* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4-4 Using Congruent Triangles: CPCTC
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
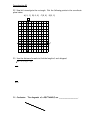
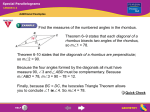
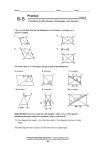
Geometry Section 6-4: SPECIAL Parallelograms Name______________________ Date_________________ Over the course of the next couple of days, we will learn,____________________ ______________________________________________________________. Part I. What you know. 1. What is an isosceles triangle? 2. In the isosceles triangle below mark the sides and angles that are congruent? 3. ABC is an isosceles triangle and BD is an altitude. Explain why we can we conclude that ABD CBD. 4. Why can we say that AD CD ? What name would we give to point D? 5. In the isosceles triangle above, BD can also be called a _____________. Part II: Investigation #1 6. Now let’s look at Rhombus MATH. Draw diagonal MT . 7. What types of triangles are MAT and MHT ? Why? 9. What is the relationship between ATM and AMT ? 10. What is the relationship between HTM and HMT ? 11. Is MAT MHT ? How? 12. What can we conclude about ATM, AMT, HTM and HMT ? 13. What name can be given to MT now that you know the relationship of the angles? 14. Now draw diagonal AH . Can you make the same conclusion about AH ? 15. Conclusion: The ________________ of a RHOMBUS, __________ opposite angles. Investigation #2 16. Let’s take another look at Rhombus MATH. Draw diagonal MT . 17. Now draw diagonal AH and label the intersection of MT and AH point K. Because a rhombus is a parallelogram, what do you know about diagonals MT and AH ? 18 What name can we give point K ? 19. Because MAT MHT are _____________ triangles, what names can be given to AK and HK ? 20. What type of angles are AKT and AKM ? 21. Conclusion: The diagonals of a RHOMBUS are _______________________ to each other. Investigation #3 22. Now let’s investigate the rectangle. Plot the following points in the coordinate plane below. A(-3, -1) B(-3, 4) C (5, 4) D(5, -1) 23. Use the distance formula to find the length of each diagonal. ( x 2 x1 ) 2 ( y 2 y1 ) 2 AC = BD = 24. Conclusion: The diagonals of a RECTANGLE are _________________. Part III Wrapping things up. 25. What are the three types of parallelograms? 26. The properties of PARALLELOGRAMS from Section 6-2: 1. In a parallelogram, opposite ___________ are ____________. 2. In a parallelogram, opposite ___________ are ____________. 3. In a parallelogram, opposite ___________ are ____________. 4. In a parallelogram, same side interior angles are ___________________. 5. In a parallelogram, diagonals ____________ each other. 27. Are the above properties of parallelograms also true for a Rectangle, Rhombus and a Square? Why or why not? 28, The properties of a RHOMBUS: - All four sides are _________________. - The diagonals are _____________________________. - The diagonals are _____________________________. 29. The properties of a RECTANGLE: - All four angles are _________________. - The diagonals are __________________. 30. The properties for a rhombus and a rectangle also true for a square? Why or why not? Part IV. Using what you’ve learned. 31. Find the measures of the numbered angles in the rhombus. 32. One diagonal of a rectangle has length 8x + 2. The other diagonal has length 5x+11. Find the length of each diagonal.