* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantitative analysis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
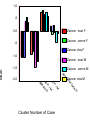
Quantitative analysis Alessandra Fermani [email protected] SPSS • 1 version 1968 IBM • Last: 22.0 (13 agosto 2013) • Language: java • Java System: Microsoft Windows, Mac OS, Linux ect… Manual and video • http://www.ateneonline.it/chiorri/studenti/isbn6 556-1_guidaSPSS.pdf • ftp://public.dhe.ibm.com/software/analytics/spss /documentation/statistics/20.0/en/client/Manual s/IBM_SPSS_Statistics_Core_System_Users_Guid e.pdf • Video (it): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ftU4TauCshg 2 windows • Data view • variable view (name, Type, with, decimals, label, values, missing, columns, align, measure) • Application Variables variable type: numeric or string Dependent: satisfation Independent: age, gender Ordinal: children, adolescents, adult etc… Likert scale eg. 1= never (disagree) 2 3 4 5 6 7 = always (agree) (odd - better) Dummy: dicotomic variables eg. Yes/no or gender Unidirectional / bidirectional relationship between variables • bidirectional (correlation, regression) • unidirectional (cause and effect) Formula: Trust index reliability significance • p<.05 good level p<.01, p<.001 • Rule of transcription: eg: (F (1,361) = 6.90, p < .01) Descriptive statistics • To take statistics: Frequencies, mean, median, mode to operate dispersion, use standard deviation (SD) Mean or average • In statistics, mean and expected value are used synonymously to refer to one measure of the central tendency either of a probability distribution or of the random variable characterized by that distribution. Eg. 10 students, grades in a test: 5,7,4,8,5,6,5,7,6,4 mean equal 5,7 because (5+7+4+8+5+6+5+7+6+4/10 = 5,7) Standard deviation Deviazione standard o varianza = dispersione dei dati attorno alla media In statistics and probability theory, the standard deviation (SD) (represented by the Greek letter sigma, σ) measures the amount of variation or dispersion from the average • Classroom A – student’s grades: 2,7,4,4,3,4,5,4,4,1,6,4,4,5,4,3 • Classroom B - student’s grades: 6,4,3,4,5,5,2,3,4,2,1,3,5,7,4,6 mean is 4 (GPA), the same in both, but classes are different. the classroom B is more different compare to classrom A and the SD is the index that measures. Median = In statistics, the median is the numerical value separating the higher half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution, from the lower half Legenda: 1 very good, 2 good, 3 not bad, 4 sufficient, 5 not sufficient 9 students scores: 1,4,1,2,3,2,5,2,4 Put in order 1,1,2,2,2,3,4,4,5 Median= (9+1)/2 = 5; 5th position therefore is 2 (good) N. divided by2 Formula i= n+1/2 Mode • The mode is the value that appears most often in a set of data. • Eg. 100 subjects are divided into three categories: 33 prefer action movies; 54 romantic ; 13 horror • The mode is «category of romantic movies» because this category is most represented Ex. 1) Find the mean, median and mode 19, 18, 21, 16, 15, 17, 20, 18 Ex. 2) Find the mean, median and mode Set A: 2, 2, 3, 5, 5, 7, 8 Set B: 2, 3, 3, 4, 6, 7 Measure The Mean To find the mean, you need to add up all the data, and then divide this total by the number of values in the data. The Median To find the median, you need to put the values in order, then find the middle value. If there are two values in the middle then you find the mean of these two values. Set A 2, 2, 3, 5, 5, 7, 8 Set B 2, 3, 3, 4, 6, 7 Adding the numbers up gives: 2 + 2 + 3 + 5 + 5 + 7 + 8 = 32 Adding the numbers up gives: 2 + 3 + 3 + 4 + 6 + 7 = 25 There are 7 values, so you divide the total by 7:32 ÷ 7 = 4.57... There are 6 values, so you divide the total by 6:25 ÷ 6 = 4.166... So the mean is 4.57 (2 d.p.) So the mean is 4.17 (2 d.p.) The numbers in order: 2 , 2 , 3 , (5) , 5 , 7 , 8 The numbers in order: 2 , 3 , (3 , 4) , 6 , 7 The middle value is marked in brackets, and it is 5. This time there are two values in the middle. They have been put in brackets. The median is found by calculating the mean of these two values:(3 + 4) ÷ 2 = 3.5 So the median is 5 RESULTS So the median is 3.5 The Mode The mode is the value which appears the most often in the data. It is possible to have more than one mode if there is more than one value which appears the most. The Range To find the range, you first need to find the lowest and highest values in the data. The range is found by subtracting the lowest value from the highest value. The data values: 2 , 2, 3 ,5 , 5, 7 , 8 The data values: 2 ,3 , 3, 4 , 6 , 7 The values which appear most often are 2 and 5. They both appear more time than any of the other data values. This time there is only one value which appears most often - the number 3. It appears more times than any of the other data values. So the modes are 2 and 5 So the mode is 3 The data values: 2, 2 , 3 , 5 , 5 , 7 ,8 The data values: 2, 3 , 3 , 4 , 6 ,7 The lowest value is 2 and the highest value is 8. Subtracting the lowest from the highest gives:8 - 2 = 6 The lowest value is 2 and the highest value is 7. Subtracting the lowest from the highest gives:7 - 2 = 5 So the range is 6 So the range is 5 Ex 1) all three averages equal 18 File eg proloco 1. Find the AGE mean and SD 2. Recod variables (and control if you have mistake in the words eg have you write always macerata? Or have write Macerata and macerata) : prov (provincia) with this values below • • • • 3. 4. 5. 6. 1 ancona 2 macerata 3 ascoli piceno 4 pesaro urbino Cross tabs gender and prov Split variable “gender” Selected females Save the sintax in a new file sintax • Chi square, T- test • ANOVA (univariate analysis) and MANOVA (multivariate analysis) compare means (variables independent or fix factor (age/gender or e.g. Motivation with variables dependent e.g. « satisfation» «pay more»). More 3 groups «v» on post hoc test-Takey • Save as excell or word – copy • Graph • Sintax Ex: file ProLoco Specify level of sign.: 0.014 .983 .000 .523 .054 .007 .002 ____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Execute an ANOVA (agerec and efficacia collettiva) a MANOVA (gender, agerec and motivation). Explain the meaning in word Execute a graphs in excell (ANOVA) Inferential Statistics • Correlation = In statistics, dependence is any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving bidirectional dependence. (2 variables are associated: perfect positive +1, perfect negative -1); • Regression = measure as independent variables (predictors) associated with the dependent variable are better Urban Bird Diversity as an Indicator of Human Social Diversity and Economic Inequality in Vancouver, British Columbia Figure 4 Figure 4: Variance decomposition based on partial redundancy analyses of the bird community in Greater Vancouver, BC. Pink represents variance explained by social and neighborhood-age variables, after removing the effects of covariates area and space (XY coordinates). Yellow represents variance explained by census tract area alone, after removing the effects of the space covariate and social + neighborhood-age variables. Green represents variance explained by space alone, after removing the effects of the area covariate and social + neighborhood-age variables. Amounts of shared variance were calculated by running a further series of partial redundancy analyses and calculating the joint or shared effects of 1) social + neighborhoodage variables, constrained by area, 2) social + neighborhood-age variables constrained by space, and 3) area, constrained by space. Eg. Correlation more/more; more/less *** = P<.001 **=.01 *=.05 you have to look minus /plus -/+ and stars/asterisk Variable Self Concept Clarity Extraversion Emotional stability Openness to experience .12** -.09* .21** -.06 -.09* .11*** -.11** .16** Educational identity Commitment Exploration in Depth Integration with linear regression Table: Standardized Betas and Proportion Explained Variance for the Regression Analyses of SCC, emot. stab. and personality on Identity (Correlation) cons/pros variance Variable Self Concept Clarity Extraversion Emotional Openness to stability experience .11** .16** .22** .16** (.02) (.13**) (.16*) (.22**) -.21** -.08* -.25** .14** (-.18**) (-.01) (-.14**) (.23**) .11** .03** .06** .08** Commitment Exploration in Depth Total R2 LOGISTIC REGRESSION • In statistics, logistic regression, or logit regression, or logit model is a regression model where the dependent variable (DV) is categorical/dummy. • logistic regression predicts the probability of particular outcomes e.g. LOG REG Note: *p<.05. **p<.01. ***p<.001. Would you be willing to spend more to be in a eco-friendly accommodation? Coeff B Sig. Exp(B) Gender (ref females) Males .619 .019* 1.857 -.776 .003** .460 1.175 .000*** 3.239 Class age (ref adults) Young people Constant Case numbers 374 Ex: file ProLoco Specify level of sign.: .016 .083 .001 .453 .056 .008 .032 ____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ Execute a correlation and a linear regression (motivation and efficacia collettiva). Explain the meaning in word • Factor analysis = (data reduction) is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. (PCA and EFA are 2 type of exploratory factor analysis; CFA confirmatory factor analysis). Cronbach’s alpha >.60 Cluster analysis = (data reduction) or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). GORE (2000) 2 steps (only Likert scale no dummy and standard. ): 1) Hierarchic for number of cluster 2) No Hierarchic (K mean) for the best classification ,5 0,0 Zscore: trust F Zscore: comm F -,5 Zscore: clos F -1,0 Zscore: trust M -1,5 Zscore: clos M e M r fo te P Cluster Number of Case l bo de /M P rte fo /M P le le P bo bo de de M -2,0 Zscore: comm M rte fo Mean 1,0 Statistical software: Why ? • To predict • To understand