* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Byzantine Empire
History of the East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
History of the Jews in the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine–Arab wars (780–1180) wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Law school of Beirut wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
Decline of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine dress wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
Constantinople wikipedia , lookup
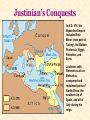
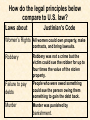
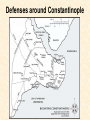
The Byzantine Empire Rise of the Byzantine Empire What did the Roman Emperor Diocletian do in A.D. 285 that ultimately paved the way for the creation of the Byzantine Empire? In A.D. 330, to which city did Constantine move the capital of the Roman Empire? Emperor Justinian • Ruled from 527-565 (37 years) • Sent his armies to regain some of the territory lost (from the western Roman Empire) to Germanic invaders • Organized and put together old Roman and Byzantine laws into one clear code of laws Justinian’s Conquests In A.D. 476, the Byzantine Empire included Asia Minor (now part of Turkey), the Balkan Peninsula, Egypt, Palestine, and Syria. Justinian, with Generals such as Belisarius, conquered and reclaimed parts of North Africa, the southern tip of Spain, and all of Italy during his reign. Corpus Juris Civilis: The Body of Civil Law • Better known as Justinian’s Code, Justinian ordered that old Roman laws be reviewed and that repetitive or outdated laws be deleted. • Taking good Roman and Byzantine Laws and adding some new ones, a collection of 10 books of law were established for the empire. • These laws influenced future laws in Europe and the United States (for example, principles were continued such as all people are equal under the law and people are innocent until proven guilty.) How do the legal principles below compare to U.S. law? Laws about Justinian’s Code Women’s Rights All women could own property, make contracts, and bring lawsuits. Robbery Robbery was not a crime but the victim could sue the robber for up to four times the value of the stolen property. Failure to pay debts People who were owed something could sue the person owing them something to gain the debt back. Murder Murder was punished by banishment. The Hagia Sophia Justinian also undertook many great building projects in Constantinople, including a number of large churches. The most famous was a magnificent church known as the Hagia Sophia, built between 532 and 537. It later became a mosque under Turkish rule. Theodora Theodora was the wife of Justinian who rose from a humble background to become not only an Empress, but an important advisor to Justinian and one of the world’s most powerful women of that time (6th century). During an early challenge to Justinian’s rule called the Nika Rebellion, she urged Justinian to stay and fight the rebels rather than flee the throne. The Christian Church Divides After several years of conflict over church authority, doctrine, and practices, the Christian Church officially divided into two parts in 1054. The division of the Church into the Roman Catholic Church (in the West) and the Orthodox Church (in the East) is known as The Great Schism. Though relations have improved in modern times, the Roman Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodox Church remain under separate leadership to this day! Defenses around Constantinople Restored section of the Walls of Theodosius. The Moat Wall and Outer Wall can be seen in the foreground, with a tower of the Inner Wall in the background (top left). Some towers stood as high as 20 meters (over 65 feet). The moat was about 20 meters wide and 10 meters deep. The Fall of Constantinople After years of decline and loss of territory due to various wars and invasions, the Byzantine Empire finally came to an end in 1453 when the Ottoman Turks under Sultan Mehmed II captured Constantinople. The city was renamed Istanbul and is now the largest city in Turkey. The army of Mehmed II readies to attack Constantinople The siege of the city by the Turks.