* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download what is an earthquake?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
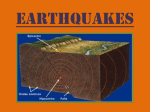
EARTHQUAKE NOTES September 12 SWBAT: define problems that may be caused by a catastrophic event resulting from plate movements and design possible devices or solutions to minimize the effects of that event on Earth’s surface and/or human structures. WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE? Earthquakes are produced when rocks break along a _______________. The term earthquake describes the sudden __________ on a fault and includes the ground shaking and radiating seismic _____________ that is caused by the slip. What Can Cause EARTHQUAKES to Occur? Tectonic plates move toward, away and past each other causing stress. Stress causes the rock to collapse. This happens at: 1. Convergent Boundaries (compression) 3. Transform Boundaries (shearing) 2. Divergent Boundaries (tension) 4. _________________ 1. Earthquakes occur along plate __________________ where ________________ builds up and forms _____________ lines •When the pressure is _________________, an earthquake occurs along the fault line. 2. Earthquakes can also occur along faults Most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions do not strike randomly, but occur in specific areas such as along PLATE BOUNDARIES . Ex) Ring of Fire: known as one of the most seismically and volcanically active zones in the world. Stronger earthquakes are more likely to occur along _______________ plate boundaries. Strong earthquakes are more common at ____________________ and __________________________ plate boundaries. PARTS OF AN EARTHQUAKE FAULT: a break in the rock of the earth’s crust or mantle where an earthquake _____________ FOCUS: the point __________ the Earth’s surface that an earthquake’s energy is _______________ from EPICENTER: the point on the Earth’s surface directly ___________ the focus where the earthquake’s energy is the ________________ SEISMIC WAVES: _______________ of ____________ that spread outwards from the focus of the earthquake What Kind Of Damage Can Earthquakes Cause? There is evidence to support the idea that tectonic activity (earthquakes, volcanoes, etc.) contributed to the ______________ (failure/death) of ancient civilizations. Based on the locations of current population centers, scientists have developed models that show that populations today may be just as vulnerable to the aftereffects of powerful earthquakes. Earthquakes can even cause giant waves called _______________________. Earthquakes and People: Many population centers are located near active fault zones and/or active plate boundaries such as the San Andreas Fault. Millions of people in these population centers have suffered personal and economic (money) losses due to volcanic and earthquake activity. When exposed to sudden ______________ (side-to-side) forces earthquakes buildings and bridges can collapse, crushing the people in and around them. Many cities now have a lot of very tall buildings. This can pose a huge problem if an earthquake occurs. Luckily over the past few decades (decade=10 years), architects and engineers have developed technologies to help these tall buildings ___________ instead of break. Because of these flexible buildings, the chances for survival of the people in them is greatly increased!