* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Now
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
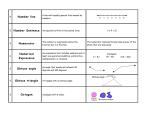
Geometry By: Daanan Hall Points Example: C • A point is an exact location. • This is an example of a point. Lines • Example: D DC C • A line is a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. • This is a line. Planes • A plane is a flat surface that extends without end in every direction. • This is a plane. Line Segment • A LINE SEGMENT HAS TWO ENDPOINTS. Example: • This is a line segment. F G Ray • A ray has one endpoint. From the endpoint, the ray extends forever in one direction only. • This is a ray. Example: Parallel Lines • Parallel lines are lines in a plane that are always the same distance apart. • This is an example. Example: Intersecting Line • Intersecting Lines cross at exactly one point. • Look on your right to see an example of a intersecting line. Example: Perpendicular Lines • Perpendicular Lines intersecting to form 90 degree angles,or right angles. • Here is a perpendicular line. Example: Skew • Skew lines are lines that are not in the same plane,are not parallel, and do not intersect. • This is a Skew line. Example: Acute Angles • An acute angle measures less than 90 degrees. • This is an acute angle Right Angles • A right angle measure 90 degrees. • This is a right angle Obtuse Angles • An obtuse angle measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. • This is an obtuse angle. Straight Angles • A straight angle measure 180 degrees. • This is a straight angle. That is my show now clap