* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13-Toxicology
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
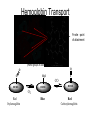
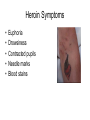
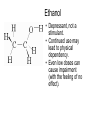
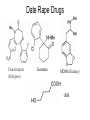
Forensic Toxicology What are toxins? Forensic Toxicology • Study of drugs and poisons and their adverse affects on the human system – Pharmacokinetics (what drug does to person?) – Pharmacodynamics (what body does to the drug?) >75% of forensic science investigations involve drug use! Drug/Toxin Vocabulary • Dose – Amount of drug that enters the body How is a dosage determined? LD (Lethal Dose)50 Lethal Dose-50 LD50 Calculations: Cyanide (for 150 lb human - ~ 70 Kg) (70Kg)(10mg/Kg) = 700 mg (0.70g) Nicotine (e.g.; from Cigarettes) (70Kg)(2 mg/Kg) = 140 mg (0.14g) (note 1 cig. = ~ 2 mg Nicotine) Ethanol Substance LD50 (mg) Aspirin Ethanol Morphine Caffeine Heroin Lead Cocaine Cyanide Nicotine Strychnine Batrachotoxin 1750 1000 500 200 150 20 17.5 10 2 0.8 0.002 (70Kg)(1000mg/Kg) = 70,000mg (70g) 2, ½ oz shots of vodka= ~28g EtOH 7 Lethal Nature and MSDS Sheets • Materials Safety Data Sheets - provide specific toxicological, chemical and physical data about a compound. – – – – – – Physical Properties and Names Chemical Reactivities Incompatibilities Safe Handling Toxicology (symptoms and means of exposure) Safety and First Aid 8 MSDS Sheets - Example NICOTINE (S)-3-(1-Methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)pyridine CAS # 54-11-5 3-(1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)pyridine RTECS # QS5250000 b-Pyridyl-a-N-methylpyrrolidine ICSC # 0519 1-Methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)pyrrolidine EC # 614-001-00-4 C10H14N2 Molecular mass: 162.2 TYPES OF HAZARD ACUTE HAZARDS/ SYMPTOMS FIRE Combustible. Gives off irritating NO open flames. or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. EXPLOSION EXPOSURE INHALATION SKIN PREVENTION FIRST AID/ FIRE FIGHTING Powder, alcohol-resistant foam, water spray, carbon dioxide. Above 95°C explosive vapor/air Above 95°C use a closed mixtures may be formed. system, ventilation. PREVENT GENERATION OF MISTS! AVOID EXPOSURE OF (PREGNANT) WOMEN! IN ALL CASES CONSULT A DOCTOR! Burning sensation. Nausea. Vomiting. Convulsions. Abdominal pain. Diarrhoea. Headache. Sweating. Weakness. Dizziness. Confusion. Ventilation, local exhaust, or breathing protection. Fresh air, rest. Refer for medical attention. MAY BE ABSORBED! Redness. Burning sensation Protective gloves. Protective clothing. Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap. Refer for medical attention. 9 Toxicity and Exposure Time • Acute Toxicity – Adverse effects within short time of toxin exposure • Chronic Toxicity – Condition caused by prolonged exposure to a toxin Poisons (and drugs) • Corrosive Poisons - Substances that actually destroy tissue outright • Metabolic Poisons - Affect biochemical mechanisms Corrosive Poisons • Substances that actually destroy tissue outright – Acids/Bases (Alkali) • Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4) • Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) • Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH; cleaners) – Death can result from a little as 1 oz. H2SO4 • Works by dehydrating tissues • Cells die fast because water is removed AND proteins are destroyed by acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Corrosive Poisons • Warning Signs: – Corrosive toxins interact with body sensory systems to alert of exposure: • Ammonia (above 0.01% in air) causes choking • Acids interact with nerves to send pain signals upon exposure – Some lack clues! • Hydrofluoric acid (very corrosive; used in electronics) destroys both tissue / bone but does not cause pain upon tissue exposure . Only sends pain when BONE is exposed. • Bases (NaOH) slippery Corrosive Poisons • Some are toxic because of reactions – Phosgene (mustard gas, and in plastics industry) - if inhaled it reacts with water in lungs to form HCl. • Causes Pulmonary edema (fluid in lungs) because it draws water from surrounding tissues - victim drowns. • Phosgene does not have good warning properties (smells like new-mown hay and lung reactions are slow. O + H2O(l) C Cl Cl 2HCl(aq) + CO 2(g) Metabolic Poisons • Affect Biochemical Mechanisms: – Carbon Monoxide (Gas) - colorless, odorless, toxic suicide or homocide. • Binds to iron in hemoglobin and only very slowly is released displacing oxygen - Carboxyhemoglobin is 140 time more stable than oxyhemoglobin • Breathing 0.1% CO in air for 4 hours converts 60% of hemoglobin to carboxyhemoglobin! • Not a cumulative poison (given time, the free hemoglobin is released) Hemoglobin Transport Fe site - point of attachment (Heme groups in orange) O O O H2O HEME HEME C CO HEME O2 Red Oxyhemoglobin Blue Red Carboxyhemoglobin Metabolic Poisons – Cyanide (suicide or homicide - Tylenol murders) • Common industrial agent (plastics formation, electroplating, metal-ore processing) • NaCN reacts with acids to form HCN (gas) - weak odor of almonds • Naturally occurs in seeds (protects seeds until they germinate). • Very fast working (seconds) • Causes asphyxiation – binds tightly with iron so that, even though lots of oxygen gets to cells, they can’t use it to support life. • Eventually, cyanide is removed by enzyme. • Administer large amounts of thiocyanate can be effective ANTIDOTE. Cyanide Poisoning Cyanide is commonly thought of as a gas, but you also can be poisoned by it if you ingest wild cherry syrup, prussic acid, bitter almond oil, or large amounts of apricot pits. Cherry seeds, peach and plum pits, corn, chickpeas, cashews, and some other fruits and vegetables contain cyanogenic (i.e., cyanide-forming) glycosides that release hydrogen cyanide when chewed or digested. However, cyanide poisoning from a food source is rare. Arsenic Poisoning • As commonly occurs in pesticides, shrimp, pressure treated wood (Paris green), old wallpaper (green color) • React with SH groups of enzymes - stopping their normal function • Accumulates in the body (not eliminated) • Used as a poison gas in WWI - led to search for antidote Mercury Poisoning • In Fluorescent lamps, dental amalgams, fungicides • Neuron toxin-many problems including: – Impaired vision, hearing, and speech – Brain damage • Interferes with enzymatic actions (seleno-enzymes which normally prevent oxidation damage) Mad Hatter’s Disease • History Lead Poisoning • Romans – Lead cooking vessels, cosmetics, Lead Plumbing (downfall of Rome - Pb in Emperor’s wine and water lead to mental illness) – See high Lead levels in bone evidence – “plumbing” from Latin word for Lead plumbum • Modern - Leaded Gas, Paint, water pipe joints – Plumbing - (joints) EPA allows max 15 ppb, many cities have 500 ppb. – Paint - PbO (white paint) - children ingest (now use TiO2 - nottoxic) • Pb displaces physiological metals in chemical reactions Types of Abused Drugs • Narcotics - relief from pain and bring sleep. – Narcotics are analgesic - relieve pain by depressing nervous system (opium, morphine, heroin, codeine, opiates - oxycontin, methadone). • Hallucinogens - alter normal thoughts, perceptions and moods (PCP, LSD, mescaline, MDMA, ecstasy). • Depressants - depress functions of central nervous system, cause calm and bring about sleep (alcohol, barbituates). Tranquilizers are depressants. • Stimulants - increase alertness and activity (cocaine, amphetamines). • Steroids - promote muscle growth (androgen, testosterone, anabolic steroids). 23 Narcotics • Oxycontin: – For Chronic Pain – One of most abused drugs in U.S – Names: Oxy, O.C., killer and hillbilly heroin – Highly addictive with physical dependence Narcotics Narcotics Unripe pod of Poppy Plant Opium is a gummy, milky juice Morphine Codeine Heroin (synthetic) Pain Relief “High”-Happiness (3-4hrs) Drowsiness Bitter Taste IV Use 35% Pure! Additives: Street Names: H, Horse, Scag, Smack, Stuff Field test uses reagent called marquis for a purple color Quinine, starch, lactose, Novocain Heroin Symptoms • • • • • Euphoria Drowsiness Contracted pupils Needle marks Blood stains Other Opiates • Methadone – Related to heroine – Eliminates the “high” if taking heroine – Helps break heroine habit Hallucinogens • Hallucinogens - alter normal thoughts, perceptions and moods (PCP, LSD, mescaline, MDMA, ecstasy). • Marijuana most common (derived from Cannabis or “hemp” plant). – Derive resin from plant secretions that is extracted with organic solvents. – In use for 1000’s of years. – Brought to the US ca. 1920. Marijuana Pot, Grass, Wacky Baccy, Hash, Ganja,, Hash Oil, weed, Tree, greens, Wild weed 5-15 ft Odd leaf number, serrated edge Crush leaves with flower, stem and seed Plant Resin=Hashish THC Active Ingrdient Can tentatively be identified by the DuquenoisLevine color test Marijuana Symptoms • • • • • • Lack of coordination-Danger to Drive! Reduced Reaction Time-Danger to Drive! Red eye Dilated pupils Increased heart rate Irrelevant giggling Spice-Synthetic Marijuana • a.k.a: “K2, Fake weed, Yucatan Fire, Skunk, Moon Rocks” • 5 active chemicals-cannabinoids • Illegal, Controlled Drugs, Schedule 1 DEA • Big use by high school age • Symptoms: rapid heart rate, vomiting, agitation, confusion, and hallucinations-psychotic reactions • Regular users may experience withdrawal and addiction symptoms. Spice Problem • Negative Traditional Drug Test Results • But…Can detect metabolites of JWH-018 in urine LSD- Street Names: Acid, Boomers, Yellow Sunshines, Cid, Doses, and Trips •Derived from Ergot Fungus (on grasses/grains) •First described in 1943 after “accidental” lab ingestion (potent - 25mg for long lasting effects!) •25 microgram causes hallucinations for 12hrs •Mood swings •Anxiety •tension lysergic acid diethylamide Purple-Blue Van Urk Presumptive Test Other Hallucinogens • Phencyclidine (PCP)- (phencyclidine) Originally an IV anesthetic but hallucinations created a problem Street Names: Angel Dust, Crystal, Hog, Supergrass, Killer Joints, Ozone, Wack, Embalming Fluid, and Rocket Fuel. • Mescaline- ancient American Indian drug derived from a cactus • Psilocybin- Street Name: Shrooms, Mushies, and Mexican Magic Mushrooms • STP- synthetic from the 1960s Other Hallucinogens • MDMA (Ecstasy, E, Adam, XTC, Fantasy, Date-Rape Drug) – – – – – – – – – – – – Get Abundant Energy Increased Color perception Dehydration-Drink a lot Enhanced empathy Brain cell damage Anxiety Panic Insomnia Hallucinations Psychosis Memory loss Hypertension Depressants • Depressants - depress functions of central nervous system, cause calm and bring about sleep (alcohol, barbituates). Tranquilizers are depressants. – Downers - relax, create feeling of well-being, produce sleep. – Act on central nervous system. – Usually taken orally. – Also includes tranquilizers (e.g., librium and Valium) and “glue sniffing” (toluene, gasoline, freon, etc.) - all effect central nervous system. Major problems chemical eposures cause permanent liver, kidney, heart and brain damage. An advanced lesson on alcohol! Alcohol • No. 1 abused drug with more related deaths per year than any other. Alcohol Specifics (Route) • Alcohol in stomach (20% absorbed) and intestine • Absorbed within minutes into bloodstream – Timing affected by: – Time taken to consume drink – Alcohol content – Amount consumed – Stomach contents Alcohol Specifics (Route) • Alcohol distributed to watery parts of body via blood • Liver, 1st stop- Begin detoxification (0.015% w/v per hour • Heart • Lungs-Alcohol vapors out with breath – Using Henry’s Law can relate amount of alcohol in breath to amount in blood • Brain-impair neuron transmission Breath Test Instruments • Breathalyzer – Blow 52.5ml of alveolar air into machine – Added to potassium dichromate, silver nitrate, sulfuric acid and water – Alcohol converts dichromate to acetic acid – Dichromate amount reduced-measured via a spectrophotometer in machine (must be calibrated! and chemicals pure) Ethanol • Depressant, not a stimulant. • Continued use may lead to physical dependency. • Even low doses can cause impairment (with the feeling of no effect). Alcohol • • • • • • • • Sedative Vasodilator=Blood increased to extremities Diuretic Respiratory Depression Gastric irritation Slur Speech Acute Toxicity=coma and death Chronic Toxicity=liver damage Other Depressants • Barbiturates (“Downers, Yellow Jackets, Blue Devils, Reds, Barbs”) – Downers- Suppress Central Nervous System – Derived from Barbituric Acid – Sedatives taken orally – Physically Addictive – Ex. Amobarbital, Secobarbital, Phenobarbital etc. Presumptive Test • DILLE-KOPPANYI • Used to test for barbiturates • Turns violet-blue Other Depressants • Methaqualone (Quaaludes) – Sedative – Muscle relaxant • Tranquilizers – Relaxed but not impaired or sleepy – Ex. Miltown, Librium, Thorazine and Valium – Physically and mentally addictive Ketamine =Horse Tranquilizer (Special K, Kit Kat) Symptoms of Tranquilizer Abuse • • • • • Slurred speech Staggered Gait Poor coordination Poor judgment Appears drunk but no alcohol smell Other Depressants • Glue Sniffing, Sniff aerosol propellants and solvents – Suppress Central Nervous System – Euphoria – Slurred speech – Impaired judgment – Double vision – Risk liver, heart, brain damage and death Glue Sniffer Meeting Club Drugs/Date Rape Drugs Date Rape Drugs Flunitrazepam (Rohypnol) Ketamine MDMA (Ecstacy) GHB Date Rape Drugs Rohypnol, Ketamine, GHB, Ecstasy • GHB (depressant) effects can be felt within 15 minutes after ingestion. Mixed with alcohol GHB can cause the central nervous system to shut down, lead to loss of consciousness, and possibly result in a coma or death. • Rohypnol (depressant) effects begin within 30 minutes, peak within 2 hours, and may persist for up to 8 hours or more, depending upon the dosage (Street Names: Roofies, Rophies, Roche, Forget-me Pill, Circles, Mexican Valium, Rib, Roach-2, Roopies, Rope, Ropies, Ruffies, and Roaches) • Ketamine (hallucinogen) causes the person to feel as if their mind is “separated” from the body. The drug causes a combination of amnesia and hallucinations. Also, it stops the feeling of pain and lowers the heart rate leading to oxygen starvation to the brain and muscles. Vet Medicine. • Ecstasy (hallucinogen)causes psychological difficulties, including confusion, depression, sleep problems, drug craving, severe anxiety, and paranoia-during and sometimes weeks after taking Ecstasy. Date Rape Drugs: What You Can Do to Protect Yourself? • • • • • • • • Don't accept drinks that you did not open yourself. Don't exchange or share drinks with anyone. Don't drink anything out of a punch bowl. Monitor the behavior of friends who seem more intoxicated than the amount of alcohol would warrant. Never consume a drink that you have not mixed yourself, or have not watched someone else prepare. Never accept a drink from someone you don't know and trust. At parties or clubs with friends never leave your drink unattended. Be aware of your surroundings - Listen for the street names of the drugs - Trust you instincts Date Rape Drug Offenders Stimulants • Stimulants - increase alertness and activity (cocaine, amphetamines). – Amphetamines - synthetic drugs that stimulate the central nervous system. – Once stimulant wears off then severe depression usually sets in - requiring more stimulant (speed binge). – Dilated pupils, insomnia, panic, confusion, increased heart rate, hypertension • Stimulants Amphetamines (uppers or speed): – Synthetic – Alert, happy, hyperactive then fatigued (excessive sleep) and depressed – Loss of appetite – IV use – Psychologically addictive Amphetamines Methamphetamines ($450-$2,000/oz) “Ice” Bath Salts • One or more synthetic chemicals related to cathinone, an amphetamine-like stimulant • Effects: euphoria and increased sociability and sex drive, but some users experience paranoia, agitation, and hallucinatory delirium; some even display psychotic and violent behavior, and deaths have been reported in several instances. • As soon as an ingredient is made illegal, chemists alter chemical’s structure. Other Stimulants • “Ice” – High, – Stay up for days then depressed, tired and hungry – Smoked – VERY POTENT – Violent, destructive, paranoid schizophrenic-like ($3,600-$7,000/oz) Before ICE After ICE Stimulants • Cocaine – Interferes with dopamine, a chemical messenger associated with pleasure; continuous stimulation of “receiving” neurons, leads to euphoria – The powdered, hydrochloride salt form of cocaine can be snorted or dissolved in water and injected. – Crack=This form of cocaine comes in a rock crystal that can be heated and its vapors smoked. The term “crack” refers to the crackling sound heard when it is heated. – acute cardiovascular or cerebrovascular emergencies, such as a heart attack or stroke. – constricted blood vessels, dilated pupils, and increased temperature, heart rate, nasal problems, head ache, fatigue and high blood pressure. Ground to powder and chemicals added Coca Plant 10 pounds of leaves= 1 ounce of cocaine Crack Cocaine Paraphenalia • http://channel.nationalgeographic.com/channel/d rugs-inc/videos/cocaine/ Steroids • Anabolic Steroids (Roids) Steroids • • • • • • • • • • • Synthetic (Like Testosterone) Enhanced Muscle Growth Risk Liver Damage Reduced sex drive (can cause impotence) Reduce sperm production (can be permanent) Severe Acne Premature baldness Masculinizing in females and infertility (i.e. pronounced jaw) Feminine characteristics in men (grow breasts) Teenage suspension of bone growth Mood swings and aggressive behavior (increases with cycling) Workload of Forensic Toxicologists Dead Person: • Murder by a poison or accidental exposure? • Overdose? • MVA-drug related? Workload of Forensic Toxicologists • Living Person: – Drink/drug driving – Drug Facilitated Sexual Assault (DFSA) – Professional/amateur athlete – Workplace drug testing Even more work for toxicologists.. • • • • • Air (ex. Asbestos, carbon monoxide) Water (ex. coal and fracking industry slurries) Soil (ex. radiation from nuclear meltdowns) Foods (ex. food poisoning) Cosmetics Where to look in body for a toxin? Specimen Collection Each has it’s own set of problems and advantages Fluids: Organs: Blood Skin Urine Lungs Vitreous Humor Hair and Fingernails Oral Fluid Liver Semen Kidney Stomach Contents Bone Bile Other (heart, brain, etc.) Vitreous Humor - clear, gel-like mass that fills the space between the lens and the retina. 81 Additional Sources Vomit Earwax Semen Feces Sweat Meconium (fetal poop) Amniotic Fluid Umbilical Cord Blood Milk 82 Issues with sampling.. • Blood Samples: 1. If taken near a solid organ after death may get very high (and inaccurate) drug concentrations 2. Toxins will diffuse out of organs after death 3. Blood should therefore be taken from femoral artery which is far from organs Issues with sampling.. • Liver - concentrates and stores drugs for long times. – good for detection but problematic for concentrations • Urine - tends to be concentrated form of compounds. – Can’t be sure of body concentration since it is unknown how long it has been accumulating in the body. Sampling • Bile - Useful for detection but not concentration. • Kidney - Similar to Bile. • Vitreous Humor - Correlates well with femoral blood for most compounds. • Hair and Fingernails - Good for some compounds with timelines possible. • Oral Fluids - Can be easily disguised. Procedure still in development . 85 Drug Metabolism Issues Analyte vs. Metabolite • Analyte= Compound analyzing for • Metabolite=body can change chemical nature of drug (Heroin converted to Morphine) • • • • • • • Drug ID Immunoassay TLC GC HPLC GC/MS***** LC/MS (AA; ICP-MS) Separation, detection, identification and measurement of drugs in biological specimens