* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Should I Do If I Have A Sick Sheep?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
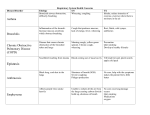
What Should I Do if I Have a Sick Sheep? Oregon Sheep Growers Annual Conference December 6, 2014 Brian J. Dietrich, DVM Call Your Vet!! What NOT to Do • • • • • Don’t do something illegal—follow labels! Don’t use the “shotgun” treatment Don’t ask “Doctor Google” Don’t throw away the answers! Don’t do nothing Wooly Bleaters A farmer told me long ago He hated sheep. Said I, “Why so?” He said, “All sheep are wooly bleaters, Time-consuming turnip eaters, Whose one ambition is to try To find a different way to die. All my working life I’ve tried To end this ovine suicide. But living isn’t in their nature– A sheep’s a kamikaze creature.” Signs of a Sick Sheep • • • • • • • • Lack of appetite Separated from flock Lagging behind group Lying down more Labored or rapid breathing Dull eyes, “depressed,” droopy ears Dirty rear end Anything unusual–know your sheep! Basic Physical Exam • General—body condition, wool, weakness, bottle jaw, pale eyes/gums • Body temperature • Respiratory—nasal discharge, coughing, increased/decreased lung sounds • Digestive—appetite, chewing cud, rumen contractions, diarrhea, drooling, bloat • Neuro—twitchy eyes, seizures, imbalance, extended limbs and neck Physical Exam, cont. • Musculoskeletal—limping, muscle twitches, fractured limb • Reproductive—in labor, retained placenta, discharge, uneven testicles, mastitis • Urinary—straining to urinate, fluid under the skin History • • • • Age, sex, breed, stage of production Feed, housing Recent changes Management, protocols, medications/supplements Skin Diseases • • • • • • • • Mineral imbalances Wool break Wool rot/lumpy wool Lice, ticks, keds Fly strike Wounds Soremouth Caseous lymphadenitis Internal or external Maggots Itching and wooludder loss Scabs on mouth, Lumps near lymph nodes Predators, fences, other Discolors wool Skin loss Weight loss/death Feed testing Disease Disease transmission Viral cause More extensive than they Blood and liver analysis Bacterial cause Result ofcontagious diarrhea, Fever Very Bacterial causefoot appear rot,Injectable/topical untreated wounds Poor nutrition Long-lived Contagious Custom mineral Shearing Stressful events parasiticides Zoonotic Disinfect, shear, formulation Antibiotics Shearing Dipping antibiotics Fly spraycare Supportive Culture abscess and cull Respiratory Diseases • • • • • • • Pneumonia OPP Lungworms Nasal bots Tumors Abscesses Indicator of other diseases—moaning, vocalizing, increased respirations Weight loss, labored Difficulty breathing Nasal discharge Anemia Labored breathing or rapid breathing Coughing Shaking head loss Pain Coughing, weight Decreased/increased lung Hardbag Weight loss Weight Feverloss Stomping feet sounds Discharge Difficulty breathing Ketosis Fecal-oral transmission Coughing Viral Cause Visible mass Pregnancy Life cycle involves Oestrus ovis snail Transmitted via milk, Some have viral cause Viral/bacterial causes Prolapse Moist pastures coughing Various bacteria Weather changes Ivermectin SQ Blood test Cull/slaughter Deworming Antibiotics Supportive No treatment Cull care Cull positive ewes Digestive Diseases • Overeating disease • Toxic plants • Grain overload/ acidosis • Bloat • Choke/blockage • Intestinal parasites • Johne’s Salivation Weight loss Lethargy, Distended Vomiting inappetence abdomen Lethargy Older ewes Difficulty breathing Anemia Abnormal Difficulty “Depressed” breathing behavior Possible diarrhea Chronic weight loss Bloat Occasional diarrhea Lethargy, “Drunk” Death inappetance Diarrhea Death Grain, fruit, veggies, Excess Excess Various gasgrain/fruit production plants Clostridium perfringens Bacterial foreign material Worms, coccidia Know Excess your froth weeds! Contagious Antacids Vaccination Stomach tube Grazing management Symptomatic Stomach Charcoal treatment tube Treatment often Test and cullfutile Surgery Genetics, nutrition Supportive Surfactants Surgery care Parasiticides Neurologic Diseases • • • • • • • Congenital Polio Listeriosis Toxic plants Meningeal worm Trauma Lead/other toxins Circling Stiff based limbs, shaking Signs on defect Various depending on Imbalance Star-gazing Various defects skull and species of of plant Twitching Imbalance spinal cord Deathweeds! Know your Viral, toxic, genetic, Bacteria indeficiency wet feeds Thiamine trauma Remove access Rapid food change Antibiotics Toxic plants Generally cull Thiamine Musculoskeletal Diseases • Injuries • Foot scald/foot rot • White muscle disease • Foot abscesses • Founder/laminitis • Tetanus/ other Clostridial Limping, Depends kneeling onfeet species to graze of Sore Lameness Stiff hind legs Raw skin/eroded bacteria No signs Various Swelling depending on Hunched backhoof FullFoul body odor rigidity location Death Sequel to grain Foreign body penetration Selenium deficiency Bacterial cause overload/lush pasture Predators, fences, trailers Clostridial Very contagious Drainspecies Prevention is key Remove feed source Repair,Soak let heal, or Injectable/oral selenium Treatment Foot trimming minimally Trim feet Antibiotics euthanize Foot effective baths Vaccination Antibiotics is key! Reproductive Diseases • Abortions – – – – – Campylobacter Chlamydia Q fever Leptosporosis Toxoplasmosis • Dystocia • Vaginal/ uterine prolapse • Mastitis • Urinary blockage Straining Late-term abortions Any stage Red, warm, Vagina swollen, vs Prolonged labor Midto late-term Late-term abortions Dribbling bloody urine Stillbirths abortions/mummies painful and cotyledons udder NoUterus progress for 30 minutes abortions Distended abdomen Weak lambs Coxiella Stillbirths/weak lambs Cold, udder May ornon-painful may not see fetus Lepto Overweight, genetics vs Zoonotic Chlamydia Zoonoticor Dystocia Calcium:Phos imbalance Campylobacter Wear mask and gloves!! Toxoplasma Various bacteria Know your limits Zoonotic Selenium/calcium Excess protein Zoonotic Call vet promptly Vaccinate deficiency No vaccine MilkTetracycline out, hot pack Vaccination Balance Vaccination Tetracycline Control rodents/kittens Antibiotics Call theration vet! Tetracycline Medical treatments Tetracycline No vaccine/treatment Cull Replace vagina/uterus Surgeryor harness Suture, retainer, The End