* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
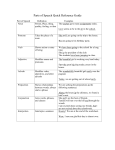
Download Grammar Help Sheet 1. Find the SIMPLE SUBJECT:
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Grammar Help Sheet 1. Find the SIMPLE SUBJECT: It is who or what the sentence is about. It is always a noun or pronoun. ¤ A NOUN is a person, place, animal, thing, or idea. ¤ A PRONOUN is a word that takes the place of a noun. 2. Find the SIMPLE PREDICATE: It is what the subject does or is. It is always a verb or verb phrase (main verb plus helping verbs). ¤ A VERB is the word or phrase that shows action or a state of being. ¤ There are 23 helping verbs: is, am, are, was, were, be, being, been has, have, had These are SOMETIMES helping verbs. do, did, does can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, must Î ALWAYS helping verbs. 3. Find the COMPLETE SUBJECT: It is the simple subject plus all the words that identify the person, place, animal, thing, or idea the sentence is about. 4. Find the COMPLETE PREDICATE: It is the simple predicate plus all the words that tell or ask something about what the subject does or is. To find specific parts of speech, first label all the other words you are sure of. For example, if you are looking for adjectives, you can label the simple subject as a noun and the simple predicate a verb. You can label other nouns and verbs you recognize (don't forget helping verbs). You can identify other words you are always sure of, such as: a, an, and the (adjectives); not (adverb); and but, and, and or (the most common conjunctions). 5. Find MODIFIERS: A. To find ADJECTIVES: 1. Identify all nouns and pronouns. 2. Find words which answer these questions about nouns and pronouns: - What kind of? - How many? - Which ones? B. To find ADVERBS: 1. Identify all verbs and adjectives. 2. Find words which answer these questions about verbs and adjectives: - When? - Where? - Why? - How? - How much? - How often? 3. Look at the adverbs you have identified. Any words which answer "how?" about them are also adverbs. 6. Find PREPOSITIONS: They are words which show a relationship between a particular noun or pronoun in the sentence and another word in the sentence. Some common prepositions are: aboard about above across after 7. 8. against along alongside among around as at before behind below beneath beside between beyond but(except) by despite down during except for from in inside into like near of off on onto out outside over past since through throughout to toward under with underneath within until without up upon Find CONJUNCTIONS. They connect words or groups of words. Common conjunctions include: and, or, nor, for, but, so, yet. Find INTERJECTIONS. An interjection is a word or short group of words used to express a feeling such as anger, fear, joy, or surprise. Interjections usually come at the beginnings of sentences, and are usually set off by a comma or exclamation point. An interjection can stand alone as a sentence--the exception to the rule that every sentence needs a subject and a predicate. Examples include: gosh, my dear, hello, good grief, oh, ouch, oops, wow, yeah, yahoo.