* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint: FDR`s Presidency
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
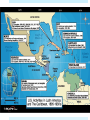
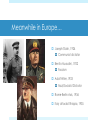
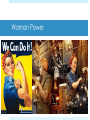
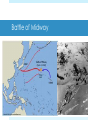
Presidency of FDR http://historymatters.gmu.edu/d/5057/ “The only thing we have to fear, is fear itself.” (1932) “I pledge a New Deal for the American people…” March 6 – 10 National Banking Holiday March 9 – June 16 Hundred Days Relief Recovery Reform Roosevelt Tackles Money and Banking Emergency Banking Relief Act, 1933 Glass-Steagall Banking Reform Act Set up the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) Surrender gold to Treasury Creating Jobs for the Jobless Civilian Conservation Corps Federal Emergency Relief Act Federal Emergency Relief Administration Agricultural Adjustment Act Home Owners’ Loan Corporation Civil Works Administration Critics of the New Deal Senator Huey Long (LA) “Share Our Wealth” Assassinated Francis E. Townsend Works Progress Administration Buildings, bridges, roads NRA and the Chicken case National Industrial Recovery Act Allowed industries to write “codes of fair competition” Under President’s control Schechter v. United States NIRA unconstitutional Upset separation of powers Battling the Bankers Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) “watch dog” on Americas bank and trading markets The TVA Tennessee Valley Authority $13 billion investment Public utility – hydroelectric power 1933 – Hundred Days “Creeping socialism in concrete” Social Security Social Security Act, 1935 Federal-state unemployment insurance Security for old age, blind, physically handicapped, delinquent children and other dependents $10 - $85/month Unskilled “New Deal” Wagner, or National Labor Relations, Act, 1935 National Labors Board created for self-organization and collective bargaining John L. Lewis creates Committee for Industrial Organization (CIO) Appealed to those rejected by the American Federation of Labor Fair Labor Standards Act Wages and Hours Bill Court Packing Scheme Roosevelt's purpose was to obtain favorable rulings regarding New Deal legislation that had been previously ruled unconstitutional Called to name 6 new justices 1 new Justice for each current justice over 70 REJECTED – MUCH criticism The Twilight of the New Deal Unemployment 25% down to 15% by 1936 “Roosevelt Recession” 1937 Hatch Act, 1939 Barred fed. Officals from active political campaigning; using gov’t money for political campaign illegal New Deal or Raw Deal “Alphabet Soup” “Bureaucratic meddling” National Debt: 19 Billion, 1932 42 Billion, 1939 Business believed infringed upon class structure – creeping socialism “administered aspirin, sedatives and Band-Aids Franklin D. Roosevelt and the Shadows of War 1933 - 1941 The London Economic Conference Summer, 1933 International conference to attack economic depression FDR promised delegation - never agreed to anything International community disheartened by US isolationist choice International Recognition Philippines Tydings-McDuffie Act, 1934 Independence granted July 4, 1946 Soviet Union US officially recognizes in 1933 A lot of protest Good Neighbor Policy Isolationism = giving up badge as world police Couldn’t afford military presence in Latin America Renounced Roosevelt Corollary to Monroe Doctrine Removed troops from Haiti and Nicaragua Annulled Platt Amendment Reciprocal Trade Agreement Secretary of State Hull Recriprocal Trade Agreement, 1934 Negotiation of tariff agreements Bilateral tariff reductions Resulted in a reduction of duties Avg. of 46 % in 1934 to 12% by 1962 Meanwhile in Europe… Joseph Stalin, 1924 Communist dictator Benito Mussolini, 1922 Fascism Adolf Hitler, 1933 Nazi/Socialist Dictator Rome-Berlin Axis, 1936 Italy attacks Ethiopia, 1935 Legislates “Neutrality” Neutrality Acts, 1935 Embargo on arms sales to all countries involved in war Germany Reoccupies Rhineland Ignored Spanish Civil War Neutrality Act, 1936 Added “civil strife” to ‘35s Neutrality Act Hitler Annexes Austria Hitler Invades Czechoslovokia Munich Conference – US ignores Hitler Threatens Poland $$$ to military Hitler invades Poland Britain and France declare War Neutrality Act, 1937 – “Cash and carry” Start of the “Blitz” in Battle of Britain Lend-Lease Act Hitler Invades Yugoslavia and Greece US sends aid to Allies US expands “escort” zone in Atlantic Hitler invades Russia Meanwhile, Japan… Invades Manchuria US ignores Panay incident US demands indemnity Japan builds up Navy ignoring Washington Conference US does nothing Japanese Offensive in S. China US sends $25 million to Chang Kaishek Occupies China Nothing because “Open Door” Policy Japan occupies Indo-China US Freezes Japanese assets in US (oil) Japanese-Sino War US embargoes strategic Material Japanese Attack Pearl Harbor Videos of Pearl Harbor America: The Story of Us – “WWII” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CuU21Z4PEfM History Channel: WWII in HD https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZJZLc5_l-_Q “You’re a sap, Mr. Jap” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sOmkvEMLIT0 America In WWII America at War ABC-1 Agreement Goal – “Germany First” Bigger Threat Take Hitler out then move to Japan US Treatment of Japanese Executive Order 9066 Over 100,000 Japanese-Americans were placed in concentration camps Washington believed they may act on the side of Japan and cripple the US Building the War Machine American factories produced an enormous amount of weaponry, such as guns and planes The War Production Board (WPB) – in charge of production War Efforts WPB halted production of passenger cars, rationed gasoline, and set a national speed limit War Labor Board – placed ceilings on wage increases Smith-Connally Anti-Strike Act – authorized government to take over businesses that went on strike. (1943) ex. coal mines, railroads, etc. Manpower and Womanpower The draft left the nation’s farms and factories shorthanded. 1942 – agreement made with Mexico to bring in braceros to work in fruit and grain crops in the West Manpower and Womanpower US Armed Services – enlisted 216,000 women in WWII. Many women took jobs outside the home in the war industry Woman Power Population 1.6 million blacks left for jobs in the North and West – Great Migration South – received most of the defense contracts in order to fix economic crisis in the South beginnings of the Sunbelt 25,000 Native Americans served in US Armed Forces Comanche in Europe and Navajo in Pacific became “code talkers” The Home Front Americans at home suffered little from the war The national debt grew from $41 billion in 1941 to $259 billion by 1945 WWII Japan attacked Guam, Wake Island, and the Philippines Gen. Douglas Macarthur led American forces at the Philippines April 9, 1942 – US had to retreat at Bataan Bataan Death March Japan and Midway May 1942 – Battle of the Coral Sea – Americans win first battle that was based on an aircraft carrier June 3-6, 1942 – Battle of Midway – Japanese retreated after losing four carriers Turning point of war in the Pacific Battle of Coral Sea Battle of Midway Toward Tokyo August 1942 - American forces gained foothold on Guadalcanal Island and the Solomon Islands in an attempt to protect the supply-lines from America to Australia through the Southwest Pacific. US Navy leapfrogged islands controlled by Japan on its way to Tokyo – “Island Hopping” Major islands of the Marianas fell to U.S. attackers in July and August 1944 From the Marianas, US B-29 bombers could reach Japan The Halting of Hitler Hitler entered the war with a superb group of U-boats Oct. 1942 – US and allied forces win at El Alamein in North Africa Sept. 1942 – Soviets drive Germans out after attack on Stalingrad North Africa To Rome Nov. 1942 – Dwight Eisenhower led troops against Axis troops in North Africa The German-Italy army was trapped in Tunisia in May 1943. Allied forces captured Sicily in August 1943 North Africa To Rome September 1943, Italy surrendered unconditionally and Mussolini was overthrown. Nazis attempted to hold on to Italy. Rome was taken on June 4, 1944 D-Day – June 6, 1944 Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin met at Tehran, Iran from Nov. 28-Dec. 1, 1943 US Gen. Eisenhower given command French Normandy was chosen as place to invade France Paris was liberated August 25, 1944 FDR’s Fourth Term Election of 1944 FDR (D) Thomas Dewey (R) FDR won by a landslide because Americans did not want a new president in the middle of a war The Last Days of Hitler Battle of the Bulge – Hitler’s last attempt at keeping war hopes alive Dec. 15, 1944 –US forces stood firm and won April 1945 – Ike’s troops reach the Elbe River, finding and liberating concentration camps The Last Days of Hitler The Soviets reached Berlin in April 1945 Adolph Hitler committed suicide April 30, 1945 April 12, 1945 – FDR died suddenly of a brain hemorrhage – Truman takes over May 7, 1945 – German government surrendered officially. Japan Dies Hard Submarines and bombers continued to inflict damage upon Japan. Leyte Gulf - series of 3 battles took place from October 23-26, 1944, knocking out Japan’s massive and powerful Navy. Iwo Jima was captured in March 1945. Needed for US bombers to land. The Atomic Bomb Potsdam Conference – Truman, Churchill, and Stalin announced that Japan must surrender or be destroyed. July 16, 1945 - first atomic bomb was detonated The Atomic Bomb Japan refused to surrender Aug. 6, 1945 – Atomic Bomb dropped on Hiroshima Japan refused to surrender “Little Man” - 1 “Fat Boy” – 2 Aug. 9, 1945 – Atomic Bomb dropped on Nagasaki The Surrender of Japan August 10, 1945 – Japan surrendered under the condition that the Emperor Hirohito be allowed to remain emperor The formal end of the war came on Sept. 2, 1945 War Casualties U.S. casualties – 1,000,000 U.S.S.R. casualties – 20,000,000 After the war, much of the world was destroyed with the exception of the United States – it was left untouched.