* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pseudotuberculosis
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
1793 Philadelphia yellow fever epidemic wikipedia , lookup
Sumy State University
Medical Institute
Department of Pediatric,
Corse of Children Infectious Diseases
Differential diagnosis
infectious diseases
with exanthemas
Part 2
Lecturer
Bynda Tetiana P.
Exanthema
Vesicular
Maculapapular
Hemorrhagic
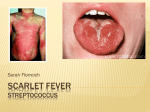
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is an acute
infectious disease,
characterized by
lesions of oropharynx
with submaxillary
lymphadenitis, fever,
toxemia, punctiform
rash and then
desquamation.
Scarlet fever
Due nonspecific prevention, antibacterial
therapy of scarlet fever during last 50-60
years – the number of patient with hard forms
of this disease had decreased. But total
morbidity is still high. Number of patients with
light scarlet fever, repeated cases of it has
increased. That is why it is hard to put the
diagnose in time. This lead to widely
spreading of streptococcal infection. That’s
why it is necessary for future doctors to know
peculiarities of clinical features, treatment,
and prevention of scarlet fever.
Epidemiology
Susceptibility to scarlet fever
depends on absence of antitoxic
immunity against erythrogenous
exotoxin of hemolytic streptococcus.
Susceptible organism – children 310 years old.
The contagious index is about 40 %.
Incubation period
The incubation period for scarlet
fever is 1 to 7 days.
The initial period - from of the
appearance of the first symptoms
to the appearance of the rash.
The disease is accompanied in abruptly
by fever, vomiting, sore throat and
constitutional symptoms such as
headache, chills and malaise.
Within 12 to 36 hours after the onset, the
typical rash appears.
The rash period
The significant findings are
Fever
Tonsillitis
Enanthem
Exanthema
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is a typical sign of scarlet
fever.
Tonsillitis may be:
catarrhal,
follicular,
lacunar or
necrotic,
which occurs on the 2nd - 4th day of the
disease.
Local hyperemia of soft palate - "flaming
fauces".
The upper border of hyperemia is on the
anterior palatal arches and on the base of the
uvula (delimited hyperemia)
The palate and uvula may be edematous, reddened, and
covered with petechiae. Note inflammation of the
oropharynx with petechiae on the soft palate, small
red spots caused by group A streptococcal pharyngitis.
Necrosis may be superficial in the form
of patches - Follicular tonsillitis
Depending on severity of the disease
necrosis may be deep, continious, locating
on the tonsils - Lacunar tonsillitis
Necrosis has a dirty-grey or
greenish color
Lacunar tonsillitis disappears
slowly in 7-10 days.
Catarrhal and folicular tonsillitis
disappears in 4-5 days.
Tonsillitis is
accompanied by
lymphadenitis.
Regional lymph
nodes become
enlarged, dense,
tender.
http://www.omcso.ru/kak-lechit-limfadenitu-detey/
If adipose tissue,
surrounding the
lymph nodes is
affected,
periadenitis,
adenophlegmon
will occur.
Dryness of the skin.
White dermographism.
The rash usually appears
within 12 hours after
onset of the illness;
occasionally it may be
delayed for 2 days.
The rash is an
erythematous punctiform
eruption that blanches on
pressure.
Elements of rash are
dusky red, minute
roseolas (may be tiny
papules) of 1–2 mm
diameter, closely
situated with each
other.
The eruption have a
rough texture.
The eruption
Papules are
usually absent on
the face, palms,
and soles, but the
face
characteristically
shows flushing
with circumoral
pallor (Filatov’s
sign).
On the body,
the rashes are
intensified in skin
folds and at sites
of pressure.
In the antecubital and axillary fosses,
linear petechiae are seen with
accentuation of the erythema
(Pastia’s lines).
The exanthema usually lasts 4 to 5 days
and then begins to desquamate, first on
the face last on the palms and soles.
Desquamation is one of the most characteristic
features of scarlet fever
Desquamation begins on the face in fine flakes toward the
end of the 1st wk. and proceeds over the trunk and finally
to the hands and feet. The duration and extent of
desquamation vary with the intensity of the rash; it may
continue for as long as 6 wk.
Tongue is white coated, from 2 to 45 days, bright-raspberry colour and
enlarged papillae of the tongue are
observed ("raspberry tongue",
"papillae tongue").
Blood test
There is leukocytosis,
neutrophilia, increased ESR.
Pseudotuberculosis
is an acute infectious disease
of the zoonotic group,
characterized by
fever, toxemia,
scarlet fever-like rash,
lesions of other organs and
systems.
Pseudotuberculosis
Incubation period is 3-18 days.
Beginning is acute with high
temperature, intoxication.
Polymorphism of complaints:
malaise, fatigue, headache, sleepless,
anorexia, arthralgias, muscle pain,
sore throat, nausea, abdominal pain,
dyspepsia.
Rush
Rash localization is like the one in
scarlet fever (on the lateral parts of the
trunk, the internal and the back parts
of crura and thighs, on the skin of the
lower abdomen, in skin folds).
Besides rash may appear on the
external surfaces of arms and
forearms, on the knee and radiocarpal
joints.
Pseudotuberculosis
Rush:
maculopapulous (like in scarlet
fever), may be erythematous;
the eruption is characterized by
dusky red, tiny papules.
Pseudotuberculosis
The rush in present on face, intensified
periorbitally (“glasses” symptom),
on the neck, hyperemia and edema of
skin on the face (“hood” symptom);
hyperemia and edema of skin
on hands (“gloves” symptom) and
feet (“socks” symptom).
http://goldstarinfo.ru/2012/11/28/psevdotuberkulez-u-detej-simptomy/
Pseudotuberculosis
on the body the rush is intensified in
skin folds, at the sites of pressure,
round the joints.
The exanthema usually lasts 4 to 5
days and then begins to
desquamate, first on the face and
last on the palms and soles.
Red dermographysm.
Pseudotuberculosis
Catharral syndrome (pharyngeal and
tonsilar erythema without the exudate,
erythema of the soft palate, conjunctivitis,
corryza.
“Strawberry” tongue also simulates the
scarlet fever.
Abdominal syndrome; tenderness during
the palpation of abdomen, may be acute
appendicitis.
Dyspepsia: nausea, vomiting, liquid feces.
Pseudotuberculosis
Hepatomegaly, rare –
splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy.
Arthritis of knees, elbows, foot and
hand small joints or arthralgia.
Hepatitis with or without the jaundice.
Toxic myocarditis.
Toxic nephritis, pyelonephritis.
Bronchitis or pneumonia may also
develop.