* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
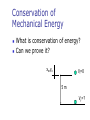
Chapter 5 Energy 1. Dot product of vectors 2. Kinetic Energy 3. Potential Energy 4. Work-Energy Theorem 5. Conservative and non-conservative forces 6. Conservation of Mechanical energy 7. Non-conservative forces and conservation of energy 8. Power 9. Work done by a variable force Forms of Energy What is energy? How many types of energy? Mechanical Chemical Electromagnetic Nuclear Transformation of energy Multiplication of two vectors What is a dot product? What does it give? How do I calculate it? Work What is work? How do I represent it? What does it do? How do I calculate it? What about units? Is it a scalar or a vector What about friction? Example - Work 1. A force of F=50 N is applied to a block at an angle of θ=30 degrees to the horizontal, the block moves on the horizontal surface (which is frictionless) by ∆x=3m, find Work done on the block. Work Kinetic Energy (KE) What is Kinetic Energy? How do I calculate it? What are its SI units? Is work related to Kinetic Energy? Example - Kinetic Energy 1. A 2.0 g bullet leaves the barrel of a gun at a speed of 25 m/s. Find a) b) The kinetic energy of the bullet. The average force exerted by the expanding gasses on the bullet as the bullet moves the length of the 42 cm long barrel. Gravitational Potential Energy (PEg) What is Gravitational Potential Energy? How do I calculate it? What are its SI units? Reference levels Example - Work and Potential Energy 1. If a woman lifts a 21.0 kg bucket from a well and does 4.0 kJ of work, how deep is the well? Assume that the speed of the bucket remains constant as it is lifted? Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem What is this theorem? What if the work is positive or negative? Work-Energy Theorem Mechanical Energy What is this theorem? Work-Energy Theorem 1. A 800 N skier and sled is at the top of a slope, as shown. At point A she has a velocity of 5m/s. Find her speed when she is at point B. Nature of Forces What are conservative forces? Examples of conservative forces? What are nonconservative forces? Examples of nonconservative forces? Internal Energy Table is frictionless Table is NOT frictionless Work and Potential Energy What is the relationship between work and potential energy? When is this relationship true? What is the relationship? Conservation of Mechanical Energy What is conservation of energy? Can we prove it? xo,yo Vi=0 5m Vf=? Example – Conservation of Energy 1. A 0.4-kg bead slides on a curved wire, starting from rest at point A as shown. If the wire is frictionless, find the speed of the bead at B and at C. Work-Energy Theorem for non-conservative forces Example – Conservation of Energy 1. A 0.4-kg bead slides on a curved wire, starting from rest at point A as shown. If the wire is frictionless between A and B and rough between B and C, find the speed of the bead at B and if the wire comes to rest at C, find the loss in mechanical energy as it goes from B to C. Potential Energy Stored in a Spring What is a spring? What does it do? How do I calculate the force due to a spring? What is a spring constant? How do I calculate the work done by a spring? Work-Energy Theorem Including a Spring- non conservative force Conservation of Energy Including a Spring Spring - Example 1. A spring that has a force constant of 1.0x103N/m is placed on a table in a vertical position as shown. A block of mass 1.60 kg is held 1.0m above the free end of the spring. The block is dropped from rest so that it falls vertically onto the spring. By what distance does the spring compress? Power What is power? How do I calculate it? What are the SI units? Power, cont. US Customary units are generally hp Need a conversion factor ft lb 1 hp 550 746 W s Can define units of work or energy in terms of units of power: kilowatt hours (kWh) are often used in electric bills This is a unit of energy, not power Example – Power 1. A load is lifted by a motor at a constant speed of 3.0 m/s. Find the power the motor must deliver Example – Power 1. Water flows over a section of Niagara Falls at the rate of 1.2x106 kg/s and falls 50 m. How much power is generated by the falling water? Center of Mass & Vertical Jumps Work Done by Varying Forces Work done by Spring Varying Force - Example 1. The figure shows the force acting on an object as a function of distance. Calculate the total work done?