* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
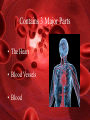
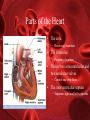
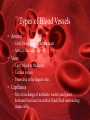
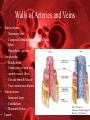
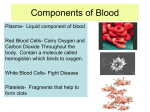
The Circulatory System Functions of the Circulatory System • Stabilizes body temperature and pH to maintain homeostasis • An organ system which distributes blood throughout the entire body – – – – Transports oxygen to body cells Transports CO2 away from cells Transportation of hormones Transportation of immune system components Contains 3 Major Parts • The Heart • Blood Vessels • Blood The Heart The Heart as a Double Pump • The heart is a double pump, simultaneously pumping blood to and from body cells through the systemic circulation and to and from the lungs in the pulmonary circulation Parts of the Heart • The atria – Receiving chambers • The ventricles – Pumping chambers • Valves: two atrioventricular and two semilunar valves – Control one-way flow • The interventricular septum – Separates right and left ventricles Blood Vessels Types of Blood Vessels • Arteries – Carry blood away from the heart – Aorta is the largest artery • Veins – Carry blood to the heart – Contain valves – Vena cava is the largest vein • Capillaries – Site of exchange of nutrients, wastes, and gases between blood and interstitial fluid (fluid surrounding tissue cells) Walls of Arteries and Veins • Tunica externa – Outermost layer – Composed of mainly elastic and collagen fibers – Strengthens, Anchors • Tunica media – Middle layer – Composed of elastic and smooth muscle fibers – Circular Smooth Muscle – Vaso-constriction/dilation • Tunica interna – Innermost layer – Endothelium – Minimize friction • Lumen Blood Functions of the Blood • Carries oxygen from the lungs to all of the cells in the body • Carries carbon dioxide from the body cells to the lungs to be exhaled • Carries waste to the kidneys to be disposed of • Carries nutrients to body cells • Contains immune system cells and molecules that help fight infection Components of Blood • Plasma – Comprise 55% of whole blood volume • Formed Elements – Comprise 45% of whole blood volume Plasma • 91% water • Contains dissolved proteins, glucose, clotting factors, mineral ions, hormones and carbon dioxide Formed Elements • Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes or RBCs) – Contain a large molecule called hemoglobin used to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide • White blood cells (Leukocytes or WBCs) – Cells of the immune system defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials • Platelets (Thrombocytes) – Special cell fragments that protect the body by forming a platelet plug to stop bleeding by ruptured vessels – Secrete chemicals that aid in blood clotting