* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View Book Sample - Cheap Assignment Help
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Linear time-invariant theory wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
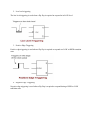
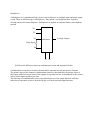
DIGITAL FUNDAMENTALS Q1:In which of the following base systems is 123 not a valid number? (a) Base 10 (b) Base 16 (c)Base 8 (d) Base 3 Answer: Base 3 Q2:.A NAND gate is called a universal logic element because (a) it is used by everybody (b) any logic function can be realized by NAND gates alone (c) all the minimization techniques are applicable for optimum NAND gate realization (d) many digital computers use NAND gates. Answer: (b) any logic function can be realized by NAND gates alone Q3: Most of the digital computers do not have floating point hardware because (a) floating point hardware is costly (b) it is slower than software (c) it is not possible to perform floating point addition by hardware (d) of no specific reason. Answer: floating point hardware is costly Q4: Positive logic in a logic circuit is one in which (a) logic 0 and 1 are represented by 0 and positive voltage respectively (b) logic 0 and, -1 are represented by negative and positive voltages respectively (c) logic 0 voltage level is higher than logic 1 voltage level (d) logic 0 voltage level is lower than logic 1 voltage level. Answer: (d) logic 0 voltage level is lower than logic 1 voltage level. Q5: Among the logic families, the family which can be used at very high frequency greater than 100 MHz in a 4 bitsynchronous counter is (a) TTLAS (c)ECL (b) CMOS (d)TTLLS Answer: ECL Q6: SR Flip flop can be converted to T-type flip-flop if ? (a) S is connected to Q (b) R is connected to Q (c) Both S and R are shortened. (d) S and R are connected to Q and Q' respectively Answer: (d) S and R are connected to Q and Q' respectively Q7: Register is a? (a) Set of capacitor used to register input instructions in a digital computer (b) Set of paper tapes and cards put in a file (c) Temporary storage unit within the CPU having dedicated or general purpose use (d) Part of the auxiliary memory Answer: (c) Temporary storage unit within the CPU having dedicated or general purpose use Q8: For which of the following flip-flop the output clearly defined for all combinations of two inputs? (a) Q type flip-flop (b) J K flip-flop (c) R S type flip-flop (d) T flip-flop Answer: J K flip-flop Q9: What is a digital-to-analog converter? (a) It allows the use of cheaper analog techniques, which are always simpler. (b) It takes the digital information from an audio CD and converts it to a usable form. (c) It converts direct current to alternating current. (d) It stores digital data on a hard drive. Answer: (c) It converts direct current to alternating current. Q10: The output of an OR gate is LOW when ________. (a) all inputs are LOW (b) any input is HIGH (c) any input is LOW (d) All inputs are HIGH Answer: (a) all inputs are LOW Q11: (a) What are minterms and maxterms? Minimize the Boolean function F=(X+X’ .Y) Minterm- A minterm is a Boolean expression resulting in 1 for the output of a single cell, and 0s for all other cells in a Karnaugh map, or truth table. Maxterm- A maxterm is a Boolean expression resulting in a 0 for the output of a single cell expression, and 1s for all other cells in the Karnaugh map, or truth table. Q12: (a) Show how a full-adder can be converted to a full-subtractor with the addition of one inverted circuit. All that has to be done is to put an inverter on the B input. Then tie the Cin input high to provide the "and then add one". Below is a full adder circuit. Full-subtractor with the addition of one inverted circuit. Q13: (a) Explain the different triggering techniques of flip-flops. The various triggering techniques are; high level triggering, low level triggering, positive edge triggering and negative edge triggering 1. High level triggering The high level triggering technique is used when a flip flop is needed to respond at its HIGH state. It is mostly identified from the straight lead from the clock input. 2. Low level triggering The low level triggering is used when a flip flop is required to respond at its LOW level. 3. Positive Edge Triggering Positive edge triggering is used when a flip flop is required to respond at a LOW to HIGH transition state. 4. Negative Edge Triggering Negative edge triggering is used when a flip flop is required to respond during a HIGH to LOW transition state. (b) Explain the working of a T flip flop. The ‘toggle’ or T flip flop is a kind of flip flop that changes its output on every clock edge thereby giving an output of half the frequency of the signal to the T input. Below is how the characteristic table for a T flip flop looks like. T 0 0 1 1 Q 0 1 0 1 Q+ 0 1 1 0 Operation Hold Hold Toggle Toggle The first column consists of the value of T which is a control input. The second column comprises of the value of the current state which the current value is being output by Q. The third column (Q+) represents the next state. A T flip flop has two possible values .The first one is when T=0.At this value the flip flop does a hold which means that the output Q is the same as it was before the clock edge. The second possible value is when T=1.At this value, the flip flop does a toggle. This means that the output is negated after the clock edge. Therefore, in a T flip flop, the current state value for another cycle can be maintained or can be toggled (negated) at the next clock edge. Q14: Discuss the following in detail: (a) Shift-registers. (b) Multiplexers. Shift registers Shift registers are registers capable of shifting binary information in one or both directions. Shift registers consist of a series of flip flops cascaded together with the output of one flip flop connected to the input of the other flip flop. All flip flops receive common clock pulses that initiate the shift from one stage to the next. They are generally provided with a Clear or Reset connection so that they can be "SET" or "RESET" as required. A shift register is controlled with certain clock pulses by inhibiting the clock from the input of the register if shift is not required. A shift register is also able to provide extra circuits to control the shift operation through the D inputs of the flip flops rather than the clock input. Multiplexers A Multiplexer is a combinational logic circuit or device that acts as a multiple-input and single output switch. There are different types of multiplexers. They include: wavelength division, frequency division and time division multiplexers. Multiplexers are applied in computer memory and telephone network X0 X1 X2 Multiplexer Y (Single Output) Many inputs Xn C1 C0 (b) Discuss the differences between combinational circuits and sequential circuits. Combinational circuits has no memory elements while sequential circuits has memory elements The present values of the outputs of combinational circuits are determined by the present values of their inputs while the present values of the outputs of sequential circuits are determined by the present values of their inputs and their past state. The behaviour of combinational circuits is described by the set of the output functions while the behaviour of sequential circuits is described by the set of next state and output functions. Q1. (a)Obtain the logic diagram of a master- slave J-K flip flop with AND and NOR gates. (b) Design a counter with the following binary sequence 0, 1, 3,7,6,4 and repeat .use T flip-flop. The number of flip flops required: Log26=3 flip flops Drawing the state table: Q2 (Present State) 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 Q1 (Present State) 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 Q0 (Present State) 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Q2+ (Next State) 0 0 X 1 0 X 1 1 Q1+ (Next State) 0 1 X 1 0 X 0 1 Q0+(Next State) T2(Excitation) T1(Excitation) T0(Excitation) 1 1 X 1 0 X 0 0 0 0 X 1 1 X 0 0 0 1 X 0 0 X 1 0 1 0 X 0 0 X 0 1 T2=Q2Q1’+Q2’Q1 T1=Q1Q0’+Q1’Q0 T0=Q2Q0+Q2’Q0’ Q2. (a)What is mantissa and exponent? Give suitable example. Mantissa is the decimal part of a logarithm. A suitable example is in the logarithm 1.556, the mantissa is 0.556. Exponent shows the number of repeated multiplication to be carried out. It is usually written as a superscript. For example 5 exponent 3 means 53, implying 5*5*5 Q3. (a) Answer the following. (1) What do you mean by minterm & maxterm Minterm- A minterm is a Boolean expression resulting in 1 for the output of a single cell, and 0s for all other cells in a Karnaugh map, or truth table. Maxterm- A maxterm is a Boolean expression resulting in a 0 for the output of a single cell expression, and 1s for all other cells in the Karnaugh map, or truth table. (2) What is a four bit binary parallel adder? A four bit binary parallel adder is a circuit, consisting of four full adders, which will add four-bit binary numbers. (b) Give the block diagram of processor unit and explain the function of different blocks. 1. Execution Unit The execution unit consists of the arithmetic and logic unit (ALU).It is also made up of the hardware that fetches, decodes and executes instructions. 2. Register set The register set allows an operation to read all inputs from the register file at the same time rather than having to read them one at a time. 3. Control Logic The control logic determines when instructions can be executed. It also controls the sequences of operations required to execute each instruction. Signals & Systems Q1 State whether the following statements are true or false and justify your statement? (a) The series interconnection of two linear time-invariant systems is itself a linear, time-invariant system? Yes. Consider two systems S1 and S2 connected in series. Assume that if x1( t ) and x2( t ) are inputs to S1 , then the outputs are y1( t ) and y2( t ), respectively. Also, assume that if y1( t ) and y2( t ) are inputs to S2 , then the outputs are z1( t ) and z2( t ), respectively. Since S1 is linear we know that for constants a, b; ax1 (t) + bx2 ( t ) s2 ay1(t) + by2 (t) Since S2 is linear we know that ay1 (t) + by2 ( t ) s2 az1(t) + bz2 (t) Hence; ax1 (t) + bx2 ( t ) s 1 s2 az1(t) + bz2 (t) (b) The series interconnection of two nonlinear systems is itself nonlinear? Consider the following; y(t) = x(t) + 1 z(t) = y(t) – 1 if they are connected in series, the z(t) = x(t) which is linear. Hence the interconnection of two non linear systems can be linear. Q2 A particular first-order casual and stable discrete-time LTI system has a step response whose maximum overshoot is 50% of its final value. If the final value is 1, determine a difference equation relating the input x[n] and output y[n] of this filter? Q3 The Laplace transform X(s) of a signal x(t) has four poles and an unknown number of zeros. The signal x(t) is known to have an impulse at t = 0. Determine what information, if any, this provides about the number of zeros and their locations? Q4 Let x(t) be a signal that has a rational Laplace transform with exactly two poles, located at s = -1 and s = -3. If g(t) = e2t x(t) and G (jw) [ the Fourier transform of g(t)] converges, determine whether x(t) is left sided, right sided, or two sided? Q5 Let x[n] be an absolutely summable signal with rational z-transform X(z). If X(z) is known to have a pole at z= ½, could x[n] be (a) (b) (c) (d) a finite-duration signal? a left-sided signal? A right-handed signal? A two-sided signal? Answer: Two-sided signal Q6 Consider a feedback system, either in continous-time or discrete-time, and suppose that the Nyquist plot for the system passes throughthe point -1/K. Is the feedback system stable or unstable for this value of the gain? Explain your answer? The feedback system is stable because the nyquist plot has circled the point (-1,0) LINEAR CIRUCUITS Q1 (A) WHICH IS THE FASTEST ADC AND WHY? Flash ADC is the fastest because change in it takes place simultaneously but not sequentially. Q2 (A) WHAT IS THE RANGE OF MODULATING INPUT VOLTAGE APPLIED TO A VCO? 3 to 6 volts (B) DRAW THE CIRCUIT OF A PLL AM DETECTOR AND EXPLAIN IT’S OPERATIONS. The input signal Vi with an input frequency fi is passed through a phase detector. A phase detector is basically a comparator which compares the input frequency fi with the feedback frequency fo .The phase detector provides an output error voltage Ver (=fi+fo),which is a DC voltage. This DC voltage is then passed on to an LPF. The LPF removes the high frequency noise and produces a steady DC level, Vf (=Fi-Fo). Vf also represents the dynamic characteristics of the PLL. The DC level is then passed on to a VCO. The output frequency of the VCO (fo) is directly proportional to the input signal. Both the input frequency and output frequency are compared and adjusted through feedback loops until the output frequency equals the input frequency. Thus the PLL works in these stages – free-running, capture and phase lock. Q3 (A) GIVE THE CONVERSATION TIME FOR (1) COUNTING ADC T con= (n/f) + T Where f =clock frequency n= Number of clock pulses T= Propagation delay (2) SUCCESSIVE APPROXIMATION ADC 7 sec, 10 bit (B) SHOW WITH THE HELP OF CIRCUIT DIAGRAM AN OP-AMP USED AS (i) SCALE CHANGER, (ii) PHASE SHIFTER (iii) INVERTING ADDER (iv)NON INVERTING ADDER Q4 (A) WHAT ARE THE MODES OF OPERATIONS OF A TIMER? The modes of operations of a Timer are: Astable mode, monostable mode and bistable mode. 1. Astable mode An astable circuit has no stable state. The output of this mode continually switches state between low and high without an intervention from the user. 2. Monostable mode Monostable circuit produces one pulse of a set length in response to a trigger input. The output of this mode stays in low state until there is a trigger input. 3. Bistable mode This mode has two stable states both high and low. A low state input makes the circuit output go into the higher state. A reset input low makes the output of the circuit go into the low state. (B) WHAT IS THE PRINCIPLE SWITCH MODE POWER SUPPLIES?DISCUSS IT’S ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES. Switch mode power supply Switch mode power supply is an electronic power supply that is integrated with the switching regulator for the purposes of converting the electrical power efficiently from one form to another with the desired characteristics. Advantages of Switch mode power supply There is greater efficiency. This is because the switching transistor dissipates little power when outside its active region. Switch mode power supply has a lighter weight and smaller size. Disadvantages of Switch mode power supply Greater complexity High amplitude and frequency energy that the low pass filter must block to avoid electromagnetic interference. Q5 (A) DESIRE THE TRANSFER FUNCTION OF A SECOND ORDER BP FILTER USING OTA’S. Volatge transfer function; High pass filter; The realization conditions are V1=V2=0, V3=Vi, g2 = 2 g1 The eqn. (1) becomes Band pass filter; The realization conditions are V1=V3=0, V2=Vi, g2 = 2 g1 The eqn. (1) becomes All pass filter; V2=0, V2=V3= Vi, g2 =2 g1 (B) EXPLAIN THE OPERATION OFFER SQUAR WAVE GENERATOR BYE DRAWING THE CAPACITOR AND OUTPUT VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS. Square Wave Generator This square wave generator is like the Schmitt trigger circuit in that the reference voltage for the comparator action depends on the output voltage. Square Waveform: Q6 (A) LIST THE NON-IDEAL dc CHARACTERISTICS OF AN OP-AMP. Finite common-mode rejection ratio dc error sources (offset current, input bias current, offset voltage) Output voltage, maximum current limits, slew rate. Common-mode input resistance (B) WHAT IS BODE PLOT? Bode Plot is a graphical representation of a linear, time-invariant system transfer function. (C) WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT PACKAGES? Dual-in-line package Metal can package Flat package (D) NAME THE TECHNOLOGY USED FOR THE FABRICATION OF TRANSISTORS OR ICS. Planar technology