* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download radio communication
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
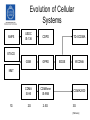
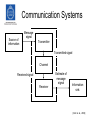
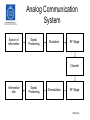
Wireless Systems IK1330 Anders Västberg [email protected] 08-790 44 55 IK1330 Wireless Systems • TEN1: 4,5 hec. – A part theory, B part problems • LAB1: 3 hec. – Three labs, propagation and planning, WLAN, measurements, • Required reading: – Stallings, W., Wireless Communications and Network, Pearson, 2005 • Course Webpage: – http://www.kth.se/student/programkurser/kurshemsidor/ict/cos/IK1330/VT10-1 • Book Webpage: – http://williamstallings.com/Wireless/Wireless2e.html Stallings: Wireless Communications and Networks [Stallings., 2005] Radio Communication • Radio or radio communication means any transmission, emission, or reception of signs, signals, writing, images, sounds or intelligence of any nature by means of electromagnetic waves of frequencies lower than three thousand gigacycles per second (3000 GHz) propagated in space without artificial guide. • Examples of radio communication systems: – – – – – – Radio broadcasting. TV broadcasting. Satellite communication. Mobile Cellular Telephony. Wireless LAN. Multimedia communication & Mobile Internet [Slimane] History • 1864: Maxwell describes radio wave mathematically • 1888: Hertz generates radio waves • 1890: Detection of radio waves • 1896: Marconi makes the first radio transmission • 1915: Radio tubes are invented • 1948: Shannon’s law • 1948: Transistor • 1960: Communication Satellites • 1981: Cellular technology Classification of radio spectrum AM broadcasting, naviation, radio beacons, distress frequencies. Broadcasting TV, satelites, Personal telephone systems, radar systems, fixed and mobile satelite services Fixed services, Fixed statelite services, Mobile serivces, Remote sensing Frequency assaignments up 60 GHz 300-3000 Hz 3-30 kHz 30-300 kHz 300-3000 KHz 3-30 MHz 30-300 MHz 300-3000 MHz 3-30 GHz 30-300 GHz Wavelength 1000 -100 km 100 -10 km 10 -1 km 1000 -100 m 100 -10 m 10 -1 m 100 -10 cm 10 -1 cm 10 -1 mm Term ELF VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF SHF EHF Time and Frequency Normals, Navigation, Underwater Communication, Remote sensing under ground, Maritme telegraphy Broadcasting, TV, FM, Mobile services for maritime, aeronautical and land, Wireless microphones, Meteor burst communicaiton Fixed point to point communication, Mobile maritime aeronautical, land services, military communication, amateur radio and broadcasting Long distance communication (fixed and marite), Broadcasting, Naviagation, Radio beacons Frequency Application The Radio Spectrum • The frequency spectrum is a shared resource. • Radio propagation does not recognize geopolitical boundaries. • International cooperation and regulations are required for an efficient use of the radio spectrum. • The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is an agency, within the UN, that takes care of this resource. – Frequency assignment. – Standardization. – Coordination and planning of the international telecommunication services. Evolution of Wireless Systems [Stallings., 2005] Evolution of Cellular Systems AMPS USDC IS-136 CDPD GSM GPRS CDMA IS-95 CDMAone IS-95B TD-SCDMA ETACS EDGE WCDMA NMT 1G 2G 2.5G CDMA2000 3G [Slimane] Radio Communication • Three main problems: – The path loss – Noise – Sharing the radio spectrum Communication Systems Source of information Message signal Transmitter Transmitted signal Channel Estimate of message signal Received signal Receiver Information sink [Ahlin et. al., 2006] Analog Communication System Source of information Signal Processing Modulator RF-Stage Channel Information sink Signal Processing Demodulator RF-Stage [Slimane] Digital Communication System Source of Information Source Encoder Channel Encoder Digital Modulator Modulator RF-Stage Channel Information Sink Source Decoder Channel Decoder Digital Demodulator Demodulator RF-Stage [Slimane] decibels • The bel is a logarithmic unit of power ratios. One bel corresponds to an increase of power by a factor of 10 relative to some reference power, Pref. P[ bel ] • The bel is a large unit, so that decibel (dB) is almost always used: P[ dB ] • P log 10 P ref P 10 log 10 P ref The above equation may also be used to express a ratio of voltages (or field strengths) provided that they appear across the same impedance (or in a medium with the same wave impedance): V[ dB] V 20 log 10 V ref [Saunders, 1999] decibels Unit Reference Power Application dBW 1W Absolute power dBm 1 mW Absolute power P [dbW] = P [dBm] - 30 dBmV 1 mV Absolute voltage, typically at the input terminals of a receiver dB any Gain or loss of a network dBmV/m 1 mV/m Electric field strength dBi Power radiated by and isotropic reference antenna Gain of an antenna dBd Power radiated by a half-wave dipole Gain of an antenna 0 dBd = 2.15 dBi [Saunders, 1999]