* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Diabetes?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
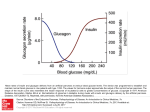
Helping Belton ISD Students Stay Safe & Healthy What BISD Staff Needs to Know About: Diabetes Basics Belton ISD Health Services UDCA_Level II Diabetes What Every BISD Staff Needs to Know About Diabetes • What is diabetes? • How to recognize and respond to the signs & symptoms of low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) & high blood glucose (hyperglycemia) • Who to contact immediately in case of an emergency What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a serious, chronic disease that impairs the body’s ability to use food. Body does not make or properly use insulin: • • • no insulin production insufficient insulin production resistance to insulin’s effects What Happens When We Eat? Insulin’s job is to get glucose into cells GLUCOSE INSULIN Diabetes occurs when there is not enough insulin for what the body needs. Without insulin, the body’s main energy source, glucose, cannot be used as fuel and builds up in the blood. Before this diabetic child received insulin he was starving because he was not receiving glucose for energy Insulin Saved His Life Two Main Types of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes • People with Type 1 Diabetes must receive insulin through either injections or an insulin pump. Insulin taken in this manner does not cure diabetes and may cause their blood glucose to become dangerously low. • They must carefully balance food, medications, and activity to keep blood glucose levels as close to normal as possible. Glucose CANNOT enter cell without…..insulin Type 2 Diabetes: The Obesity Cycle • Type 2 Diabetes is the most common form • • • • • typically afflicting obese adults and youth. The larger you are, the more insulin your body has to make. High insulin levels cause an increase in appetite Increase food intake cause the body to make more insulin. Insulin does not work well in fatty tissue. Type 2 diabetics can control their disease through diet and exercise alone or may require oral medications or insulin injections. Diabetes is Managed, But it Does Not Go Away GOAL: To maintain target blood glucose Diabetes Management 24/7 Constant Juggling: Insulin/medication with: Exercise BG & BG Food intake BG Know How to Recognize and Respond to the Signs & Symptoms of High Blood Glucose • Allow student to check their blood glucose • Stop testing/ class work/exercise. The student’s diabetic plan specifies when they may resume these activities • Do not send a symptomatic student to the clinic unescorted. Send with a responsible buddy/adult. • Provide/encourage access to water and bathroom • Seek help from the student’s unlicensed diabetic care assistant (UDCA) or school nurse • Maintain confidentiality Know How to Recognize and Respond to the Signs & Symptoms of Low Blood Glucose • Allow student to check their blood glucose and eat a snack • Stop testing/ class work/exercise. The student’s diabetic plan specifies when they may resume these activities • Do not send a symptomatic student to the clinic unescorted. Send with a responsible buddy/adult. • Seek help from the student’s unlicensed diabetic care assistant (UDCA) or school nurse • Maintain confidentiality Assistance in Diabetes Management Routine Care: • Many students will be able to handle all or almost all routine diabetes care by themselves • Some students, because of age, developmental level, or inexperience, will need help from school staff. Urgent Care: • Any student with diabetes may need help with emergency medical care. Care in the Schools: School Nurses and Others Nurse will: • Coordinate diabetes care • Supervise diabetes care • Provide direct care (when available) However, a nurse is not always available. Non-medical school staff can be trained to assist students • For both routine and emergency care • Including checking blood glucose, administering insulin and glucagon injections Every Diabetic Should Have a Diabetes Care Plan that gives Instructions on : •Daily schedule/Routine Care •Student’s Participation in their Care •Location of Equipment & Supplies •Emergency Contact Info •Physician Contact Info •Names and contact info of Trained Staff (nurse & UDCAs) The Diabetes Plan should include a Quick Reference Plan or an Emergency Care Plan Summarizes how to recognize and treat hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia • Distribute to all personnel who have responsibility for students with diabetes • Helping the Diabetic Student Succeed • All BISD staff need to have a basic understanding of diabetes and to recognize and respond to the signs & symptoms of low and high blood glucose • Some may need to learn the knowledge and skills to assist the student in an emergency situation • Others may be assigned to be an unlicensed diabetic assistant(UDCA). They will be taught the knowledge and be allowed to practice and demonstrate the skills so that they can be responsible for all aspects of the diabetic care. Legal Considerations Nutrition & Physical Activity Considerations How to Check Blood Sugar How to Give Glucagon How to Intervene when Blood Sugar is Low How to Intervene When Blood Sugar is High How to Check Ketones How To Give Insulin (Syringe, pen, or pump) Please contact the campus nurse for any questions.