* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
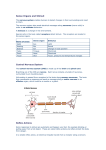
Nervous system Nervous system Basic unit: Neurones Sensory neurones receptors CNS Motor neurones CNS effectors Association neurones linking sensory & motor neurones A neuron Sensory neurone Motor neurone Association neurone Neurones Cell body Dendrites sense organ/ other neurones cell body Axon cell body other neurones/ effectors Nerve fibre coverings Neurilemma, Schwann cells, Myelin sheath 3 classes of neurons A neurone postsynaptic to one cell can be presynaptic to another Resting Membranes Potential The nerve fibre is at rest +ve outside, -ve inside Diffusion i.e. K+ diffuses outward Active transport i.e. K+ in & Na+ out by Na- K pump Ions Na+ K+ Inside 16 100 Outside 140 4.4 Action Potential Stimulation of an axon by an electrical impulse change in the potential across the axon membrane ( -70mV +40mV) Depolarization + Repolarization + hyperpolarization An action potential I. Resting State Neither Channel is open II. Depolarization Na+ gates open but K+ channels remain closed Na+ flows inward membrane potential+ve III. Repolarization Na+ channels but K+ channels open K+ moves outward membrane potential -ve IV. Hyperpolarization Na+ channels close but K+ channels remain open further K+ moves outward membrane potential further -ve All- or- none Law Strong enough stimulation ( above THRESHOLD ) Depolarization Not strong enough stimulation ( below THRESHOLD) Nothing Refractory period ~ 1 ms the period of membrane depolarization the period when the axon can’t conduct another impulse Speed of impulse conduction Myelinated vs non-myelinated nerve Rate of impulse transmission in myelinated fibre > that of non- myelinated fibre Diameter of fibre fibre diameter, speed Body temperature temp., speed Synapes The junctions between neurones Presynaptic membrane ~ attachment of vesicles, release of neurotransmitter Synaptic vesicle ~ contain neurotransmitter i.e.acetylcholine, noradrenaline Synaptic cleft ~ small gap Postsynaptic membrane ~ receptor sites Mitochondria ~ resynthesis of neurotransmitter Electro-chemical transmission I The nerve impulses travel along the axon of synaptic neurone Electro-chemical transmission II arrival of nerve impulses at axon of presynaptic neurone, permeability of presynaptic membrane to Ca+ Electro-chemical transmission III Synaptic vesicles fuses with presynaptic membrane & rupture Neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft Electro-chemical transmission IV Neurotransmitters diffuses across cleft Neurotransmitters attach to receptor sites, permeability of postsynaptic membrane Electro-chemical transmission V Local depolarization is triggered ↓ Nerve impulse propagate in postsynaptic axon Fate of neurotransmitters Cholinesterase break down the neurotransmitters choline & ethanoic acid Choline is reabsorbed & resyntheisied to recycle new neurotransmitter again Neuromuscular Junction ~ motor end- plate synapse between the nerve terminals of a motor neurone & the muscle fibre deep fold surface area the muscle fibre responses by contraction Motor end-plate Nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain +Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Cranial nerves + spinal nerves Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Sympathetic + parasympathetic Central Nervous System (C.N.S.) Spinal cord transmit impulses brain act as reflex centres Central canal Grey matter Meninges Spinal nerve Spinal cord Reflexes Reflex is innate automatic response involving parts of the body rather than the whole Reflex arc = receptor + sensory neurone + association neurone + motor neurone+ effectors Types of reflex action I Inherited reflexes no need of learning & experience polysynaptic reflex sensory + association + motor neurones e.g. The withdrawal reflexes monosynaptic reflex sensory + motor neurones e.g. Knee-jerk action, iris-pupil reflex, balancing, breathing rate & blood pressure Types of reflex action Conditioned reflex action a result of learning & experience e.g. typing, playing piano, cycling, swimming promote survival Properties of reflexes Certain stimulus same response No prior thought or planning for the response Involuntary and fast in action response Keeping body from harms survival Reflex action vs voluntary action Reflex action ~ not involve cerebrum ~ unconscious, involuntary & automatic ~ same stimulus same response ~ fast ~ spinal cord & medulla oblongata Voluntary action ~ involve cerebrum ~ conscious, voluntary & not automatic ~ same stimulus different response ~ slow ~ cerebrum Central Nervous System Brain a. Brainstem ~ medulla + pons + midbrain b. Cerebellum c. Cerebrum ~ cortex + basal ganglia + thalamus + hypothalamus + other areas Cerebrum Dicephalon Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Cerebellum Spinal cord Meninges & cerebrospinal fluid Meninges ~ 3 layers protective membranes Cerebrospinal fluid ~ fluid inside the brain & between the inner two layers of meninges Blood CSF Brain ventricle surrounding Central canal the brain & of spinal cord spinal cord reabsorbed into capillaries Functions of CSF Protect & support the brain & spinal cord maintain uniform pressure as cushion & shock absorber as medium for exchanging Flow of CSF Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Occipital lobe Temporal lobe Cerebrum Right + left hemisphere ( connected by Corpus callosum ) Functions: higher mental processes initiation & control of the voluntary muscle contraction perception Function of cerebrum Decorticate animals Frog ~ behaves normally Dog ~ blind, no senses of smell& hearing but able to walk & swallow Human ~ no breaths & swallow, no learning & no voluntary action die quickly Hypothalamus Thermoreulartory centre ~ heat gain vs heat loss centres Neuro- secretion ~ Thyroid stimulating hormone releasing hormone, ADH Interoreceptors & co-ordinator Hypithalamus Cerebellum Impulse from Impulse from eyes & ear muscle & joints Cerebellum indicate body position Provide ‘i’ about the head position Impulses from the cerebellum Influence the contraction of skeletal muscle Balance Medulla oblongata I Continuous with spinal cord Cardiac centre Cardiac centre parasympathetic nerve fibre Sympathetic nerve fibre + The rate & force of heart beat, cardiac activity Medulla oblongata II Respiratory centre Excess CO2 or deficiency O2 in blood Phrenic nerve(+) Intercostal nerve (+) diaphragm activity contraction of ICM Vigorous breathing movement ( depth & rate) Medulla oblongata III Vasomotor centre Stimulation arterial baroreceptors or emotions vasomotor centre in medulla Autonomic nervous system (ANS) Responses Blood vessels constriction or dilation Medulla oblongata IV Autonomic reflex centres Irritating substances are present in the stomach or respiratory tract Reflex centre in medulla oblongata Reflex actions of vomiting, coughing & sneezing Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 12 pairs cranial nerves + 31 pairs spinal nerves Spinal nerves: emerge from spinal cord Cranial nerves: emerge from brain Connect the brain & spinal cord with receptors & effectors Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Sympathetic nerves + parasympathetic nerves Antagonistic system Sympathetic system ~ “fight or flight” action heart rate, dilates bronchi & arteries to muscle but constrict arteries to gut, glycogen glucose, adrenaline Parasympathetic system~ conservation opposite to sympathetic system ANS Antagonistic characters Sympathetic system dilation of pupil secretion of tear secretion of saliva heart beat arteries constrictBp gut movement bronchi dilate bladder relax sweat Parasympathetic system pupil constrict normal secretion of tear secretion of watery saliva heart beat arteries dilate Bp gut movement bronchi dilate bladder contract Symp. Vs Parasymp. Origin: spinal nerve Diffuse effect Neurotransmitter: Noradrenaline Prepare for stress; excitatory homeostatic effect Ready for emergency Origin: cranial nerve/ spinal nerve Localised effect Neurotransmitter: acetylcholine Maintain in steady state; Inhibitory homeostatic effect Conservation Interrelation of CNS & ANS Visual interpretation as danger CNS ANS nerve ending adrenal medulla adrenaline effectors blood streamadrenaline Nervous system Hormonal system Hormones Synthesized by endocrine gland Carried in blood to target sites Steroid Protein Fatty acids Mechanism of Hormone action Cell membrane level ~ facilitate/ inhibit transport substances into the cell Enzymes system level ~ second messenger Cellular organelles level ~ influences electron transport chain Gene level Mechanisms of hormones secretion I Nervous control Adrenaline danger eye optic nerve CNS(fear) ANS sympathetic nerve adrenal medulla Adrenaline Oxytocin sucking on nipples spinal nerve CNS pituitary gland oxytocin Mechanism of hormone secretion II Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Bp baroreceptors ADH hypothalamus posterior pituitary Bp baroreceptors ADH Mechanism of hormone secretion III Hormonal control Negative feedback mechanism TSH stimulation to Thyroid gland thyroxin stimulation pituitary gland TSH ~ maintain a constant concentration of thyroxin in blood Mechanism of hormone secretion IV Positive feedback LH stimulation to ovary oestrogen LH ….. ~ but its continued release is prevented by the later release of progesterone Endocrine Glands Ductless gland ~ hormones are released directly into blood instead of passing a duct Glands External Hormone secretion Pancreas Pancreatic Insulin & juice glucagon Testis Sperms Male sex hormones Ovary Eggs Female sex hormones Endocrine Glands Pituitary gland Thyroid gland ~ thyroxine (T4) Pancreas ~ exocrine & endocrine ~ glucagon& insulin Parathyroid gland ~ parahormone Adrenal gland Pituitary gland Situated at the base of the brain Has 2 portions: anterior pituitary & posterior pituitary Produces a lage number of hormones Receive information form hypothalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Hormones secreted by the pituitary gland Thyroid stimulating hormone Adrenocorticotrophic hormone Follicle stimulating hormone Luteinizing hormone Prolactin Growth hormone Antidiuretic hormone Oxytocin Thyroid gland Found in the neck clost to the larynx Produces thyroxine(T4) Parathyroid glands Embedded in the posterior surface of thyroid glands. Produce parathormone which maintains the level of Calcium. Parathormone increases the absorption of calcium from the gut. Adrenal glands Situated above each kidney. Have 2 parts: adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. Produces hormone: ~ cortisol ~ aldosterone ~adrenaline ~ norepinephrine Pancreas In a loop of the small intestine just below the stomach. Has both exocrine and endocrine functions. α-cell produces glucagon → ↑blood glucose; glycogen → glucose β-cell produces →↓blood glucose; glucose →glycogen Nervous vs Hormonal System Similarities Co-ordinate various activities Message : receptors effectors Most important controlling organ are in the head: brain & pituitary gland Reciprocal pattern of control: Sympathetic vs parasympathetic -ve feedback vs +ve feedback mechanism Endocrine vs Nervous control Endocrine Not obey All-or-none Law Transmission via blood vessels Slow & gradual action Long lasting effect Wide spread influence Exact response Master: pituitary gland Nervous Obeys All-or-none Law Transmission via nerve fibres Quick action Short-lived effect Localized influence Widespread response Master: nervous system Significance of endocrine system As simple transmitter of information As limit control As reciprocal or -ve feedback system As evoking ‘Explosive reaction’ by +ve feedback control