* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10R - donnellymath
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Conic section wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
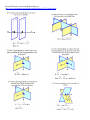
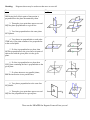
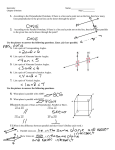
Name _______________________________________________ Date ________________________________ 10R Points, Lines and Planes WS TERM DIAGRAM Period ______________________________ DEFINITION Point Indicates a location. Named w/ capital letter Line A set of continuous points the extends endlessly in both directions. Named with a lower case letter or by two points. Plane A flat surface with no thickness. Extends indefinitely in all directions. Formed by three noncollinear points. Could also be named with a capital letter. Line Segment Part of a line consisting of two points. Named with its two endpoints. Ray Part of a line consisting of an endpoint and the set of points on other side. Named by endpoint then another point on line. Opposite Ray Rays that have the same endpoint and lie on the same line. Collinear Points Points that are on the same line. Coplanar Points Points that are on the same plane. Angle Union of two rays that have the same endpoint (vertex). Named with three points, the vertex, or label interior with a number. Parallel Lines Lines that do not intersect and have equal slopes Skew Lines Lines that are in different planes that do not intersect, but are NOT parallel. Perpendicular Lines Lines that intersect forming right angles and have negative reciprocals for slopes Linear Pair When the exterior sides of adjacent angles lie on opposite rays. Midpoint Divides a segment into two congruent segments. Bisector (Angles/Segments) Divides an angle or segment into two congruent angles or segments. Segment/Angle Addition Postulate If point X is between points A and B, then AX+XB = AB If OX is between the sides of <AOB, then m<AOX+<XOB = m<AOB Congruent -Shapes: same size and shape -Segments: same length -Angle: same measure Dimension -A figure with no dimension cannot be measured (no length) -A one-dimensional figure has a length. -A two-dimensional figure has a length and a width -A three-dimensional figure has a length, width, and height Intersection of two lines 1 point Intersection of two planes 1 line Intersection of line and plane 1 point Pictures/Theorems come from RegentsPrep.org (http://www.regentsprep.org/Regents/math/geometry/GG1/Lplanes.htm) Matching: Diagrams shown may be used more than once or not at all. Fact: Diagram: _____1. A line perpendicular to each of two intersecting lines at their point of intersection is perpendicular to the plane determined by them. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. _____2. Through a given point there passes one and only one plane perpendicular to a given line. _____3. Two lines perpendicular to the same plane are coplanar. _____4. Two planes are perpendicular to each other if and only if one plane contains a line perpendicular to the second plane. _____5. If a line is perpendicular to a plane, then any line perpendicular to the given line at its point of intersection with the given plane is in the given plane. _____6. If a line is perpendicular to a plane then every plane containing the line is perpendicular to the given plane. _____7. If a plane intersects two parallel planes, then the intersection is two parallel lines. _____8. Two planes perpendicular to the same line are parallel. _____9. Through a given point there passes one and only one line perpendicular to a given plane. These are the 9 FACTS the Regents Exam will test you on!