* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final exam
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Juno (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Tunguska event wikipedia , lookup
Near-Earth object wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Philae (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Comet Shoemaker–Levy 9 wikipedia , lookup
Stardust (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Halley's Comet wikipedia , lookup
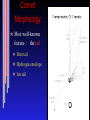
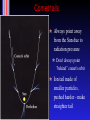
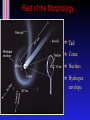
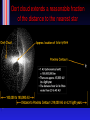
Final exam In SRC C, noon, Mon. Dec 11 2.5 hours in length, don't be late! Same rules as midterm Formula sheet and data given You need a scientific calculator Have 2 pieces of photo identification If you have 3 or more midterms in 24 hours, you must inform all your instructors by Nov 29th (Wednesday!) Comets! Omens of disaster or pretty to look at? Probes of planet formation in the outer S.S. Omens of disaster Battle of Hastings, 1066, in the Bayou tapestry Actually Halley's comet Became first predicted comet in 1705 Comets vs Asteroids Both are minor planets Can think of them as `leftover planetesimals' Asteroids Circular orbits, between 2 4 AU Rocky planetesimals Comets Big, eccentric orbits : some get inside Earth's orbit (with aphelion at or outside Jupiter, some got out as far as 50,000 AU "Dirty snowballs" mostly ice and some rock Orbits Big elliptical orbits (unlike asteroids) Composition "Dirty snowball" Mostly ice (water ice, carbon dioxide ice, methane ice, ammonia ice) Some rocky materials mixed in See http://www.solarviews.com/eng/edu/comets.htm for instructions on how to create a comet nucleus for yourself! Ice => condensed in low temperature regions Leftover planetesimals which formed outside Jupiter's orbit Comet Morphology Most wellknown feature : the tail Gas and dust evaporated from comet nucleus very diffuse Dust tail (white) Ion tail (blue) Comet Morphology Most wellknown feature : the tail Dust tail Hydrogen envelope Ion tail Comet tails Always point away from the Sun due to radiation pressure Don't always point "behind" comet's orbit Ion tail made of smaller particles, pushed harder make straighter tail Comet pills Many strange gases detected spectroscopically including cyanide 1910 : doctors sold "comet pills" to ward off ill effects of Earth passing through tail of Comet Halley Actually tails very diffuse but small particles are kicked off surface of comet and left behind its path When Earth passes through these get meteor showers Meteor showers appear to come from a 'radiant' Meteors appear to come from a single point This is an 'illusion'; it just appears to do so because the meteors are coming from a single direction in space (see text) The annual Leonid meteor shower ❑ ❑ ❑ ❑ Leonid shower has on occasion HUGE output (>500/minute!) Woodcut (left): shows spectacular 1833 display over U.S.A. Peak: midNovember each year (search on web). 2005 was poor (full Moon). Look easterly. Need dark sky, dress warm! Another Leonid storm observation ❑ ❑ Woodcut from 1833 Too bad storms are rare. Rest of the Morphology Tail Coma Nucleus Hydrogen envelope Coma Shell of evaporating gas and dust ~106 km across A closer look... (nucleus) Closest look : Giotto (ESA) flew within 600 km of Comet Halley nucleus (1986) ~10 km across Future missions Stardust, Deep Impact, Rosetta will fly by comets and even capture material from surface. Or hit it! (July 4/2005) Comets populations Split into different groups. The ACTIVE comets come close to Earth. Jupiter Family comets (JFCs) Orbit the Sun in less than 20 years; tied to Jupiter That means (P2=a3 ! ) that a<7.3 AU Halleytype comets Orbit with periods between 20 and 200 years Includes Halley (P=76 years), with retrograde orbit Long period comets (LPCs) Orbits greater than 200 years can travel 105 AU from the Sun Orbits Different groups have different orbits JFC's : small inclinations and small periods LPC's : random inclinations and long periods This means they came from different sources! JFC's from the Kuiper Belt Region from 301000 AU flattened disk provides low inclination JFCs LPC's from Oort Cloud Extends out from 1000 AU to 50,000 AU Where are these structures? Oort cloud extends a reasonable fraction of the distance to the nearest star Life of a comet After the formation of the Solar system : live in Kuiper Belt or Oort Cloud for > 4 Gyr Perturbed from peaceful orbit into elliptical orbit Many are ejected from the Solar System, but... ...a few enter the inner solar system and become "active comets" How do they die? Can't keep evaporating ice forever! Some get ices evaporated away and become 'extinct' Most eventually ejected by Jupiter But, the solar system is full of things to run into ... ShoemakerLevy 9 Illustrates both tides and fragmentation due to fragility of the cometary nucleus