: - area: 0.66 x 0.56 deg = 0.37 deg2 - size: 60 70 cm2 - number of CCDs: 17 x 8=136 - CCDs: 2780 x 2150 pixels - 120´´/s 0.86s per CCD Pixels: - size: 9 x 27 m2 (37 x 111 mas) - read in TDI mode Broad-band photometry: - 4 band (chromatic correction) On-board source detection Requirements and constraints: – – – unbiased sky sampling (mag, colour, resolution, etc.) no all-sky catalogue at GAIA resolution (0.1 arcsec) to V~20 cannot transmit entire sky at 0.1 arcsec resolution (telemetry limitations) Solution: on-board detection and sampling – – – – no input catalogue or observing programme (big effort for Hipparcos) good detection efficiency to V~21 mag maximum star density: ~ 3 million stars/deg2 (Baade’s Window) reduces data rate from several Gbps to a few Mbps Will therefore also detect: – – – – supernovae: 105 expected microlensing events: ~1000 photometric variable stars (eclipsing binaries, Cepheids, etc) Solar System objects, including near-Earth asteroids and KBOs Sky scanning principle 55o to Sun 120 ´´/s (3 hours) Precession rate: 0.20 ´´/s (76 days) Spin axis: Scan rate: Continuously observing Full sky coverage Each position observed 67 times (on average) per astrometric instrument Scanning law Observations over 5 months Ecliptic co-ordinates Astrometric accuracies G (~V mag) 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Parallax 4 4 4 5 7 11 17 27 45 80 160 500 Position 3 3 3 4 6 9 15 23 39 70 140 440 Annual proper motion 3 3 3 4 5 8 13 20 34 60 120 380 5-year accuracies in as Derived from detailed analysis: • image formation (polychromatic PSF) • evaluation vs. spectral type/reddening • comprehensive detector signal model • sky background and image saturation • attitude rate errors and sky scanning • on-board detection probability • on-ground location estimation (centroid to 0.001 pixel in hardest case) • error margin of 20 per cent included • results folded with Galaxy model Fraction of stars with given relative parallax error vs. magnitude (towards Galactic poles) CCD centroiding tests Astrium contract (Sep 2000) ‘GAIA-mode’ operation EEV CCD 42-10 13m pixels Illumination: 240,000 eFrequencies: TDI: 2.43 kHz Readout: 90 kHz Differential centroid errors: rms = 0.0038 pixels (1.2 theoretical limit) 1 as is a very small angle ... • Earth-Sun system seen from 1 Mpc (by definition) • the Earth seen from the Pleiades (100 pc) • Baden-Württemberg seen from Centauri (1.3 pc) • a grain of rice seen on the Moon (380 000 km) • a human hair observed in Kabul from Heidelberg (5000 km) Astrometric reduction • Approximate single epoch astrometry (<<1´´) from star mapper and GAIA orbit/attitude • Great circle scans 1D positions in two fields separated by a well-known basic angle (monitored) Object matching in different scans (e.g. GSC II method) Full sphere reduction to determine 5 astrometric parameters per star by a global iterative method (>100 measures) Binary models fitted to systems with large residuals GAIA observations of quasars (known and new) put the astrometry on a quasi-inertial reference system • • • • GAIA spectrophotometry and radial velocities • High resolution spectra for: - 3rd component of space motion - perspective acceleration - stellar abundances, rotation velocities • Medium band photometer for: - classification of all objects - physical parametrization of stars Teff, log g, [Fe/H], [/H], A() Radial Velocity Measurement Concept F3 giant S/N = 7 (single measurement) S/N = 130 (summed over mission) Radial Velocity and Photometric Instrument • Mounted on same toroidal support • Observes same scanning circles • Independent star mappers • Photometry for all stars (to 20 mag) • Radial velocities to ~ 18 mag 1-10 km/s accuracy • 0.5´´ spatial resolution Spectral Sequences around Ca II Effect of temperature: A to M stars Effect of metal abundance in G stars Photometric system and accuracies • 11 medium band (in Spectro, 100 obs.) F33 B45 B63 B82 • 4 broad band filters (in Astro, 2x67 obs.) • SNR: 100-500 at V=15 (10-100 at V=20) (end of mission) GAIA and our Galaxy 10 as = 10% distances at 10 kpc 10 as/yr = 1 km/sec at 20 kpc GAIA: Why a survey to 20 mag? Population Tracer Mv l b d Av V1 V2 T 1 1 1 mag deg deg kpc mag mag mag km/s as/yr - - Bulge gM HB MS -1 +0.5 +4.5 Spiral arms Cepheids B-M supergiants Perseus Arm (B) Thin disk 0 0 1 <20 <20 -4 8 8 8 2-10 2-10 0-2 15 17 19 20 20 21 100 100 100 10 20 60 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.10 0.20 0.60 -4 -5 -2 All All 140 <10 <10 <10 10 10 2 3-7 3-7 2-6 14 13 12 18 17 16 7 7 10 5 4 3 0.03 0.03 0.01 0.06 0.05 0.01 gK GK -1 -1 0 180 <15 <15 8 10 1-5 1-5 14 15 18 19 40 10 6 8 0.01 0.04 0.06 0.10 Disk warp gM -1 All <20 10 1-5 15 19 10 8 0.04 0.10 Thick disk Miras, gK HB Miras, gK HB -1 +0.5 -1 +0.5 0 0 180 180 <30 <30 <30 <30 8 8 20 20 2 2 2 2 15 15 15 15 19 19 21 19 50 50 30 30 10 20 25 60 0.01 0.02 0.08 0.20 0.10 0.20 0.65 1.50 Halo gG HB -1 +0.5 All All <20 >20 8 30 2-3 0 13 13 21 21 100 100 10 35 0.01 0.05 0.10 1.40 Gravity, K-z dK dF8-dG2 +7-8 +5-6 All All All All 2 2 0 0 12 12 20 20 20 20 60 20 0.01 0.01 0.16 0.05 Globular clusters gK +1 All All 50 0 12 21 100 10 0.01 0.10 Satellite orbits gM -1 All All 100 0 13 20 100 60 0.30 8.00 GAIA capabilities Distances: <0.1% for 700 000 stars <1% for 21 million Transverse motions: <0.5% km/s for 44 million <3 km/s for 210 million <10 km/s for 440 million <10% for 220 million Radial velocities to a few km/s complete to V=17-18 15-band photometry (250-950nm) at ~100 epochs over 4 years Complete survey of the sky to V=20, observing 109 objects: 108 binary star systems (detected astrometrically; 105 orbits) 200 000 disk white dwarfs 50 000 brown dwarfs 50 000 planetary systems 106-107 resolved galaxies 105 quasars 105 extragalactic supernovae 105-106 Solar System objects (65 000 presently known) Exosolar planets: Detection domains No sin i ambiguity in mass determination from astrometry Expected astrometric planetary discoveries • Monitoring of hundreds of thousands of stars to 200 pc for 1MJ planets with P < 10 years: – complete census of all stellar types (P=2-9 years) – actual masses, not just lower limits (m sin i) – 20,000-30,000 planets expected to 150-200 pc – e.g. 47 UMa: astrometric displacement 360 as • Orbits for many (~ 5000) systems • Masses down to 10 MEarth to 10 pc General Relativity Solar eclipse (image) (light bending) Light Bending at L2 by solar system bodies Klioner (2002) de Bruijne (2002) Gravitational light deflection de Bruijne (2002) General Relativity • Parametrized Post-Newtonian (PPN) formulation – = 1.0 for General Relativity (GR) – alternative scalar-tensor theories deviate by 10-5- 10-7 • GAIA will measure to 510-7 from positional displacement at large angles from the Sun – currently known to 10-5 – GAIA tests GR at 10-100 times lower mass than presently – effect of Sun: 4 mas at 90o; Jovian limb: 17 mas; Earth: 40 as • Microlensing: photometric (~1000) and astrometric (few) events Galaxies, quasars, and the reference frame • • • • Parallax distances, orbits, and internal dynamics of nearby galaxies Galaxy survey (106-107 resolved at 0.1´´ in four bands, 0.5´´ in 11 bands) ~500,000 quasars: kinematic and photometric detection ~100,000 supernovae • Galactocentric acceleration: 0.2 nm/s2 (aberration) = 4 as/yr • Globally accurate reference frame to ~0.4 as/yr Schedule 2000 2004 2008 2012 2016 2020 Acceptance Technology Development Design, Build, Test Launch Observations Analysis Catalogue Organisation of scientific work GAIA Science Team (12 people) Satellite/Payload Specific Objects Data Processing Error Budget Multiple Stars Data Base Focal Plane/Detection Planetary Systems Simulations Photometry Variable Stars Imaging Radial Velocity Solar System Objects Classification Calibration Relativistic Model Sampling/Telemetry Science Alerts Working groups: about 150 European ‘core’ and ‘associate’ members GAIA Science Team (GST) Frederic Arenou (Meudon) Coryn Bailer-Jones (MPIA, Heidelberg) Ulrich Bastian (ARI, Heidelberg) Erik Hoeg (Copenhagen) Andrew Holland (Leicester) Carme Jordi (Barcelona) David Katz (Meudon) Maria Lattanzi (Torino) Lennart Lindegren (Lund) Xavier Luri (Barcelona) Francois Mignard (Nice) Michael Perryman (Project Scientist, ESA) Current GAIA activities ESA/industrial: • • • • • • Phased array antenna (Alcatel) High stability optical bench (Astrium) Telemetry budget and compression algorithms (ESA) FEEPs: will be based on SMART-2 activities (ESA + industry) Proof of concept data reduction system (Barcelona + GMV) New important industrial study contracts (CCD and focal plane study, mirrors) are on hold due to internal ESA SPC/IPC conflict Scientific community (working groups): • • • • • On-board detection algorithms Detailed specification of radial velocity instrument Definition of optimal photometric system Simulations of data stream Development of object classification and physical parametrization methods Data processing demonstration (GDAAS) • • • • • • under development since mid-2000 (GMV/UB/CESCA) sky divided into hierarchical triangular mesh (level 6) presently: 8 nodes, 4 processors per node, 0.5 Tbyte disk telemetry ingestion, object matching, sphere iteration iterative processing for 1 million stars (final results April 2002) platform for further development/experimentation Database Processing 1 1 Database Processing Master N N Special Processing Object classification/physical parametrization • classification as star, galaxy, quasar, supernovae, solar system objects etc. • determination of physical parameters: - Teff, logg, [Fe/H], [/H], A(), Vrot, Vrad, activity etc. • combination with parallax to determine stellar: - luminosity, radius, (mass, age) • use all available data (photometric, spectroscopic, astrometric) • must be able to cope with: - unresolved binaries (help from astrometry) - photometric variability (can exploit, e.g. Cepheids, RR Lyrae) - missing and censored data (unbiased: not a ‘pre-cleaned’ data set) • multidimensional iterative methods: - cluster analysis, k-nn, neural networks, interpolation methods • required for astrometric reduction (identification of quasars, variables etc.) produce detailed classification catalogue of all 109 objects Recent developments Oct. 2000: GAIA approved by SPC for launch by 2012 Nov. 2001: Ministerial meeting reduces science budget by 435 MEuro over 2002-2006 (20% reduction) Nov. 2001: ESA+Astrium start to identify cost savings Dec. 2001: SPC requests review of whole ESA science program April 2002: AWG subgroup (Rix, Aerts, Ward) reports on GAIA to AWG; (AWG to SSAC to SPC) April 2002: Astrium presents revised GAIA design to GST May 2002: ESA/Astrium deliver final report to SPC June 2002: SPC decide on future science program GAIA cost saving measures (ongoing) Substantial savings possible if released from ESA constraints: 1. 2. 3. re-use of satellite subsystem designs from other missions cheaper contract competition mechanism Soyuz-Fregat launch instead of Ariane 5 (110 40 MEuro) - smaller mirrors in along-scan direction, accommodated by increased across-scan dimension, field-of-view size... Other possible cost savings from: • • • • • smaller solar array/sunshield by reducing solar aspect angle (accommodate for lost astrometric precision in optics) C-SiC optical bench unification of pixel scales field superposition (as in Hipparcos) smaller ESA project team Cost reduction from 570 to 400-450 MEuro possible without any reduction in accuracies or scientific goals Main performances and capabilities Accuracies: – – – – 4 as at V=10 10 as at V=15 200 as at V=20 radial velocities to few km/s complete to V=17-18 10 as distances to 1% at 1 kpc or 10% at 10 kpc (V=15) 10 as/yr at 20 kpc 1 km/s Capabilities: – sky survey in four bands at ~0.1 arcsec spatial resolution to V=20 – 15 band multi-epoch photometry to V=20 – dense quasar link to inertial reference frame every star observed in the Galaxy and Local Group will be seen to move GAIA will quantify a 6-D phase space for over 300 million stars and a 5-D phase-space for over 109 stars GAIA and our Galaxy 10 as = 10% distances at 10 kpc 10 as/yr = 1 km/sec at 20 kpc Perryman et al. (1997) Hyades 60,000 years Hyades (animation) core radius 3 pc Aldebaran (non-member) direction of motion Gravitational light deflection de Bruijne (2002) GAIA stands for ... Global Astrometric Interferometer for Astrophysics Galactic Astrophysics through Imaging and Astrometry General Astrometric Instrument for Astronomy Great Accuracy In Astrometry Great Advances In Astrophysics