* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
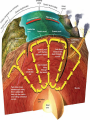
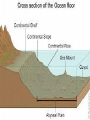
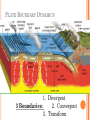
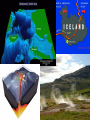
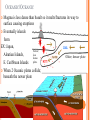
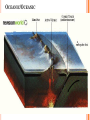
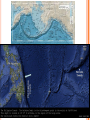
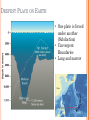
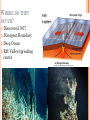
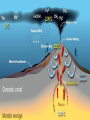
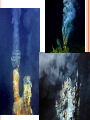
PLATE TECTONICS PRODUCING OCEAN PROCESSES • Warm Water is LESS dense, so it RISES. • Colder Water is MORE dense, so it SINKS. Convection- transfer of heat Earth and Convection ABYSSAL PLAINS Flat areas of ocean floor Between ocean trenches and continental rises Formed by Mantle Convection Uneven rock surface becomes covered with fine-grained sediment Depth between 3000 & 6000 m below sea level PLATE BOUNDARY DYNAMICS 1. Divergent 3 Boundaries: 2. Convergent 3. Transform EFFECTS OF DIVERGENT BOUNDARY: Mid-Oceanic Ridges Underwater Mountain Ridges Formed by upward movement & spreading of underlying magma Sea Floor Spreading This is an eruptive fissure that was found several kilometers from the mid-ocean ridge. DIVERGENT BOUNDARY: ICELAND (MID-ATLANTIC RIDGE) Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Iceland ICELAND PLATE BOUNDARY The East Africa Rift Valley is in a very early stage of development; above ocean, has created lakes The Red Sea is an example of a more completely developed rift. The plates have fully separated and the central rift valley has dropped below sea level EVOLUTION OF DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES EFFECTS OF CONVERGENT Zone of progressively deeper earthquakes Chain of Volcanoes Tsunamis Ocean Trench (OCEAN-CONT) OCEANIC/OCEANIC Magma is less dense than basalt so it melts/fractures its way to surface causing eruptions Eventually islands form EX: Japan, Newer; less Aleutian Islands, Older; denser plate dense plate E. Caribbean Islands When 2 Oceanic plates collide; ______________________________ beneath the newer plate OCEANIC/OCEANIC EFFECTS Cleveland Volcano, Aleutian Islan DEEPEST PLACE ON EARTH • One plate is forced under another (Subduction) • Convergent Boundaries • Long and narrow Left: Trieste: bathyscaphe January, 1960 Right: James Cameron Green Machine March, 2012 DIVE TO CHALLENGER DEEP IN THE MARIANA TRENCH http://youtu.be/Y2tm4 0uMhDI EARTHQUAKE Sudden release of energy in Earth’s crust, creating seismic waves Arises from Convergent , specifically Transform Boundaries If two plates are unable to slip past each other they LOCK, strain (energy) builds up When the plates start moving again, stored energy gets released TRANSFORM BOUNDARY Plates slide past one another EX: 1. San Andreas Fault 2. Alpine Fault in New Zealand 3. Along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge TSUNAMI Long wavelength wave produced by the sudden movement of a very large volume of water Convergent plate boundary, abrupt slippage of one plate against another results in an underwater earthquake and then a tsunami Deep Water= wave (small) travels quickly Shallow Water (coastal waters)= slows down and forms large, destructive waves Japan Tsunami 2011 VOLCANO Opening in Earth’s crust Hot gases and molten rock to escape Thinning of the crust= Divergent Mainly under the sea New sea floor Mid-ocean ridges If these rise above sea level, volcanic islands may be formed (ICELAND) Also form when plates move towards each other=Convergent HYDROTHERMAL VENTS WHERE DO THEY OCCUR? Discovered 1977 Divergent Boundary Deep Ocean Rift Valley/spreading center HOW DOES IT WORK? HOW DOES IT WORK? 1. 2. 3. 4. Cold seawater (2OC) seeps into cracks and fissures along boundaries Seawater continues to seep deeper into crust. Water heats by underlying magma under the ocean floor Hot Water is forced back up to ocean floor, carrying dissolved minerals • All oxygen is removed Water becomes acidic Water picks up dissolved metals (Fe, Cu, Zn) & Hydrogen sulfide HYDROTHERMAL VENTS FORM: 1. 2. Hot hydrothermal fluid (less dense) (water), carrying dissolved metals & hydrogen sulfide. Hydrothermal liquids exit vent/chimney & mix w/ cold seawater. a) 3. 4. Metals carried in fluid combine w/ sulphur to form black minerals (metal sulfides; AKA “black smokers”) As it cools, the dissolved minerals starts to precipitate out Precipitates form the chimney HYDROTHERMAL VENTS Found at depths of over 2000 m Pressure is HIGH (over 200 atmospheres High Pressure= super heated water= reach temperatures higher than 100 degrees Celsius Discovering Hydrothermal Vents